Summary
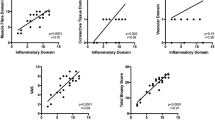
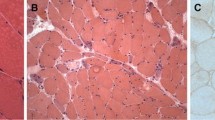
In ten patients with inclusion body myositis (IBM) five muscular biopsies showed profuse inflammatory exudates and three showed a few scattered inflammatory cells with partial invasion in some muscle fibers. No inflammatory cells were seen in two cases. In all patients, histopathological, histomorphometric and immunocytochemical studies were performed. Immunocytochemistry for the class I and class II major histocompatibility complex gene product (MHC) was performed in all cases and in ten control muscles including: normal muscles [3], dermatomyositis [3], polymyositis [3], scleroderma [1]. In the five cases of IBM with inflammatory exudates, subsets of lymphocytes were analyzed with a panel of monoclonal antibodies against B cells, T4 cells, T8 cells, K and natural killer cells and macrophages. Some muscle fibers expressed class I MHC antigens in the inflammatory cases of IBM. These fibers were near the inflammatory exudates and occasionally showed a partial invasion. No expression of class I MHC was found in normal muscles and in non-inflammatory cases of IBM. The antigen which triggers the mononuclear cells in the inflammatory forms of IBM is probably not the filamentous inclusions in rimmed vacuoles. In other inflammatory myopathies, expression of class I MHC was present on all fibers in polymyositis, only in the perifascicular area in dermatomyositis and in scleroderma. It could be suggested that the term “inclusion body muscle disease” be applied to cases with rimmed vacuoles and “IBM-like” filaments without inflammatory cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arahata K, Engel AG (1984) Monoclonal antibody analysis of mononuclear cells in myopathies. I. Quantitation of subsets according to diagnosis and sites of accumulation and demonstration and counts of muscle fibers invaded by T cells. Ann Neurol 16:193–208
Araharata K, Engel AG (1984) Monoclonal antibody analysis of mononuclear cells in myopathies. III. Immunoelectron microscopy aspects of cell-mediated muscle fiber injury. Ann Neurol 19:112–125
Arahata K, Engel AG (1988) Monoclonal antibody analysis of mononuclear cells in myopathies. IV. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity and muscle fiber necrosis. Ann Neurol 23:168–173
Arahata K, Engel AG (1988) Monoclonal antibody analysis of mononuclear cells in myopathies. V. Identification and quantitation of T8 cytotoxic and T8 suppressor cells. Ann Neurol 23:493–499
Borg K, Solders G, Borg J, Edström L, Kristensson K (1988) Neurogenic involvement in distal myopathy (Welander). Abstracts of the 9th International Meeting on Neuromuscular Disease. Marseille, p 54
Brooke MH, Engel WK (1969) The histographic analysis of human muscle biopsies with regard to fiber types. Adult male and female. Neurology 19:221–233
Carpenter S, Karpati G, Heller I, Eisen A (1978) Inclusion body myositis. A distinct variety of idiopathic inflammatory myopathy. Neurology 28:8–17
Carpenter S, Karpati G (1984) Inflammatory myopathies inclusion body myositis. Pathology of skeletal muscle. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp 559–571
Chou SM (1986) Inclusion body myositis. A chronic persistent mumps myositis. Hum Pathol 17:765–777
Cole AJ, Kuzniecky R, Karpati G, Carpenter S, Andermann E, Andermann F (1988) Familial myopathy with changes resembling inclusion body myositis and periventricular leucoencephalopathy: a new syndrome. Brain 111:1025–1037
Daar AS, Fuggle SV, Fabre JW, Ting A, Morris PJ (1984) The detailed distribution of HLA A, B, C antigens in normal human organs. Transplantation 38:287–292
Dubowitz V, Brooke MH (1973) Muscle biopsy: a modern approach. Saunders, London, pp 20–23
Eisen A, Berry K, Gibson G (1983) Inclusion body myositis (IBM). Myopathy or neuropathy? Neurology 33:1109–1114
Engel AG, Arahata K (1984) Monoclonal antibody analysis of mononuclear cells in myopathies. II. Phenotypes of autoinvasive cells in polymyositis and inclusion body myositis. Ann Neurol 16:209–215
