Summary
Preliminary isometric responses of the paramyosin smooth body wall muscles of Paragordius varius (Nematomorpha) are reported.
-
1.
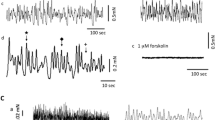
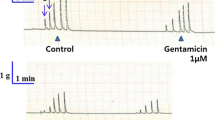
Brief a.c. or d. c. pulses give typical phasic responses, although the time relations are different (Fig. 1A).
-
2.
Longer d.c. (5 sec) (Fig. 1A) as well as ACh (10−6 M) stimulation (Fig. 1B) yield tonic contractions with slow decay of developed tension.
-
3.
5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) and piperazine citrate (PIP) both relax tonically contracted muscle, but the pattern of subsequent responses to d.c. or ACh stimulation are different (Fig. 1B).
-
4.
Tonic tension as a result of ACh (10−6 M) stimulation is decreased proportionately as the concentration of 5-HT is incrementally increased from 10−14 to 10−7 M (Fig. 1C).
-
5.
Repetitive a.c. stimulation does not show summation, while similar d.c. stimulation characteristically yields summation (Fig. 1D).
-
6.
The occurrence of paramyosin smooth muscle and its properties serves as a basis for understanding the “tight coiling” phenomenon common to fresh-water nematomorphs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldwin, E., Moyle, V.: An isolated nerve-muscle preparation from Ascaris lumbricoides. J. exp. Biol. 23, 277–291 (1947).
Bear, R. S.: X-ray diffraction on protein fibers II. Feather rachis, porcupine quill tip and clam muscle. J. Amer. chem. Soc. 66, 2043–2045 (1944).
—, Selby, C. C.: The structure of paramyosin fibrils according to X-ray diffraction. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 2, 55–69 (1956).
Flood, P. R., Guthrie, D. M., Banks, J. R.: Paramyosin muscle in the notochord of Amphioxus. Nature (Lond.) 222 (5188), 87–88 (1969).
Goodwin, C. G., Vaughan-Williams, E. M.: Inhibition and neuromuscular paralysis in Ascaris lumbricoides. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 168, 857–871 (1963).
Hall, C. E., Jakus, M. A., Schmitt, F. O.: The structure of certain muscle fibers as revealed by the use of electron stains. J. appl. Physiol. 16, 459–465 (1945).
Hanson, J., Lowy, J.: Evidence for a sliding filament contractile mechanism in tonic smooth muscles of lamellibranch molluscs. Nature (Lond.) 184, 286–287 (1959).
—: Structure and function of the contractile apparatus in muscles of invertebrate animals, chap. IX. In: G. H. Bourne (ed.), The structure and function of muscle, vol. I. New York: Academic Press Inc. 1960.
—: The structure of molluscan tonic muscles, chap. 35. In: J. Gergely (ed.), Biochemistry of muscle contraction. Boston: Little, Brown & Co. 1964.
Heumann, H. G., Zebe, E.: Über Feinbau und Funktionsweise der Fasern aus dem Hautmuskelschlauch des Regenwurms, Lumbricus terrestris L. Z. Zellforsch. 78, 131–150 (1967).
Hidaka, T., Osa, T., Twarog, B. M.: The action of 5-hydroxytryptamine on Mytilus smooth muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 192, 869–877 (1967).
Hoyle, G.: “Catch”mechanisms of molluscs, chap. 15 F. In: G. A. Kerkut (ed.), Experiments in physiology and biochemistry, vol.1. New York: Academic Press, Inc. 1968.
Ikemoto, N.: Further studies in electron microscopic structures of the obliquestriated muscle of the earthworm, Eisenia foefida. Biol. J. Okayama Univ. 9 (3–4), 81–126 (1963).
Jewell, B. R.: The nature of the phasic and tonic responses of the anterior byssal retractor muscle of Mytilus. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 149, 154–177 (1959).
Johnson, W. H., Twarog, B. M.: Basis for prolonged contractions in molluscan muscles. J. gen. Physiol. 43, 941–960 (1960).
May, A.: Contributions to the life history of Gordius and Paragordius. III. Biol. Monogr. 5, No 2 (1919).
Norton, S., de Beer, E. J.: Investigations on the action of piperazine on Ascaris lumbricoides. Amer. J. trop. Med. 6, 898–905 (1957).
Philpott, D. E., Kahlbrock, M., Szent-Györgyi, A. G.: Filamentous organization of molluscan muscles. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 3, 254–269 (1960).
Prosser, C. L., Brown, F. A., Jr.: Comparative animal physiology. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders Co. 1961.
Rauther, M.: Zur Kenntnis und Beurteilung von Nectonema. Zool. Anz. 43, 561–568 (1914).
Staubesand, J., Kersting, K. H.: Feinbau und Organisation der Muskelzellen des Regenwurmes. Z. Zellforsch. 62, 416–442 (1964).
Swanson, C. J.: An ultrastructural, biochemical and functional analysis of the bodywalls of Paragordius varius (Leidy), and Gordius robustus Leidy; (Aschelminthes, Nematomorpha, Gordioidea). Ph. D. dissertation, University of Illinois, Urbana, 1970.
Szent-Györgyi, A. G.: Proteins of the myofibril, chap. I. In: G. H. Bourne (ed.), The structure and function of muscle, vol. II. New York: Academic Press, Inc. 1960.
Twarog, B. M.: Responses of a molluscan smooth muscle to acetylcholine and 5-hydroxytryptamine. J. Cell. Comp. Physiol. 44, 141–163 (1954).
—: Catch and the mechanism of action of 5-hydroxytryptamine on molluscan muscle: A speculation. Life Sci. 5, 1201–1213 (1966).
—: The regulation of catch in molluscan muscle. J. gen. Physiol. 50, 157–169 (1967).
Welsch, U.: Über den Feinbau der Chorda dorsalis von Branchiostoma lanceolatum. Z. Zellforsch. 87, 69–81 (1968).
—, Storch, V.: Zur Feinstruktur der Chorda dorsalis niederer Chordaten (Dendrodoa grossularia (v. Beneden) und Oikopleura diocia (Fol.). Z. Zellforsch. 93, 547–559 (1969).
Winton, F. R.: The change in viscosity of an unstriated muscle (Mytilus edulis) during and after stimulation with alternating, interrupted, and uninterrupted direct currents. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 88, 492–511 (1937).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swanson, C.J. Isometric responses of the paramyosin smooth muscle of Paragordius varius (Leidy), (Aschelminthes, Nematomorpha). Z. vergl. Physiologie 74, 403–410 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00341404
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00341404