Summary
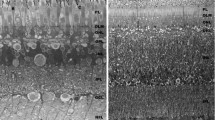
Comparative studies were made on albino and gray rats by measuring several morphological characteristics seen in cross-sections of the optic nerve. The total cross-sectional area of the optic nerve was about 30% smaller in the albino than in the gray rat, while the fiber density was 1.4 times higher in the albino than in the gray rat. The estimated total fiber count was about the same in the two strains: around 100,000 to 110,000 fibers. Except for a few unmyelinated fibers (less than 1%) all fibers were myelinated. Axon diameters of the optic nerve fibers were distributed in smaller values for the albino than for the gray rat, though the overall diameter range was similar (0.2–3.0 μm). The myelin sheath was also thinner in the albino than in the gray rat.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Binggeli RL, Paule WJ (1969) The pigeon retina: Quantitative aspects of the optic nerve and ganglion cell layer. J Comp Neurol 137: 1–18
Birch D, Jacobs GH (1979) Spatial contrast sensitivity in albino and pigmented rats. Vision Res 19: 933–937
Bishop GH, Clare MH, Landau WM (1971) The relation of axon sheath thickness to fiber size in the central nervous system of vertebrates. Int J Neurosci 2: 69–78
Bruesh SR, Arey LB (1942) The number of myelinated and unmyelinated fibers in the optic nerve of vertebrates. J Comp Neurol 77: 631–665
Creel DJ, Dustman RE, Beck EC (1970) Differences in visually evoked responses in albino versus hooded rats. Exp Neurol 29: 298–309
Creel DJ, Giolli RA (1976) Retinogeniculate projections in albino and ocularly hypopigmented rats. J Comp Neurol 166: 445–456
DeJuan J, Iniguez C, Carreres J (1978) Number, diameter and distribution of the rat optic nerve fibers. Acta Anat 102: 294–299
Forrester F, Peters A (1967) Nerve fibers in optic nerve of rat. Nature 214: 245–247
Freeman B (1978) Myelin sheath thickness and conduction latency groups in the cat optic nerve. J Comp Neurol 181: 183–196
Friede RL, Miyaghishi T, Hu KH (1971) Axon calibre, neurofilaments, microtubules, sheath thickness and cholesterol in the cat optic nerve fibers. J Anat 108: 365–373
Fukuda Y, Sugimoto T, Shirokawa T (1982) Strain differences in quantitative analysis of the rat optic nerve. Exp Neurol 75: 525–532
Giolli RA, Creel DJ (1973) The primary optic projections in pigmented and albino guinea pigs: An experimental degeneration study. Brain Res 55: 25–39
Guillery RW, Scott GL, Cattanach BM, Deol MS (1973) Genetic mechanisms determining the central visual pathways of mice. Science 179: 1014–1016
Guillery RW, Okoro AN, Witkop CJ Jr (1975) Abnormal visual pathways in the brain of a human albino. Brain Res 96: 373–377
Guillery RW, Oberdorfer MD, Murphy EH (1979) Abnormal retino-geniculate and geniculo-cortical pathways in several genetically distinct color phases of the mink (Mustela vision). J Comp Neurol 185: 623–656
Hokoç JN, Oswaldo-Cruz E (1978) Quantitative analysis of the opossum's optic nerve: An electron microscope study. J Comp Neurol 178: 773–782
Hughes A (1977) The pigmented-rat optic nerve: Fiber count and fiber diameter spectrum. J Comp Neurol 176: 263–268
Lashley KS (1930) The mechanism of vision: III. The comparative visual acuity of pigmented and albino rats. J Genet Psychol 37: 481–484
Lund RD (1965) Uncrossed visual pathways of hooded and albino rats. Science 149: 1506–1507
Lund RD, Lund JS, Wise RP (1974) The organization of the retinal projection to the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus in pigmented and albino rats. J Comp Neurol 158: 383–404
Peters A, Palay SL, Webster HF (1976) The fine structure of the nervous system: The neurons and supporting cells. Saunders, Philadelphia London Tronto pp 181–263
Rhoades RW, Hsu L, Parfett G (1979) An electronmicroscopic analysis of the optic nerve in the golden hamster. J Comp Neurol 186: 491–504
Sima A (1974) Relation between the number of myelin lamellae and axon circumference in fibers of ventral and dorsal roots and optic nerve in normal, undernourished, and rehabilitated rats. Acta Physiol Scand: Suppl 410
Skoff RP, Toland D, Nast E (1980) Pattern of myelination and distribution of neuroglial cells along the developing optic system of the rat and rabbit. J Comp Neurol 191: 237–253
Treff WM, Meyer-König E, Schlote W (1972) Morphometric analysis of a fiber system in the central nervous system. J Microsc 95: 337–343
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This paper is dedicated to Dr. Kitsuya Iwama, emeritus Professor of Osaka University Medical School, on his retirement
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sugimoto, T., Fukuda, Y. & Wakakuwa, K. Quantitative analysis of a cross-sectional area of the optic nerve: A comparison between albino and pigmented rats. Exp Brain Res 54, 266–274 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00236226
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00236226