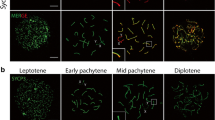
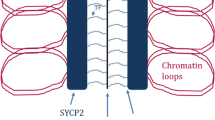
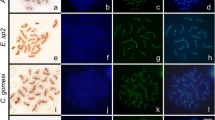
Abstract
Genetic variability in sexually reproducing organisms results from an exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes. The genetic exchange mechanism is dependent on the synaptonemal complex (SC), a protein structure localized between the homologous chromosomes. The current structural models of the mammalian SC are based on electron microscopy, superresolution, and expansion microscopy studies using chemical fixatives and sample dehydration of gonads, which are methodologies known to produce structural artifacts. To further analyze the structure of the SC, without chemical fixation, we have adapted a cryo-fixation method for electron microscopy where pachytene cells are isolated from mouse testis by FACS, followed by cryo-fixation, cryo-substitution, and electron tomography. In parallel, we performed conventional chemical fixation and electron tomography on mouse seminiferous tubules to compare the SC structure obtained with the two fixation methods. We found several differences in the structure and organization of the SC in cryo-fixed samples when compared to chemically preserved samples. We found the central region of the SC to be wider and the transverse filaments to be more densely packed in the central region of the SC.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CE:
-
Central element
- CR:
-
Central region
- EM:
-
Electron microscopy
- ET:
-
Electron tomography
- FACS:
-
Fluorescence-activated cell sorting
- FS:
-
Freeze-substitution
- HPF:
-
High-pressure freezing
- LEs:
-
Lateral elements
- nda:
-
Neighbor density analysis
- SC:
-
Synaptonemal complex
- TFs:
-
Transverse filaments
- 3D:
-
Three-dimensional
References
Bastos H, Lassalle B, Chicheportiche A et al (2005) Flow cytometric characterization of viable meiotic and postmeiotic cells by Hoechst 33342 in mouse spermatogenesis. Cytom A 65:40–49. https://doi.org/10.1002/cyto.a.20129
Bolcun-Filas E, Costa Y, Speed R et al (2007) SYCE2 is required for synaptonemal complex assembly, double strand break repair, and homologous recombination. J Cell Biol 176:741–747. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200610027
Bolcun-Filas E, Hall E, Speed R et al (2009) Mutation of the mouse Syce1 gene disrupts synapsis and suggests a link between synaptonemal complex structural components and DNA repair. PLoS Genet 5:e1000393. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1000393
Bollschweiler D, Radu L, Joudeh L et al (2019) Molecular architecture of the SYCP3 fibre and its interaction with DNA. Open Biol 9:190094. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsob.190094
Bonilla E (1977) Staining of transverse tubular system of skeletal muscle by tannic acid-glutaraldehyde fixation. J Ultrastruct Res:162–165.https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-5320(77)90028-4
Cahoon CK, Yu Z, Wang Y et al (2017) Superresolution expansion microscopy reveals the three-dimensional organization of the Drosophila synaptonemal complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:E6857–E6866. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1705623114
Collins KA, Unruh JR, Slaughter BD et al (2014) Corolla is a novel protein that contributes to the architecture of the synaptonemal complex of Drosophila. Genetics 198:219–228. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.114.165290
Costa Y, Speed R, Ollinger R et al (2005) Two novel proteins recruited by synaptonemal complex protein 1 (SYCP1) are at the centre of meiosis. J Cell Sci 118:2755–2762. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.02402
Cotta-Pereira G, Rodrigo FG, David-Ferreira JF (1976) The use of tannic acid-glutaraldehyde in the study of elastic and elastic-related fibers. Stain Technol 51:7–11. https://doi.org/10.3109/10520297609116662
Davies OR, Maman JD, Pellegrini L (2012) Structural analysis of the human SYCE2-TEX12 complex provides molecular insights into synaptonemal complex assembly. Open Biol 2:120099. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsob.120099
de Vries FA, de Boer E, van den Bosch M et al (2005) Mouse Sycp1 functions in synaptonemal complex assembly, meiotic recombination, and XY body formation. Genes Dev 19:1376–1389. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.329705
Dempster WT (1960) Rates of penetration of fixing fluids. Am J Anat 107:59–72. https://doi.org/10.1002/aja.1001070105
Dernburg AF, McDonald K, Moulder G et al (1998) Meiotic recombination in C. elegans initiates by a conserved mechanism and is dispensable for homologous chromosome synapsis. Cell 94:387–398
Dobson MJ, Pearlman RE, Karaiskakis A et al (1994) Synaptonemal complex proteins: occurrence, epitope mapping and chromosome disjunction. J Cell Sci 107(Pt 1):2749–60