Figarella-Branger D, Pellissier JF, Serratrice G, Pouget J, Bianco N (1989) Etude immunocytochimique des formes inflammatoires de myopathies facio-scapulo-humérales et corrélation avec d'autres myosites. Ann Pathol 9:100–108
Flyer DC, Burakoff SJ, Faller DV (1985) Retrovirus induced changes in major histocompatibility complex antigen expression influence susceptibility to lysis by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol 135:2287–2292
Fukuhara N, Kumamoto T, Tsubaki T (1980) Rimmed vacuoles. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 51:229–235
Fukuhara N, Kumamoto T, Tsubaki T, Mayuzumi T, Nitta H (1982) Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy and distal myopathy. Acta Neurol Scand 65:458–467
Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger H (1981) Use of avidin-biotinperoxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques. A comparison between ABC and unlabelled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem 29:577–580
Isenberg DA, Rowe S, Shearer R, Novick D, Beverley PCL (1986) Localization of interferons and interleukin 2 in polymyositis and muscular dystrophy. Clin Exp Immunol 63:450–458
Julien J, Vital C, Vallat JM, Lagueny A, Sapina D (1982) Inclusion body myositis clinical biological and ultrastructural study. J Neurol Sci 55:15–24
Karpati G, Pouliot Y, Carpenter S (1988) Expression of immunoreactive major histocompatibility complex products in human skeletal muscles. Ann Neurol 23:64–72
Ketelsen UP, Beckmann R, Zimmermann H, Sauer M (1977) Inclusion body myositis. A “slow-virus” infection of skeletal musculature? Klin Wochenschr 55:1063–1066
Kumamoto T, Fukuhara N, Nagashimo M, Kando T, Wakabayashi M (1982) Distal myopathy: histochemical and ultrastructural studies. Arch Neurol 39:367–371
Lotz BP, Engel AG, Nishino H, Stevens JC, Litchy WJ (1989) Inclusion body myositis. Observations in 40 patients. Brain 112:727–747
McDouall RM, Dunn MJ, Dubowitz V (1989) Expression of class I and class II MHC antigens in neuromuscular diseases. J Neurol Sci 89:213–226
Matsubara S, Tanabe H (1982) Hereditary distal myopathy with filamentous inclusions. Acta Neurol Scand 65:363–368
Nishino H, Engel AG, Rima BK (1989) The mumps virus hypothesis of inclusion body myositis. Ann Neurol 25:260–264
Nonaka I, Sunohara N, Ishiura S, Satoyoshi E (1981) Familial distal myopathy with rimmed vacuole and lamellar (myeloid) body formation. J Neurol Sci 51:141–155
Nonaka I, Sunohara N, Satoyoshi E, Terasawa K, Yonemoto K (1985) Autonomal recessive distal muscular dystrophy: a comparative study with distal myopathy with rimmed vacuole formation. Ann Neurol 17:51–59
Ringel SP, Kenny CE, Neville HE, Giorn OR, Carry MR (1987) Spectrum of inclusion body myositis. Arch Neurol 44:1154–1157
Rosa F, Hatat D, Abadie A, Fellous M (1985) Regulation of histocompatibility antigens by interferon. Ann Inst Pasteur Immunol 136:103–119
Sawchak JA, Kula RW, Sher JH, Shafiq SA, Clark LM (1983) Clinicopathologic investigations in patients with inclusion body myositis. Neurology 33 [Suppl 2]:237
Schwartz RH (1985) T lymphocyte recognition of antigen in association with gene products of the major histocompatibility complex. Annu Rev Immunol 3:237–261
Serratrice G, Pellissier JF (1987) Myopathies oculaires. Etude nosologique de 49 cas. Presse Med 16:1969–1974
Serratrice G, Pellissier JF, Pouget J, Figarella-Branger D (1989) Formes cliniques des myosites a inclusions: 12 cas. Rev Neurol (Paris) 145:781–788
Smith T, Chad D (1984) Intranuclear inclusions in oculopharyngeal dystrophy. Muscle Nerve 7:339–341
Yunis EJ, Samaha FJ (1971) Inclusion body myositis. Lab Invest 25:240–248
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Figarella-Branger, D., Pellissier, J.F., Bianco, N. et al. Inflammatory and non-inflammatory inclusion body myositis. Acta Neuropathol 79, 528–536 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00296113
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00296113