Summary
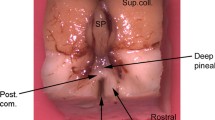
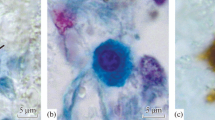
The aim of this study was to examine whether rod-opsin and S-antigen immunoreactions were present in the pineal organ of adult man and how these immunoreactions were correlated with neuronal markers, e.g., synaptophysin, and neurofilaments L, H and M. Three perfusion-fixed epithalamic regions including the pineal organ and five pineal glands obtained at routine autopsy were used. The specimens were taken from female or male patients, 25 to 85 years of age. All immunoreactions were performed using highly specific, well-characterized antibodies. Rod-opsin and S-antigen-immunoreactive pinealocytes occurred in all pineal organs investigated; however, the immunoreaction was restricted to small subpopulations of pinealocytes (rod-opsin immunoreaction: approximately 3%–5%; S-antigen immunoreaction: approximately 5%–10% of the total population). In contrast, immunoreactions for synaptophysin and neurofilaments M and H were present in numerous pinealocytes. Immunoreactivity for neurofilament L was not found. These data suggest that the cellular composition of the human pineal organ is heterogeneous. Moreover, the presence of rod-opsin and S-antigen immunoreactions in the human pineal organ indicates that it may be affected by autoimmune retinal diseases that are provoked by antibodies against these proteins, as is the case in rodents and non-human primates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bridges CDB, Landers RA, Fong SL, Liou GI (1986) Interstitial retinol-binding protein (IRBP) in rat and bovine pineal organs: evolutionary vestige or functional molecule? In: O'Brien P, Klein DC (eds) Pineal retinal relationships. Academic Press, Orlando, pp 383–400
Collin J-P (1971) Differentiation and regression of the cells of the sensory line in the epiphysis cerebri. In: Wolstenholme GEW, Knight J (eds) The pineal gland. Churchill-Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp 79–125
Collins VP (1987) Pineocytoma with neuronal differentiation demonstrated immunocytochemically. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand [A] 95:113–117
Dizhoor AM, Ray S, Kumar S, Niemi G, Spencer M, Brolley D, Walsh KA, Philipov PP, Hurley JB, Stryer L (1991) Recoverin: a calcium sensitive activator of retinal rod guanylate cyclase. Science 251:915–918
Dodt E (1973) The parietal eye (pineal and parapineal organs) of lower vertebrates. In: Jung R (ed) Handbook of sensory physiology, vol 7, part 3B. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 113–140
Eakin RM (1973) The third eye. University of California Press, Berkeley
Foster RG, Timmers AM, Schalken JJ, Grip WJ de (1989) A comparison of some photoreceptor characteristics in the pineal and retina. II. The Djungarian hamster (Phodopus sungorus). J Comp Physiol [A] 165:565–572
Frisch K von (1911) Beitrage zur Physiologie der Pigmenzellen in der Fischhaut. Pfluegers Arch Ges Physiol 138:319–387
Gery I, Mochizuki M, Nussenblatt RG (1986) Retinal specific antigens and immunopathogenic processes they provoke. Prog Retinal Res 5:75–109
Hirose S, Singh VK, Donoso LA, Shinohara T, Kotake S, Tanaka T, Kuwabara T, Yamaki K, Gery I, Nussenblatt RB (1989) An 18-mer peptide derived from the retinal S-antigen induces uveitis and pinealitis in primates. Clin Exp Immunol 77:106–111
Kalsow CM, Wacker WB (1973) Localization of a uveitogenic soluble retinal antigen in the normal guinea pig eye by an indirect fluorescent antibody technique. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 44:11–20
Kalsow CM, Wacker WB (1977) Pineal reactivity of antiretina sera. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 16:181–184
Korf HW (1986) Zur Frage photoneuroendokriner Zellen und Systeme. Vergleichende Untersuchungen am Pinealkomplex. Thesis, Fachbereich Humanmedizin, Universität Gießen
Korf HW, Ekström P (1987) Photoreceptor differentiation and neuronal organization of the pineal organ. In: Trentini GP, Gaetani C de, Pévet P (eds) Fundamentals and clinics in pineal research. Raven Press, New York, pp 35–47
