Abstract
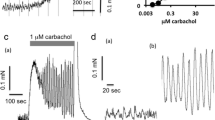
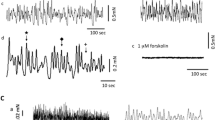
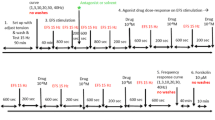
It has been reported that several aminoglycoside antibiotics have a potential of prolonging the action of non-depolarizing muscle relaxants by drug interactions acting pre-synaptically to inhibit acetylcholine release, but antibiotics itself also have a strong effect on relaxing the smooth muscle. In this study, four antibiotics of aminoglycosides such as gentamicin, streptomycin, kanamycin and neomycin were compared with skeletal muscle relaxants baclofen, tubocurarine, pancuronium and succinylcholine, and a smooth muscle relaxant, papaverine. The muscle strips isolated from the rat bladder were stimulated with pulse trains of 40 V in amplitude and 10 s in duration, with pulse duration of 1 ms at the frequency of 1–8 Hz, at 1, 2, 4, 6, 8 Hz respectively. To test the effect of four antibiotics on bladder smooth muscle relaxation, each of them was treated cumulatively from 1 μM to 0.1 mM with an interval of 5 min. Among the four antibiotics, gentamicin and neomycin inhibited the EFS response. The skeletal muscle relaxants (baclofen, tubocurarine, pancuronium and succinylcholine) and inhibitory neurotransmitters (GABA and glycine) did not show any significant effect. However, papaverine, had a significant effect in the relaxation of the smooth muscle. It was suggested that the aminoglycoside antibiotics have inhibitory effect on the bladder smooth muscle.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altinkurt O, Kanzik I (1980) Inhibitory effects of streptomycin on bronchoconstrictor, hypotensive and inflammatory responses to bradykinin and histamine. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 246:277–285
Aragon C, Lopez-Corcuera B (2003) Structure, function and regulation of glycine neurotransporters. Eur J Pharmacol 479:249–262
Bartholini G (1985) GABA receptor agonists: pharmacological spectrum and therapeutic actions. Med Res Rev 5:55–75
Beebe FA, Barkin RL, Barkin S (2005) A clinical and pharmacologic review of skeletal muscle relaxants for musculoskeletal conditions. Am J Ther 12:151–171
Brooks PL, Peever JH (2010) GABAergic and glycinergic control of upper airway motoneurons in rapid eye movement sleep. Adv Exp Med Biol 669:259–262
Burkett L, Bikhazi GB, Thomas KC Jr, Rosenthal DA, Wirta MG, Foldes FF (1979) Mutual potentiation of the neuromuscular effects of antibiotics and relaxants. Anesth Analg 58:107–115
Cho YR, Jang HS, Kim W, Park SY, Sohn UD (2010) P2X and P2Y receptors mediate contraction induced by electrical field stimulation in feline esophageal smooth muscle. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 14:311–316
Corrado AP, de Morais IP, Prado WA (1989) Aminoglycoside antibiotics as a tool for the study of the biological role of calcium ions. Historical overview. Acta Physiol Pharmacol Latinoam Farmacol 39:419–430
Davidoff RA (1985) Antispasticity drugs: mechanisms of action. Ann Neurol 17:107–116
de Groat WC, Booth AM (1980) Inhibition and facilitation in parasympathetic ganglia of the urinary bladder. Fed Proc 39:2990–2996
Eckly-Michel AE, Le Bec A, Lugnier C (1997) Chelerythrine, a protein kinase C inhibitor, interacts with cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Eur J Pharmacol 324:85–88
Ellis KO, Castellion AW, Honkomp LJ, Wessels FL, Carpenter JE, Halliday RP (1973) Dantrolene, a direct acting skeletal muscle relaxant. J Pharm Sci 62:948–951
Gergawy M, Vollrath B, Cook D (1998) The mechanism by which aminoglycoside antibiotics cause vasodilation of canine cerebral arteries. Br J Pharmacol 125:1150–1157
Hague BA, Martinez EA, Hartsfield SM (1997) Effects of high-dose gentamicin sulfate on neuromuscular blockade in halothane-anesthetized horses. Am J Vet Res 58:1324–1326
Herbert JM, Augereau JM, Gleye J, Maffrand JP (1990) Chelerythrine is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 172:993–999
