Abstract
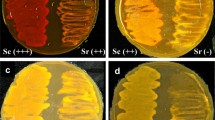
Excretion of an extracellular protease of Serratia marcescens ATCC 25419 occurred during logarithmic growth and was highest (per cell) when cultures reached the stationary growth phase. Production of the extracellular protease was induced by leucine or casein in minimal medium or by growth in tryptone-yeast medium. In the late stationary phase an intracellular protease activity accumulated which was also observed in mutants with very low extracellular protease activity. The excreted protease was the dominant protein in the growth medium. The protease was purified to homogeneity by column chromatography on Bio-Gel P-100 and on DEAE-cellulose. Quantitative amino acid analysis revealed the absence of sulfurcontaining amino acids. The enzyme consists of one polypeptide chain. A molecular weight of 51,000 and 55,000 was estimated using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and chromatography on Bio-Gel P-100 respectively. The enzyme cleaved only N-α-benzoyl-DL-lysine-and-arginine-nitroanilides but not the corresponding leucine or tyrosine derivatives nor a set of diand tripeptides.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SDS:
-
sodium dodecylsulfate
References
Appel, W.: Aminosäurearylamidasen (“Leucin-Nitranilidase”). In: Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse (H. U. Bergmeyer, ed.), pp. 995–1004. Weinheim: Verlag Chemie 1974
Braun, V., Rehn, K., Wolff, H.: Supramolecular structure of the rigid layer of the cell wall of Salmonella, Serratia, Proteus, and Pseudomonas fluorescens. Number of lipoprotein molecules in a membrane layer. Biochemistry 9, 5041–5049 (1970)
Braun, V., Schaller, K., Wabl, M. R.: Isolation, characterization, and action of colicin M. Antmicrob. Agents Chemother. 5, 520–533 (1974)
Braun, V.: Structure-function relationships of the Gram-negative bacterial cell envelope. In: Relations between structure and function in the prokaryotic cell (R. Y. Stanier, H. J. Rogers, B. J. Ward eds.) Vol. 28, pp. 111–138. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1978
Bromke, B. J., Hammel, J. M.: Regulation of extracellular protease formation by Serratia marcescens. Can. J. Microbiol. 25, 47–52 (1978)
Castaneda-Agullo, M.: Studies on the biosynthesis of extracellular proteases by bacteria. I. Serratia marcescens. Synthetic and gelatin media. J. Gen. Physiol. 39, 369–375 (1956)
Grimont, P. A. D., Grimont, F.: Proteinase zymograms of Serratia marcescens as an epidemiological tool. Current Microbiol. 1, 15–18 (1978)
Hardy, K. G.: Colicinogeny and related phenomena. Bacteriol. Rev. 39, 464–515 (1975)
Heller, K. B.: Outer membrane of Serratia marcescens: Apparent molecular weight of heat-modifiable proteins in gels with different acrylamide concentrations. J. Bacteriol. 137, 670–672 (1979)
Herschman, H. R., Helinski, D. R.: Purification and characterization of colicin E2 and colicin E3. J. Biol. Chem. 242, 5360–5368 (1967)
Hirs, C. H. W.: Oxidation of ribonuclease with performic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 219, 611–621 (1956)
McLaughlin, R. E., Keller, J. C.: Antibiotic control of an epizootic caused by Serratia marcescens Bizio in the Boll Weevil, Anthonomus grandis Boheman. Pathol. 6, 481–485 (1964)
Loriya, Z. K., Bryukner, B., Egorov, N. S.: Nature of the true inducer of the synthesis of extracellular protease by Serratia marcescens. Mikrobiologiya 46, 440–446 (1977)
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., Randall, R. J.: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951)
Lugtenberg, B., Meijers, J., Peters, R., van der Hoek, P., van Alphen, L.: Electrophoretic resolution of the “major outer membrane proteins” of Escherichia coli K-12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 58, 254–258 (1975)
Miyata, K., Maejima, K., Tomoda, K., Isono, M.: Serratia protease. Purification and general properties of the enzyme. Agric. Biol. Chem. 34, 310–318 (1970)
Murakami, M., Fukunaga, K., Matsuhashi, M., Ouo, M.: Stimulative effect of proteins on protease formation of Serratia sp. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 192, 378–380 (1969)
Mock, M., Schwartz, M.: Mechanism of colicin E3 production in strains harboring wild-type or mutant plasmids. J. Bacteriol. 136, 700–707 (1978)
Prestidge, L., Gage, V., Spizizen, J.: Protease activities during the course of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 107, 815–823 (1971)
Ryden, A. C., v. Hofsten, B.: Some properties of the extracellular proteinase and the cell-bound peptidase of Serratia. Acta Chem. Scand. 22, 2803–2808 (1968)
Winkler, U., Heller, B., Felle, B.: Pleiotropic consequences of mutations towards antibiotic-hypersensitivity in Serratia marcescens. Arch. Microbiol. 116, 259–268 (1978)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Braun, V., Schmitz, G. Excretion of a protease by Serratia marcescens . Arch. Microbiol. 124, 55–61 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00407028
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00407028