Korf HW, Foster RG, Ekström P, Schalken JJ (1985a) Opsin-like immunoreaction in the retinae and pineal organs of four mammalian species. Cell Tissue Res 242:645–648
Korf HW, Møller M, Gery I, Zigler JS, Klein DC (1985b) Immunocytochemical demonstration of retinal S-antigen in the pineal organ of four mammalian species. Cell Tissue Res 239:81–85
Korf HW, Klein DC, Zigler JS, Gery I, Schachenmayr W (1986a) S-antigen-like immunoreactivity in a human pineocytoma. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 69:165–167
Korf HW, Oksche A, Ekström P, Veen T van, Zigler JS, Gery I, Klein DC (1986b) S-antigen immunocytochemistry. In: O'Brien P, Klein DC (eds) Pineal and retinal relationships. Academic Press, Orlando, pp 343–355
Korf HW, Bruce JA, Vistica B, Rollag M, Stein BM, Klein DC (1989) Immunoreactive S-antigen in cerebrospinal fluid: a marker of pineal parenchymal tumors? J Neurosurg 70:682–687
Korf HW, Sato T, Oksche A (1990) Complex relationships between the pineal organ and the medial habenular nucleus-pretectal region of the mouse as revealed by S-antigen immunocytochemistry. Cell Tissue Res 261:493–500
Müller B, Peichl L, Grip WJ de, Gery I, Korf HW (1989) Opsin-and S-antigen-like immunoreactions in photoreceptors of the tree shrew retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 30:530–535
Oksche A (1971) Sensory and glandular elements of the pineal organ. In: Wolstenholme GEW, Knight J (eds) The pineal gland. Churchill-Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp 127–146
Oksche A, Korf HW, Rodríguez EM (1987) Pinealocytes as photoneuroendocrine units of neuronal origin: concepts and evidence. In: Reiter RJ, Fraschini F (eds) Advances in pineal research, vol 2. Libbey, London, pp 1–18
Palczewski K, Carruth ME, Adamus G, McDowell J, Hargrave PA (1990) Molecular, enzymatic and functional properties of rhodopsin kinase from rat pineal gland. Vision Res 30:1129–1137
Perentes E, Rubinstein LJ, Herman MM, Donoso LA (1986) S-antigen immunoreactivity in human pineal glands and pineal parenchymal tumors. A monoclonal antibody study. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 71:224–227
Pfister C, Chabre M, Plouet J, Tuyen VV, Kozak Y de, Faure J-P, Kühn H (1985) Retinal S-antigen identified as the 48 K protein regulating light-dependent phosphodiesterase in rods. Science 228:891–893
Redecker P, Grube D, Jahn R (1990) Immunohistochemical localization of synaptophysin (p38) in the pineal gland of the Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus). Anat Embryol 181:433–440
Rodrigues MM, Hackett J, Gaskins R, Wiggert B, Lee L, Redmont M, Chader GJ (1986) Interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein in retinal rod cells and pineal gland. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 27:844–850
Rodríguez EM, Korf H-W, Oksche A, Yulis CR, Hein S (1988) Pinealocytes immunoreactive with antisera against secretory glycoproteins of the subcommissural organ: a comparative study. Cell Tissue Res 254:469–480
Tsin ATC, Philips TS, Reiter RJ (1990) An evaluation on the level of retinoids in the bovine pineal body. Adv Pineal Res 3:147–150
Veen T van, Eloffson R, Hartwig HG, Gery I, Mochizuki M, Klein DC (1986a) Retinal S-antigen: immunocytochemical and immunochemical studies on the distribution in animal photoreceptors and pineal organs. Exp Biol 45:15–25
Veen T van, Katial A, Shinohara T, Banett DJ, Wiggert B, Chader GJ, Nickerson JM (1986b) Retinal photoreceptor neurons and pinealocytes accumulate mRNA for interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein (IRBP). FEBS Lett 208:133–137
Vollrath L, Schröder H (1987) Neuronal properties of mammalian pinealocytes? In: Trentini GP, Gaetani C de, Pévet P (eds) Fundamentals and clinics in pineal research. Raven Press, New York, pp 13–23
Wald G (1968) The molecular basis of visual excitation. Nature 219:800–807
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, SK., Klein, D.C. & Korf, HW. Immunocytochemical demonstration of rod-opsin, S-antigen, and neuron-specific proteins in the human pineal gland. Cell Tissue Res 267, 493–498 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00319371
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00319371