Abstract
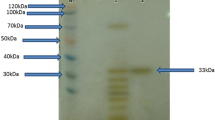
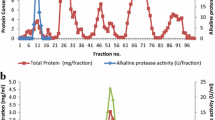
An extracellular, halophilic, alkalithermophilic serine protease from the halo-alkaliphilic Alkalibacillus sp. NM-Da2 was purified to homogeneity by ethanol precipitation and anion-exchange chromatography. The purified protease was a monomeric enzyme with an approximate molecular mass of 35 kDa and exhibited maximal activity at 2.7 M NaCl, pH55 °C 9 and 56 °C. The protease showed great temperature stability, retaining greater than 80 % of initial activity after 2 h incubation at 55 °C. The protease was also extremely pH tolerant, retaining 80 % of initial activity at pH55 °C 10.5 after 30 min incubation. Protease hydrolyzed complex substrates, displaying activity on yeast extract, tryptone, casein, gelatin and peptone. Protease activity was inhibited at casein concentrations greater than 1.2 mg/mL. The enzyme was stable and active in 40 % (v/v) solutions of isopropanol, ethanol and benzene and was stable in the presence of the polysorbate surfactant Tween 80. Activity was stimulated with the oxidizing agent hydrogen peroxide. Inhibition with phenyl methylsulfonylfluoride indicates it is a serine protease. Synthetic saline wastewater treated with the protease showed 50 % protein removal after 5 h. Being halophilic, alkaliphilic and thermophilic, in addition to being resistant to organic solvents, this protease has potential for various applications in biotechnological and pharmaceutical industries.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anson ML (1938) Estimation of cathepsin and the partial purification of cathepsin. J Gen Physiol 22:79–89
Arabaci N, Yasemin C, Maasoglu Y, Arikan B (2013) Partial purification and characterization of thermostable, alkaline and chelator-resistant protease from a newly isolated Bacillus sp. CY7 and its potential applications in various industries JABS 7:14-19
Borkar S (2015) Alkaliphilic bacteria: diversity, physiology and industrial applications. In: Borkar S (ed) Bioprospects of Coastal Eubacteria. Springer International Publishing, Switzerland, pp 59–83
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chanalia P, Gandhi D, Jodha D, Singh J (2011) Applications of microbial proteases in pharmaceutical industry: an overview Rev Med Microbiol 22:96–101
DasSarma S, DasSarma P (2015) Halophiles and their enzymes: negativity put to good use. Curr Opin Microbiol 25:120–126
Delgado-Garcia M, Valdvia-Urdiales B, Aguilar-Gonzalez CN, Contreras-Esquivel JC, Rodriquez-Herrera R (2012) Halophilic hydrolases as a new tool for biotechnological industries. J Sci Food Agric 92:2575–2580
Gupta A, Khare SK (2009) Enzymes from solvent-tolerant microbes: useful biocatalysts for nonaqueous enzymology. Crit Rev Biotechnol 29:44–54
Gupta R, Beg QK, Lorenz P (2002) Bacterial alkaline proteases: molecular approaches and industrial applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59:15–32
Jain D, Pancha I, Mishra SK, Shrivastav A, Mishra S (2012) Purification and characterization of haloalkaline thermoactive, solvent stable and SDS-induced protease from Bacillus sp: a potential additive for laundry detergents. Bioresour Technol 115:228–236
Jisha VN et al (2013) Versatility of microbial proteases. Adv Enzyme Res 1:39–51
Joo HS, Kumar CG, Park GC, Palik SR, Chang CS (2003) Oxidant and SDS-stable alkaline protease from Bacillus clausii I-52: production and some properties. J Appl Microbiol 5:267–272
Joshi S, Satyanarayana T (2013) Characteristics and applications of a recombinant alkaline serine protease from a novel bacterium Bacillus lehensis. Bioresour Technol 131:76–85
Karbalaei-Heidari HR, Shahbazi M, Absalan G (2013) Characterization of a novel organic solvent tolerant protease from a moderately halophilic bacterium and its behavior in ionic liquids. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 170:573–586
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lee M, Dordick JS (2002) Enzyme activation for nonaqueous media. Curr Opin Biotechnol 13:376–384
