Summary
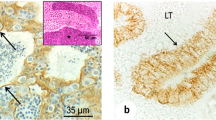
The distribution of type IV collagen and laminin was studied by immunocytochemistry during rat gonadal morphogenesis and postnatal development of the testis and epididymis. Immunostaining appeared as early as the 12th day of gestation along the basement membranes of the mesonephric-gonadal complex. The connection between some mesonephric tubules and coelomic epithelium was seen between the 12th and 13th day of gestation. Discontinuous immunostained basement membranes delineated the differentiating sexual cords in 13-day-old fetuses; this process probably began in the inner part of the gonadal ridge. The seminiferous cords surrounded by a continuous immunoreactive basement membrane are separated from the coelomic epithelium by the differentiating tunica albuginea in 14-day-old fetuses. During the postnatal maturation of epididymis and testis, the differentiation of peritubular cells is accompanied by a progressive organisation of the extracellular matrix into a continuous basement membrane. This change is associated with a gradual condensation of peritubular cells inducing an increase of immunostaining. In adult animals, the tubular wall of epididymis is thicker than the lamina propria of seminiferous tubules. Both type IV collagen and laminin immunostaining paralleled during ontogenesis at the light-microscope level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agelopoulou R, Magre S (1987) Expression of fibronectin and laminin in fetal male gonads in vivo and in vitro with and without testicular morphogenesis. Cell Differ 21:31–36
Bernfield M, Banerjee SD, Koda JE, Rapraeger AC (1984) Remodelling of the basement membrane: morphogenesis and maturation. In: Porter R, Whelan J (eds) Basement membranes and cell movement. Pitman, London, pp 179–196 (Ciba Foundation Symposium 108)
Borland K, Muffly KE, Hall PF (1986) Production of components of extracellular matrix by cultured rat Sertoli cells. Biol Reprod 35:997–1008
Byskov AG (1986) Differentiation of mammalian embryonic gonad. Physiol Rev 66:71–117
Cunha GR, Chung LWK, Shannon JM, Reese BA (1980) Stromal-epithelial interactions in sex differentiation. Biol Reprod 22:19–42
Cunha GR, Shannon JM, Neubauer BL, Sawyer LM, Fujii H, Taguchi O, Chung LWK (1981) Mesenchymal-epithelial interactions in sex differentiation. Hum Genet 58:68–77
Francavilla S, De Martino C, Scorza Barcellona P, Natali PG (1983) Ultrastructural and immunohistochemical studies of rat epididymis. Cell Tissue Res 233:523–537
Francavilla S, Moscardelli S, Properzi G, De Matteis MA, Scorza Barcellona P, Natali PG, De Martino C (1987) Postnatal development of epididymis and ductus deferens in the rat. A correlation between the ultrastructure of the epithelium and tubule wall, and the fluorescence-microscopic distribution of actin, myosin, fibronectin, and basement membrane. Cell Tissue Res 249:257–265
Gondos B (1980) Development and differentiation of the testis and male reproductive tract. In: Steinberger A, Steinberger E (eds) Testicular development, structure and function. Raven Press, New York, pp 3–20
Jost A, Magre S, Agelopoulou R (1981) Early stages of testicular differentiation in the rat. Hum Genet 58:59–63
Lundberg JM, Hökfelt T, Martling CR, Saria A, Cuello C (1984) Substance P-immunoreactive sensory nerves in the lower respiratory tract of various mammals including man. Cell Tissue Res 235:251–261
Merchant H (1975) Rat gonadal and ovarian organogenesis with and without germ cells. An ultrastructural study. Dev Biol 44:1–21
Paranko J (1987) Expression of type I and III collagen during morphogenesis of fetal rat testis and ovary. Anat Rec 219:91–101
Paranko J, Pelliniemi LJ, Vaheri A, Foidart JM, Lakkala-Paranko T (1983) Morphogenesis and fibronectin in sexual differentiation of rat embryonic gonads. Differentiation 23:S72-S81
Pelliniemi LJ, Paranko J, Grund SK, Frojdman K, Foidart JM, Lakkala-Paranko T (1984) Extracellular matrix in testicular differentiation. Ann NY Acad Sci 438:405–416
Skinner MK, Tung PS, Fritz IB (1985) Cooperativity between Sertoli cells and testicular peritubular cells in the production and deposition of extracellular matrix components. J Cell Biol 100:1941–1947
Skinner MK, Takacs K, Coffey RJ (1989) Transforming growth factor-α gene expression and action in the seminiferous tubule: peritubular cell-Sertoli cell interactions. Endocrinology 124:845–854
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gelly, J.L., Richoux, J.P., Leheup, B.P. et al. Immunolocalization of type IV collagen and laminin during rat gonadal morphogenesis and postnatal development of the testis and epididymis. Histochemistry 93, 31–37 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00266844
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00266844