Summary
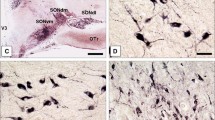
We report the histological findings in a case of hereditary diabetes insipidus (HDI) using vasopressin (VP) immunohistochemistry. The hypothalamus displayed a marked loss of magnocellular VP neurons, with preservation of the smaller cells. The neurohypophysis was severely atrophic with scanty immunoreactivity. Our results support the hypothesis that HDI results from a selective degeneration of VP neurons affecting chiefly the magnocellular elements projecting to the neurohypophysis. The sparing of the parvocellular component may reflect the projection of these neurons to non-pituitary targets.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blotner H (1958) Primary or idiopathic diabetes insipidus: a system disease. Metabolism 7:191–200
Braverman LE, Mancini JP, McGoldrick DM (1965) Hereditary diabetes insipidus. A case report with autopsy findings. Ann Intern Med 63:503–508
Dierickx K, Vandesande F (1977) Immunocytochemical localization of the vasopressinergic and the oxytocinergic neurons in the human hypothalamus. Cell Tissue Res 184:15–27
Green JR, Buchan GC, Alvord EC Jr, Swanson A (1967) Hereditary and idiopathic diabetes insipidus. Brain 90:707–715
MacCubbin DA, Van Buren JM (1963) A quantitative evaluation of hypothalamic degeneration and its relation to diabetes insipidus following interruption of human hypophyseal stalk. Brain 86:443–464
Morton A (1969) A quantitative analysis of the normal neuron population of the hypothalamic magnocellular nuclei in man and of their projections to the neurohypophysis. J Comp Neurol 136:143–158
Sofroniew MV (1985) Vasopressin, oxytocin and their related neurophysins. In: Björklund A, Hökfelt T (eds) Handbook of chemical neuroanatomy, vol 4. GABA and neuropeptides in the CNS, part 1. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 93–165
Sofroniew MV, Weindl A (1980) Identification of parvocellular vasopressin and neurophysin neurons in the suprachiasmatic nucleus of a variety of mammals including primates. J Comp Neurol 193:659–675
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bergeron, C., Kovacs, K., Ezrin, C. et al. Hereditary diabetes insipidus: an immunohistochemical study of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. Acta Neuropathol 81, 345–348 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00305879
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00305879