Abstract
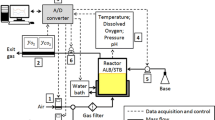
A coupled reactor system, consisting of one aerated stirred reactor and one anaerobic plug flow reactor was constructed. Circulation of microbial cells in this system, is chosen to represent the insufficient mixing conditions, present in a large scale vessel. Hereby it is shown, that oscillating oxygen concentrations, give effects on E.coli metabolism. The hydrogen production, resulting from mixed acid fermentation of anaerobically grown cells, is used to indicate the metabolic changes. These changes are measured as hydrogen concentration in the gas outlet of the aerated fermenter, with a Pd-MOS sensor. The dependency of the hydrogen evolution on the anaerobic residence time is shown, and the relevance of this model system for studies on the bioreactor performance, are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oosterhuis, N. M. G.; Kossen, N. W. F.: Dissolved oxygen concentration profiles in a production scale bioreactor. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 26 (1984) 546–555
Manfredini, R.; Cavallera, V.; Marini, L.; Donati, G.: Mixing and oxygen transfer in conventional stirred fermentors. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 25 (1983) 3115–3131
Vardar, F.; Lilly, M. D.: Effects of cycling oxygen concentrations on product formation in penicillin fermentations. Eur. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 14 (1982) 203–211
Larsson, G.; Enfors, S.-O.: Influence of oxygen starvation on the respiratory capacity of Penicillium chrysogenum. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 21 (1985) 228–233
Cleland, N.; Hörnsten, E. G.; Elwing, H.; Enfors, S.-O.; Lundström, I.: Measurement of hydrogen evolution by oxygen-limited E. coli by means of a hydrogen sensitive Pd-MOS sensor. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 20 (1984) 268–270
Cleland, N.; Enfors, S.-O.: A biological system for studies on mixing in bioreactors. Bioprocess Engineering 2 (1987) 115–120
Holme, T.; Arvidsson, S.; Lindholm, B.; Pavlu, B.: Enzymes laboratory scale production. Proc. Biochem. 5 (1970) 1–5
Cleland, N.; Larsson, G.; Enfors, S.-O.: Characterisation of a biological test system for studies on insufficient mixing in bioreactors: H2 evolution from E. coli. Bioprocess Engineering 5 (1990) 79–84
Gas absorption. In: Perry and Chilton (Ed:): Chemical Engineers' Handbook, Fifth Edition, section 14–3. McGraw-Hill 1973
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larsson, G., Enfors, S.O. Kinetics of escherichia coli hydrogen production during short term repeated aerobic-anaerobic fluctuations. Bioprocess Engineering 9, 167–172 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00389925
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00389925