Dong H, Roeder GS (2000) Organization of the yeast Zip1 protein within the central region of the synaptonemal complex. J Cell Biol 148:417–426
Dunce JM, Dunne OM, Ratcliff M et al (2018) Structural basis of meiotic chromosome synapsis through SYCP1 self-assembly. Nat Struct Mol Biol 25:557–569. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-018-0078-9
Dunce JM, Salmon LJ, Davies OR (2021) Structural basis of meiotic chromosome synaptic elongation through hierarchical fibrous assembly of SYCE2-TEX12. Nat Struct Mol Biol 28:681–693. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-021-00636-z
Dunne OM, Davies OR (2019a) A molecular model for self-assembly of the synaptonemal complex protein SYCE3. J Biol Chem 294:9260–9275. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA119.008404
Dunne OM, Davies OR (2019b) Molecular structure of human synaptonemal complex protein SYCE1. Chromosoma 128:223–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-018-00688-z
Fiserova J, Spink M, Richards SA et al (2014) Entry into the nuclear pore complex is controlled by a cytoplasmic exclusion zone containing dynamic GLFG-repeat nucleoporin domains. J Cell Sci 127:124–136. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.133272
Frotscher M, Zhao S, Graber W et al (2007) New ways of looking at synapses. Histochem Cell Biol 128:91–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-007-0305-7
Geisinger A, Benavente R (2016) Mutations in Genes Coding for Synaptonemal Complex Proteins and Their Impact on Human Fertility. Cytogenet Genome Res 150:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1159/000453344
Giddings TH (2003) Freeze-substitution protocols for improved visualization of membranes in high-pressure frozen samples. J Microsc 212:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2818.2003.01228.x
Gómez-H L, Felipe-Medina N, Sánchez-Martín M et al (2016) C14ORF39/SIX6OS1 is a constituent of the synaptonemal complex and is essential for mouse fertility. Nat Commun 7:13298. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13298
Hamer G, Gell K, Kouznetsova A et al (2006) Characterization of a novel meiosis-specific protein within the central element of the synaptonemal complex. J Cell Sci 119:4025–4032. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.03182
Hamer G, Wang H, Bolcun-Filas E et al (2008) Progression of meiotic recombination requires structural maturation of the central element of the synaptonemal complex. J Cell Sci 121:2445–2451. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.033233
Hata S, Pastor Peidro A, Panic M et al (2019) The balance between KIFC3 and EG5 tetrameric kinesins controls the onset of mitotic spindle assembly. Nat Cell Biol 21:1138–1151. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-019-0382-6
Hernández-Hernández A, Masich S, Fukuda T et al (2016) The central element of the synaptonemal complex in mice is organized as a bilayered junction structure. J Cell Sci 129:2239–2249. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.182477
Heumann JM, Hoenger A, Mastronarde DN (2011) Clustering and variance maps for cryo-electron tomography using wedge-masked differences. J Struct Biol 175:288–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2011.05.011
Höög JL, Schwartz C, Noon AT et al (2007) Organization of interphase microtubules in fission yeast analyzed by electron tomography. Dev Cell 12:349–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2007.01.020
Humphryes N, Leung WK, Argunhan B et al (2013) The Ecm11-Gmc2 complex promotes synaptonemal complex formation through assembly of transverse filaments in budding yeast. PLoS Genet 9:e1003194. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003194
Jiménez N, Vocking K, van Donselaar EG et al (2009) Tannic acid-mediated osmium impregnation after freeze-substitution: a strategy to enhance membrane contrast for electron tomography. J Struct Biol 166:103–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2008.12.009
Kiseleva E, Richardson AC, Fiserova J et al (2014) Imaging yeast NPCs: from classical electron microscopy to Immuno-SEM. Methods Cell Biol 122:59–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-417160-2.00003-5
Köhler S, Wojcik M, Xu K, Dernburg AF (2017) Superresolution microscopy reveals the three-dimensional organization of meiotic chromosome axes in intact Caenorhabditis elegans tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:E4734–E4743. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1702312114
Kremer JR, Mastronarde DN, McIntosh JR (1996) Computer visualization of three-dimensional image data using IMOD. J Struct Biol 116:71–76. https://doi.org/10.1006/jsbi.1996.0013
Li Y, Almassalha LM, Chandler JE et al (2017) The effects of chemical fixation on the cellular nanostructure. Exp Cell Res 358:253–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.06.022
