Summary
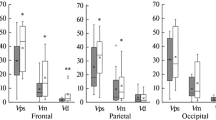
Isotope tracer methods for measuring regional cerebral blood flow or metabolism do not provide data on the dynamics of the fast adjustment of local cerebral blood flow. Measuring intracranial flow patterns of the posterior cerebral artery by means or 2 MHz pulsed transcranial Doppler ultrasonography demonstrated that detailed dynamic effects of various visual patterns on local cerebral perfusion can be recorded, and that visual stimuli of different complexity as well as the strategy of stimulus perception cause distinct flow velocity changes in the occipital cortex involved in information processing. This type of on-line analysis may become a powerful tool for detecting fast autoregulatory mechanisms in relation to purely functional cerebral changes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaslid R (1986) Transcranial Doppier examination techniques. In: Aaslid R (ed) Transcranial Doppier sonography. Springer, Wien New York, pp 39–59
Aaslid R (1987) Visually evoked dynamic blood flow response of the human cerebral circulation. Stroke 18:771–775
Aaslid R, Markwalder TM, Nornes H (1982) Noninvasive transcranial Doppler ultrasound recording of flow velocity in basal cerebral arteries. J Neurosurg 57:769–774
Bishop CCR, Powell S, Rutt D, Browse NL (1986) Transcranial Doppler measurement of middle cerebral artery blood flow velocity: a validation study. Stroke 17:913–915
Boehmer RD (1987) Continuous, real-time, noninvasive monitor of blood pressure: Penaz methodology applied to the finger. J Clin Monit 3:282–287
Brown JL (1965) Afterimages. In: Graham CH (ed) Vision and visual perception. Wiley, New York
Creutzfeldt OD (1983) Cortex cerebri: Leistung, strukturelle und funktioneile Organisation der Hirnrinde. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo
Fox PT, Raichle ME (1986) Focal physiological uncoupling of cerebral blood flow and oxidative metabolism during somatosensory stimulation in human subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 83:1140–1144
Halliday AM, McDonald WI (1981) Visual evoked potentials. In: Stalberg E, Young RR (eds) Clinical neurophysiology. Butterworth, London Boston Sydney Wellington Durban Toronto, pp 228–258
Heiss WD, Beil C, Herholz K, Pawlik G, Wagner R, Wienhard K (1985) Atlas of positron emission tomography of the brain. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo
Howarth CI (1961) On-off interaction in the human electroretinogram. J Opt Soc Am 51:345–352
Huber P, Handa J (1967) Effect of contrast material, hypercapnia, hyperventilation, hypertonic glucose and papaverine on the diameter of the cerebral arteriesangiographic determination in man. Invest Radiol 2:17–32
Kirkham FJ, Padayachee TS, Parsons S, Seargeant LS, House FR, Gosling RG (1986) Transcranial measurement of blood velocities in the basal cerebral arteries using pulsed Doppler ultrasound: velocity as an index of flow. Ultrasound Med Biol 12:15–21
Lassen NA, Ingvar DH (1963) Regional cerebral blood flow measurement in man. Arch Neurol 9:615–622
Lassen NA, Ingvar DH, Skinhoj E (1978) Brain function and blood flow. Sci Am 239:62–71
Livingstone MS, Hubel DH (1987) Psychophysical evidence for separate channels for the perception of form, colour, movement, and depth. J Neurosci 7:3416–3468
Lou HC, Edvinsson L, MacKenzie ET (1987) The concept of coupling blood flow to brain function: revision required? Ann Neurol 22:289–297
Meyer JS, Hayman LA, Amano T, Nakajima S, Shaw T, Lauzon P, Derman S, Karacan I, Harati Y (1981) Mapping of local blood flow of human brain by CT scanning during stable xenon inhalation. Stroke 12:426–436
Paulson OB, Newman EA (1987) Does the release of potassium from astrocyte endfeet regulate cerebral blood flow? Science 237:896–898
Phelps ME, Mazziotta JC, Huang SC (1982) Study of cerebral function with positron computed tomography. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2:113–162
Raichle ME, Herscovitch P, Mintun MA, Martin WRW, Powers W (1984) Dynamic measurements of local blood flow and metabolism in the study of higher cortical function in humans with positron emission tomography. Ann Neurol 15:S48-S49
Silver IA (1978) Cellular microenvironment in relation to local blood flow. In: Elliott K, O'Connor M (eds) Cerebral vascular smooth muscle and its control. Ciba Foundation symposium 56. Elsevier, New York, pp 49–61
Wesseling KH, de Witt B, Settels JJ, Klawer WH (1982) On the indirect registration of finger blood pressure after Penaz. Funkt Biol Med 1:245–250
Winn HR, Rubio R, Berne RM (1979) Brain adenosine production during 60 s of ischemia. Circ Res 45:486–492
Winn HR, Rubio R, Berne RM (1981) The role of adenosin in the regulation of cerebral blood flow. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1:239–244
Zeal AA, Rhoton AL Jr (1978) Microsurgical anatomy of the posterior cerebral artery. J Neurosurg 48:534–559
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB 330 “Organprotektion”)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Conrad, B., Klingelhöfer, J. Dynamics of regional cerebral blood flow for various visual stimuli. Exp Brain Res 77, 437–441 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00275003
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00275003