Abstract
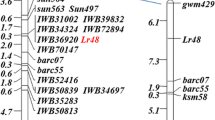
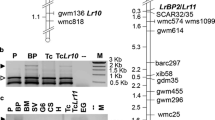
Near-isogenic lines (NILs) for the leaf rust resistance gene Lr9 were screened for polymorphisms at the molecular level. RAPD (random amplified polymorphic DNA) primers as well as RFLP (restriction fragment length polymorphism) markers were used. Out of 395 RAPD primers tested, three showed polymorphisms between NILs, i.e., an additional band was found in resistant lines. One of these polymorphic bands was cloned and sequenced. Specific primers were synthesized, and after amplification only resistant lines showed an amplified product. Thus, these primers define a sequence-tagged site that is specific for the translocated fragment carrying the Lr9 gene. A cross between a resistant NIL and the spelt (Triticum spelta) variety ‘Oberkulmer’ was made, and F2 plants were analyzed for genetic linkage. All three polymorphisms detected by the PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and one RFLP marker (cMWG684) showed complete linkage to the Lr9 gene in 156 and 133 plants analyzed, respectively. A second RFLP marker (PSR546) was closely linked (8±2.4 cM) to the Lr9 gene and the other four DNA markers. As this marker maps to the distal part of the long arm of chromosome 6B of wheat, Lr9 and the other DNA markers also map to the distal region of 6BL. All three PCR markers detected the Lr9 gene in independently derived breeding lines and varieties, thus proving their general applicability in wheat breeding programs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn SN, Bollich CN, Tanksley SD (1992) RFLP tagging of a gene for aroma in rice. Theor Appl Genet 84:825–828
Allard RW (1956) Formulas and tables to facilitate the calculation of recombination values in heredity. Hilgardia 24:235–279
Baum M, Lagudah ES, Appels R (1992) Wide crosses in cereals. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 43:117–143
Bentolila S, Guitton C, Bouvet N, Sailland A, Nykaza S, Freyssinet G (1991) Identification of an RFLP marker tightly linked to the Ht1 gene in maize. Theor Appl Genet 82:393–398
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnik M, Davis RW (1980) Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 32:314–331
Chao S, Sharp PJ, Worland AJ, Warham EJ, Koebner RMD, Gale MD (1989) RFLP-based genetic maps of wheat homoeologous group 7 chromosomes. Theor Appl Genet 78:495–504
Denissen CJM, van der Putten PEL (1991) Pathogenicity of wheat leaf rust (Puccinia recondita f. sp. tritici) in the Netherlands. Cereal Rusts Mildew Bull 19:20–26
Dente L, Cesareni G, Cortese R (1983) PEMBL — A new family of singlestranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res 11:1645–1655
Devos KM, Gale MD (1992) The use of random amplified polymorphic DNA markers in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 84:567–572
Devos KM, Atkinson MD, Chinoy CN, Liu CJ, Gale MD (1992) RFLP-based genetic map of the homoeologous group 3 chromosomes of wheat and rye. Theor Appl Genet 83:931–939
Devos KM, Millan T, Gale MD (1993) Comparative RFLP maps of the homoeologous group-2 chromosomes of wheat, rye and barley. Theor Appl Genet 85:784–792
Fried PM, Winzeler H (1990) Variation of characters in near-isogenic lines of wheat with added genes for leaf rust resistance. Euphytica 45:87–92
Graner A, Siedler H, Jahoor A, Herrmann RG, Wenzel G (1990) Assessment of the degree and type of restriction fragment length polymorphism in barley (Hordeum vulgare). Theor Appl Genet 80:826–832
Graner A, Jahoor A, Schondelmaier J, Siedler H, Pillen K, Fischbeck G, Wenzel G, Herrmann RG (1991) Construction of an RFLP map in barley. Theor Appl Genet 83:250–256
Hartl L, Weiss H, Zeller FJ, Jahoor A (1993) Use of RFLP markers for the identification of alleles of the Pm3 locus conferring powdery mildew resistance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 86:959–963
Hinze K, Thompson RD, Ritter E, Salamini F, Schulze-Lefert P (1991) Restriction fragment length polymorphism-mediated targeting of the ml-o resistance locus in barley (Hordeum vulgare). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:3691–3695
Islam AKMR, Shepherd KW, Sparrow DHB (1981) Isolation and characterization of euplasmic wheat-barley chromosome addition lines. Heredity 46:161–174
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Liu YG, Tsunewaki K (1991) Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis in wheat. II. Linkage maps of the RFLP sites in common wheat. Jpn J Genet 66:617–633
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Olson M, Hood L, Cantor CH, Botstein D (1989) A common language for physical mapping of the human genome. Science 24:1434–1435
Paran I, Michelmore RW (1993) Development of reliable PCR-based markers linked to downy mildew resistance genes in lettuce. Theor Appl Genet 85:985–993
Poinso B, Ollivier B (1988) Virulence of Puccinia recondita tritici on some near-isogenic lines in southern France in 1986–1987. In: Zwatz B (ed) Proc. 7th Eur Mediterr Cereal Rusts Conf 1988. Federal Institute of Plant Protection, Vienna, pp 116–118
Roelfs AP, Singh RP, Saari EE (1992) Rust diseases of wheat: concepts and methods of disease management. CIMMYT, Mexico, D.F.
Schüller C, Backes G, Fischbeck G, Jahoor A (1992) RFLP markers to identify the alleles on the Mla locus conferring powdery mildew resistance in barley. Theor Appl Genet 84:330–338
Sears ER (1956) The transfer of leaf rust resistance from Aegilops umbellulata into wheat. Brookhaven Symp Biol 9:1–21
Sears ER (1961) Identification of the wheat chromosome carrying leaf rust resistance from Aegilops umbellulata. Wheat Inf Serv 12:12–13
Sears ER (1966) Chromosome mapping with the aid of telocentrics. In: MacKey J (ed) Proc 2nd Int Wheat Genet Symp. Hereditas Suppl 2, Lund, pp 370–381
Soliman AS, Heyne EY, Johnston CO (1963) Resistance to leaf rust in wheat derived from Chinese Aegilops umbellulata translocation lines. Crop Sci 3:254–256
von Kröcher C, Bartels G, Fehrmann H (1992) Studies on the physiological specialization of leaf rust in wheat (Puccinia recondita Rob. ex Desm. f. sp. tritici Eriks. & Henn.). J Plant Dis Prot 99:137–144
Williams GK, Kubelik AR, Kenneth JL, Rafalski A, Scott VT (1990) DNA polymorphism amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6531–6535
Young ND, Tanksley SD (1989) RFLP analysis of the size of chromosomal segments retained around the Tm-2 locus of tomato during backcross breeding. Theor Appl Genet 77:353–359
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. Wenzel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schachermayr, G., Siedler, H., Gale, M.D. et al. Identification and localization of molecular markers linked to the Lr9 leaf rust resistance gene of wheat. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 88, 110–115 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222402
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222402