Hester RK (1983) The effects of gentamicin on tension responses to norepinephrine and KCl and Ca++ binding and fluxes in canine renal vein. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 264:118–134
Iguchi M, Nakajima T, Hisada T, Sugimoto T, Kurachi Y (1992) On the mechanism of papaverine inhibition of the voltage-dependent Ca++ current in isolated smooth muscle cells from the guinea pig trachea. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 263:194–200
Karatas Y, Ergun Y, Gocmen C, Secilmis A, Singirik E, Dikmen A, Baysal F (2000) Possible postsynaptic action of aminoglycosides in the frog rectus abdominis. Acta Med Okayama 54:49–56
Milanov IG (1992) Mechanisms of baclofen action on spasticity. Acta Neurol Scand 85:305–310
Min CH, Wang Y, Bae J, Han JH, Sohn UD (2015) The inhibitory mechanism of gentamicin on electrical field stimulation response in rat bladder smooth muscle. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 19:473–478
Mogami H, Lloyd Mills C, Gallacher DV (1997) Phospholipase C inhibitor, U73122, releases intracellular Ca2+, potentiates Ins(1,4,5) P3-mediated Ca2+ release and directly activates ion channels in mouse pancreatic acinar cells. Biochem J 324(Pt 2):645–651
Paradelis AG, Triantaphyllidis C, Giala MM (1980) Neuromuscular blocking activity of aminoglycoside antibiotics. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 2:45–51
Persson K, Svane D, Glavind B, Uvelius B, Forman A, Andersson KE (1996) Effects of ovariectomy on mechanical properties and collagen content in rabbit lower urinary tract smooth muscle. Scand J Urol Nephrol 30:7–14
Pittinger C, Adamson R (1972) Antibiotic blockade of neuromuscular function. Annu Rev Pharmacol 12:169–184
Raezer DM, Wein AJ, Jacobowitz D, Corriere JN Jr (1973) Autonomic innervation of canine urinary bladder. Cholinergic and adrenergic contributions and interaction of sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems in bladder function. Urology 2:211–221
Saha JK, Sengupta JN, Goyal RK (1992) Role of chloride ions in lower esophageal sphincter tone and relaxation. Am J Physiol 263:G115–G126
Santi R, Ferrari M, Contessa AR (1964) On the mechanism of spasmolytic effect of papaverine and certain derivatives. Biochem Pharmacol 13:153–158
Simpson RK Jr, Robertson CS, Goodman JC (1996) The role of glycine in spinal shock. J Spinal Cord Med 19:215–224
Smith LR, Meyer G, Lieber RL (2013) Systems analysis of biological networks in skeletal muscle function. Wiley Interdisc Rev 5:55–71
Todd JK, Mack AJ (1969) A study of human bladder detrusor muscle. Br J Urol 41:448–454
Torocsik A, Oberfrank F, Sershen H, Lajtha A, Nemesy K, Vizi ES (1991) Characterization of somatodendritic neuronal nicotinic receptors located on the myenteric plexus. Eur J Pharmacol 202:297–302
Wakabayashi Y, Makiura Y, Tomoyoshi T, Kitahama K, Geffard M, Maeda T (1994) Adrenergic innervation of the urinary bladder body in the cat with special reference to structure of the detrusor muscle: an immunohistochemical study of noradrenaline and its synthesizing enzymes. Arch Histol Cytol 57:277–289
Wright JM, Collier B (1977) The effects of neomycin upon transmitter release and action. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 200:576–587
Wright EA, McQuillen MP (1971) Antibiotic-induced neuromuscular blockade. Ann N Y Acad Sci 183:358–368
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology [Grant 2011-0012139].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Chang Ho Min and Young Sil Min are equally contributed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Min, C.H., Min, Y.S., Lee, S.J. et al. The comparative effects of aminoglycoside antibiotics and muscle relaxants on electrical field stimulation response in rat bladder smooth muscle. Arch. Pharm. Res. 39, 863–870 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-016-0765-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-016-0765-1