Summary
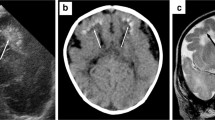
Three cases of Fahr's syndrome are described. All patients had disturbances of calcium metabolism and had had a meningoencephalitis in childhood. It is suggested that gliovascular changes, induced by cerebral inflammation, can later facilitate the occurrence of calcification of the striopallidodentate system when abnormality of calcium metabolism develops.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brannan TS, Burger AA, Chaudhary MY (1980) Bilateral basal ganglia calcifications visualised on CT scan. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 43:403–406
Bruyn GW, Bots GTAM, Staal A (1964) Familial bilateral vascular calcification in the central nervous system. Psychiatr Neurol Neurochir 67:342–376
Danowski TS, Lasser EG, Wechsler RL (1960) Calcification of the basal ganglia in postthyroidectomy hypoparathyroidism. Metabolism 9:1064–1065
Denny-Brown D (1962) The occurrence of two general types of change in degenerative affections of the basal ganglia. In: van Bogaert L (ed) Livre jubilaire. Les editions “Acta Medica Belgica”, Bruxelles, pp 215–221
Fahr T (1931) Idiopathische Verkalkung der Hirngefabe. Zentralbl Allg Pathol 50:129–133
Hastrup J, Reske-Nielson E (1965) Symmetrical brain calcifications in infants. Acta Neurol Scand [Suppl 13] 41:637
Jesserer H (1951) Das Krankheitsbild der Kryptogenetischen Nebenschilddrüseninsuffizienz. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 76:1552–1557
Koller WC, Cochran JW, Klawans HL (1979) Calcification of the basal ganglia. Computerized tomography and clinical correlation. Neurology (Minneap) 29:328–333
Lowenthal A (1948) La calcification vasculaire intracérébrale non-arterioscléreuse de Fahr, est-elle la manifestation cérébrale d'une perturbation des fonctions parathyrodiennes? Acta Neurol Belg 48:613–632
Lowenthal A, Bruyn GW (1968) Calcification of the striopallidodentate system. In: Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW (eds) Handbook of clinical neurology, vol 6. North-Holland, Amsterdam, pp 703–725
Ludin HP (1980) Electromyography in practice. Thieme and Stratton, New York
Margolin D, Hammerstad J, Orwoll E, McClung M, Calhoun D (1980) Intracranial calcification in hyperparathyroidism associated with gait apraxia and parkinsonism. Neurology (Minneap) 30:1005–1007
Metzger J, Weill F, Cabanis EA, Bobbeville JF, Ben-Hamida M (1975) Les calcifications intracraniennes. In: Fishgold H (ed) Traité de radiodiagnostic-neuroradiologie, vol 14. Masson, Paris, pp 3–76
Muenter MD, Whisnant TP (1968) Basal ganglia calcifications, hypoparathyroidism and extraphyramidal manifestations. Neurology (Minneap) 18:1075–1083
Rand CW, Olsen CW, Courville CB (1943) Gross calcareous deposits in the corpora striata and dentate nuclei: report of two cases with comments on certain etiologic factors. Bull Los Ang Neurol Soc 8:118
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morgante, L., Vita, G., Meduri, M. et al. Fahr's syndrome: local inflammatory factors in the pathogenesis of calcification. J Neurol 233, 19–22 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00313985
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00313985