Abstract
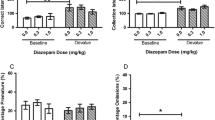
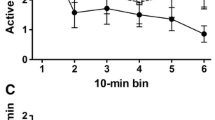
The effects of the chronic administration of dexamphetamine, (one of five doses from 0.1 to 1.6 mg/kg), amylobarbitone sodium, (one of five doses from 1.0 to 16.0 mg/kg) and a mixture of the two (all of five doses, all at a constant ratio of 1.10 by weight) on sensory contingent bar pressing (SCBP) were investigated. 144 female Wistar rats bar pressed for 3 sec light and sound change as the only reward for their behaviour. The dose-response relationship under both dexamphetamine and the mixture took the form of an inverted U shaped function. Responding was not affected by amylobarbitone. The optimum doses of dexamphetamine and the mixture produced the same significant increase in SCBP, an effect which emerged over the initial trails. The results suggest that response feedback from the environment is magnified and thereby increases the reward value of SCBP. SCBP seems to have a number of advantages for the study of psychoactive drugs and intrinsic motivation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berlyne, D. E.: The reward value of indifferent stimulation. In: Reinforcement. J. T. Tapp, G. W. Meier (Eds.) New York: Academic Press 1969.
Berlyne, D. E., Koenig, I. V. D., Hirota, T.: Novelty, arousal, and the reinforcement of diversive exploration. J. comp. physiol. Psychol. 62, 222–226 (1966).
De Oliveira, L., Graeff, F. G.: Comparisons between the effects of apomorphine and amphetamine on operant behaviour. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 18, 159–165 (1972).
Glick, D. S.: Facilitation or impairment of learning by dexamphetamine as a function of stimuli. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 21, 353–360 (1971).
Glow, P. H.: Some acquisition and performance characteristics of response contingent sensory reinforcement. Australian J. Psychol. 22, 145–154 (1970).
Glow, P. H., Roberts, J. E., Russell, A.: Response contingent auditory reinforcement in the rat. Aust. J. Psychol. 23, 125–131 (1971).
Kiernan, C. C.: Modification of the effects of amphetamine sulphate by past experience in the hooded rat. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 8, 23–31 (1965).
Kumar, R.: Psycho-active drugs, exploratory activity and fear. Nature (Lond.) 218, 587–588 (1968).
Kumar, R.: Extinction of Fear I: Effects of amylobarbitone and dexamphetamine given separately and in combination on fear and exploratory behaviour in rats. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 19, 163–187 (1971).
Lyon, M., Randrup, A.: The dose-response effect of amphetamine upon avoidance behaviour in the rat seen as a function of increasing stereotypy. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 23, 334–347 (1972).
Miller, N. E.: The analyses of motivational effects illustrated by experiments on amylobarbitone sodium. In: Animal behaviour and drug action. H. Steinberg, A. V. S. De Reuck, J. Knight (Eds.). London: Churchill 1964.
Olds, J.: The central nervous system and the reinforcement of behaviour. Amer. Psychologist 24, 114–132 (1969).
Porsolt, R. D., Joyce, D., Summerfield, A.: Lack of tolerance to an amphetamine-barbiturate mixture and to its components. Nature (Lond.) 223, 1277–1278 (1969).
Rushton, R., Steinberg, H.: Mutual potentiation of amphetamine and amylobarbitone measured by activity in rats. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 31, 295–305 (1963).
Rushton, R., Steinberg, H.: Modification of behavioural effects of drugs by past experience. In: Animal behaviour and drug action. H. Steinberg, A. V. S. De Reuck, J. Knight (Eds.), pp. 207–223. London: Churchill 1964.
Rushton, R., Steinberg, H., Tinson, C.: Effects of a single experience on subsequent reactions to drugs. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 20, 99–105 (1963).
Steinberg, H., Rushton, R., Tinson, C.: Modification of the effects of amphetamine-barbiturate mixture by the past experience of rats. Nature (Lond.) 192, 533–535 (1961).
Stretch, R.: Effects of amphetamine and pentobarbitone on exploratory behaviour in rats. Nature (Lond.) 199, 787–789 (1963).
Stein, L.: Amphetamine and neural reward mechanisms. In: Animal behaviour and drug action. H. Steinberg, A. V. S. De Reuck, J. Knight (Eds.), pp. 91–113. London: Churchill 1964.
Weijnen, J. A. W. M.: Effects of amphetamine-amylobarbitone mixtures on ambulation of rats in Y-mazes. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 5, 180–184 (1969).
Winer, B. J.: Statistical principles in experimental designs. New York: McGraw-Hill 1970.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors wish to acknowledge the assistance of J. C. Cooke and M. Reid in the conduct of the experiment.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Glow, P.H., Russell, A. Effects of dexamphetamine, amylobarbitone sodium and their mixture on sensory contingent bar pressing behaviour in the rat. Psychopharmacologia 31, 239–251 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00422514
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00422514