Liu JG, Yuan L, Brundell E et al (1996) Localization of the N-terminus of SCP1 to the central element of the synaptonemal complex and evidence for direct interactions between the N-termini of SCP1 molecules organized head-to-head. Exp Cell Res 226:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1006/excr.1996.0197
MacQueen AJ, Colaiacovo MP, McDonald K, Villeneuve AM (2002) Synapsis-dependent and -independent mechanisms stabilize homolog pairing during meiotic prophase in C. elegans. Genes Dev 16:2428–2442. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1011602
Marsh BJ, Mastronarde DN, Buttle KF et al (2001) Organellar relationships in the Golgi region of the pancreatic beta cell line, HIT-T15, visualized by high resolution electron tomography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:2399–2406. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.051631998
Marsh BJ, Pavelka M (2013) Viewing Golgi structure and function from a different perspective–insights from electron tomography. Methods Cell Biol 118:259–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-417164-0.00016-1
Mastronarde DN (1997) Dual-axis tomography: an approach with alignment methods that preserve resolution. J Struct Biol 120:343–352. https://doi.org/10.1006/jsbi.1997.3919
McDonald KL (2014) Out with the old and in with the new: rapid specimen preparation procedures for electron microscopy of sectioned biological material. Protoplasma 251:429–448. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-013-0575-y
McEwen BF, Renken C, Marko M, Mannella C (2008) Chapter 6: Principles and practice in electron tomography. Methods Cell Biol 89:129–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0091-679X(08)00606-7
Mielanczyk L, Matysiak N, Michalski M et al (2014) Closer to the native state. Critical evaluation of cryo-techniques for Transmission Electron Microscopy: preparation of biological samples. Folia Histochem Cytobiol 52:1–17. https://doi.org/10.5603/FHC.2014.0001
Moses MJ (1968) SYNAPTINEMAL COMPLEX. Annu Rev Genet 2:363–412. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ge.02.120168.002051
Murk JLAN, Posthuma G, Koster AJ et al (2003) Influence of aldehyde fixation on the morphology of endosomes and lysosomes: quantitative analysis and electron tomography. J Microsc 212:81–90. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2818.2003.01238.x
Nicastro D, Schwartz C, Pierson J et al (2006) The molecular architecture of axonemes revealed by cryoelectron tomography. Science 313:944–948. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1128618
Ortiz R, Kouznetsova A, Echeverria-Martinez OM et al (2016) The width of the lateral element of the synaptonemal complex is determined by a multilayered organization of its components. Exp Cell Res 344:22–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.03.025
Rog O, Köhler S, Dernburg AF (2017) The synaptonemal complex has liquid crystalline properties and spatially regulates meiotic recombination factors. ELife 6.https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.21455
Rong M, Matsuda A, Hiraoka Y, Lee J (2016) Meiotic cohesin subunits RAD21L and REC8 are positioned at distinct regions between lateral elements and transverse filaments in the synaptonemal complex of mouse spermatocytes. J Reprod Dev 62:623–630. https://doi.org/10.1262/jrd.2016-127
Sánchez-Sáez F, Gómez-H L, Dunne OM et al (2020) Meiotic chromosome synapsis depends on multivalent SYCE1-SIX6OS1 interactions that are disrupted in cases of human infertility. Sci Adv 6.https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abb1660
Schmekel K, Daneholt B (1995) The central region of the synaptonemal complex revealed in three dimensions. Trends Cell Biol 5:239–242
Schmekel K, Meuwissen RL, Dietrich AJ et al (1996) Organization of SCP1 protein molecules within synaptonemal complexes of the rat. Exp Cell Res 226:20–30. https://doi.org/10.1006/excr.1996.0198
Schmekel K, Skoglund U, Daneholt B (1993) The three-dimensional structure of the central region in a synaptonemal complex: a comparison between rat and two insect species, Drosophila melanogaster and Blaps cribrosa. Chromosoma 102:682–692
Schramm S, Fraune J, Naumann R et al (2011) A novel mouse synaptonemal complex protein is essential for loading of central element proteins, recombination, and fertility. PLoS Genet 7:e1002088. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002088
Schücker K, Holm T, Franke C et al (2015) Elucidation of synaptonemal complex organization by super-resolution imaging with isotropic resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:2029–2033. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1414814112
Schücker K, Sauer M, Benavente R (2018) Superresolution imaging of the synaptonemal complex. Methods Cell Biol 145:335–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.mcb.2018.03.033