Lefebvre O, Moletta R (2006) Treatment of organic pollution in industrial saline wastewater: a literature review. Water Res 40:3671–3682
Maruthiah T, Esakkiraj P, Prabakaran G, Palavesam A, Immanuel G (2013) Purification and characterization of moderately halophilic alkaline serine protease from marine Bacillus subtilis AP-MSU 6 Biocat Agri. Biotechnol 2:116–119
Maruthiah T, Immanuel G, Palavesam A (2015) Purification and characterization of halophilic organic solvent tolerant protease from marine Bacillus sp. APCMST-RS7 and its antioxidant potentials Proc Natl Acad Sci, India, Sect B Biol Sci. doi:10.1007/s40011-40015-40603-40010
Mesbah NM, Wiegel J (2012) Life under multiple extreme conditions: diversity and physiology of the halophilic alkalithermophiles App. Environ Microbiol 78:4074–4082
Mesbah NM, Wiegel J (2014) Purification and biochemical characterization of halophilic, alkalithermophilic protease AbCP from Alkalibacillus sp. NM-Fa4. J Mol Catal B Enzymatic 105:74–81
Ogino H, Ishikawa H (2001) Enzymes which are stable in the presence of organic solvents. J Biosci Bioeng 91:109–116
Oren A (2010) Industrial and environmental applications of halophilic microorganisms. Environ Technol 31:825–834
Powers JC, Asgian JL, Ekici OD, James KE (2002) Irreversible inhibitors of serine, cysteine and threonine proteases. Chem Rev 102:4639–4750
Raddadi N, Cherif A, Daffonchio D, Neifar M, Fava F (2015) Biotechnological applications of extremophiles, extremozymes and extremolytes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:7907–7913
Rosenberg L et al (2004) Safety and efficacy of a proteolytic enzyme for enzymatic burn debridement: A preliminary report. Burns 8:843–850
Sarethy IP, Saxena Y, Kapoor A, Sharma M, Sharma SK, Gupta V, Gupta S (2011) Alkaliphilic bacteria: applications in industrial biotechnology. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38:769–790
Sarmiento F, Peralta R, Blamey JM (2015) Cold and hot extremozymes: industrial relevance and current trends Front Bioeng. Biotechnol 3:148
Schmidt TM, Bleakley B, Nealson KH (1988) Characterization of an extracellular protease from the insect pathogen Xenorhabdus luminescens App. Environ Microbiol 54:2793–2797
Selim S, Hagagy N, Abdel-Aziz M, El-Meleigy E, Pessione E (2014) Thermostable alkaline halophilic-protease production by Natronolimnobius innermongolicus WN18. Nat Prod Res 28:1476–1479
Singh SK, Singh SP, Tripathi VR, Garg SK (2012) Purification, characterization and secondary structure elucidation of a detergent stable, halotolerant, thermoalkaline protease from Bacillus cereus SIU1. Process Biochem 47:1479–1487
Sinha R, Khare SK (2013) Characterization of detergent compatible protease of a halophilic Bacillus sp. EMB9: Differential role of metal ions in stability and activity. Bioresour Technol 145:357–361
Synowiecki J (2015) Some applications of thermophiles and their enzymes for protein processing. Afr J Biotechnol 9:7020–7025
Wiegel J (1998) Anaerobic alkalithermophiles, a novel group of extremophiles. Extremophiles 2:247–267
Wilson K (1997) Preparation of genomic DNA from Bacteria. In: Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (eds) Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. Wiley, New York, pp 2.4.1–2.4.5
Yin J, Chen J-C, Wu Q, Chen G-Q (2015) Halophiles, coming stars for industrial biotechnology. Biotechnol Adv 33:1433–1442
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the US, Egypt Science and Technology Joint Fund in cooperation with the Suez Canal University (Egypt) under Project number 1841 and the University of Georgia (USA) under Project Number NSF-OISE-1132412.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by L. Huang.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel-Hamed, A.R., Abo-Elmatty, D.M., Wiegel, J. et al. Biochemical characterization of a halophilic, alkalithermophilic protease from Alkalibacillus sp. NM-Da2. Extremophiles 20, 885–894 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-016-0879-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-016-0879-x