Shiurba R (2001) Freeze-substitution: origins and applications. Int Rev Cytol 206:45–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0074-7696(01)06019-3
Sobol MA, Philimonenko VV, Philimonenko AA, Hozak P (2012) Quantitative evaluation of freeze-substitution effects on preservation of nuclear antigens during preparation of biological samples for immunoelectron microscopy. Histochem Cell Biol 138:167–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-012-0931-6
Solari AJ, Moses MJ (1973) The structure of the central region in the synaptonemal complexes of hamster and cricket spermatocytes. J Cell Biol 56:145–152
Spindler M-C, Filbeck S, Stigloher C, Benavente R (2019) Quantitative basis of meiotic chromosome synapsis analyzed by electron tomography. Sci Rep 9:16102. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-52455-4
Studer D, Humbel BM, Chiquet M (2008) Electron microscopy of high pressure frozen samples: bridging the gap between cellular ultrastructure and atomic resolution. Histochem Cell Biol 130:877–889. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-008-0500-1
Syrjänen JL, Pellegrini L, Davies OR (2014) A molecular model for the role of SYCP3 in meiotic chromosome organisation. Elife 3.https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.02963
Tung KS, Roeder GS (1998) Meiotic chromosome morphology and behavior in zip1 mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 149:817–832
Vanhecke D, Graber W, Studer D (2008) Close-to-native ultrastructural preservation by high pressure freezing. Methods Cell Biol 88:151–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0091-679x(08)00409-3
Velamoor S, Richena M, Mitchell A et al (2020) High-pressure freezing followed by freeze substitution of a complex and variable density miniorgan: the wool follicle. J Microsc 278:18–28. https://doi.org/10.1111/jmi.12875
Voelkel-Meiman K, Moustafa SS, Lefrançois P et al (2012) Full-length synaptonemal complex grows continuously during meiotic prophase in budding yeast. PLoS Genet 8:e1002993. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002993
Voelkel-Meiman K, Taylor LF, Mukherjee P et al (2013) SUMO localizes to the central element of synaptonemal complex and is required for the full synapsis of meiotic chromosomes in budding yeast. PLoS Genet 9:e1003837. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003837
Westergaard M, von Wettstein D (1972) The synaptinemal complex. Annu Rev Genet 6:71–110. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ge.06.120172.000443
Xu H, Tong Z, Ye Q et al (2019) Molecular organization of mammalian meiotic chromosome axis revealed by expansion STORM microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116:18423–18428. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1902440116
Zickler D, Kleckner N (2015) Recombination, pairing, and synapsis of homologs during meiosis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 7:1–28. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a016626
Zwettler FU, Spindler M-C, Reinhard S et al (2020) Tracking down the molecular architecture of the synaptonemal complex by expansion microscopy. Nat Commun 11:3222. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-17017-7
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Electron Tomography Facility at Karolinska Institute for providing its services.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Swedish Research Council (2017–01853 to C.H) and the Hospital Infantil de México Federico Gómez (HIM/2018/079 SSA 1518 and HIM/2021/061 to A.H.H).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.H.H and C.H conceived the experiments. A.H.H designed and performed most of the experiments. R.O performed sample sectioning and data analysis. S.M performed data acquisition and tomogram generation. C.H, O.M.E, and A.H.H contributed with reagents, equipment, and funding. A.H.H and C.H supervised the experiments and data analyses. AHH and C.H wrote the manuscript. All the authors discussed the data and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Aurora Ruiz-Herrera
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file4 (MOV 16195 KB)
Supplementary file5 (MOV 12443 KB)
Supplementary file6 (MOV 13840 KB)
Supplementary file7 (MOV 13172 KB)
Supplementary file8 (MOV 16831 KB)
Supplementary file9 (MOV 13998 KB)
Supplementary file10 (MOV 15183 KB)
Supplementary file11 (MOV 7884 KB)
Supplementary file12 (MOV 7131 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ortiz, R., Echeverría, O.M., Masich, S. et al. A cryo-fixation protocol to study the structure of the synaptonemal complex. Chromosome Res 30, 385–400 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-022-09689-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-022-09689-2