Summary
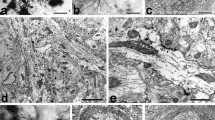
Neuronal projections from one optic lobe to other parts of the brain were stained in the cricket Gryllus campestris using the cobalt sulphide technique and Timm's sulphide-silver method.
The results are: Four tracts directly connect the medulla with the lobula and medulla of the contralateral optic lobe. Direct medullar projections end mainly in the non-glomerular neuropile of the protocerebrum, but also penetrate the calyx of the mushroom bodies, pons and central body in small numbers. A few somata which send fibres into the medulla lie in the pars intercerebralis, in the protocerebrum ventral to the opposite β-lobe, the outer margin of the medulla of the contralateral optic lobe and between deutoand tritocerebrum.
The anatomical and physiological relevance of the stained connections is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bishop, L. G., Keehn, D. G., McCann, G. D.: Motion detection by intemeurons of optic lobes and brain of the flies Calliphora phaenicia and Musca domestica. J. Neurophysiol. 31, 509–525 (1968)
Brady, J.: The physiology of insect circadian rhythms. Adv. Ins. Physiol. 10, 1–116 (1974)
Burtt, E. T., Catton, W. T.: Electrical responses to visual stimulation in the optic lobes of the locust and certain other insects. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 133, 68–88 (1956)
Collett, T.: Centripetal and centrifugal visual cells in medulla of the insect optic lobe. J. Neurophysiol. 33, 239–256 (1970)
Collett, T.: Visual neurones in the anterior optic tract of the privet hawk moth. J. comp. Physiol. 78, 396–433 (1972)
Götz, K. G.: Flight control in the fruitfly Drosophila by visual perception of motion. Kybernetik 4, 199–208 (1968)
Götz, K. G.: Processing of cues from the moving environment in the Drosophila navigation system. In: R. Wehner (ed.), Information processing in the visual systems of Arthropods p. 225–263. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer (1972)
Goodman, C.: Anatomy of locust ocellar interneurons: Constancy and variability. J. comp. Physiol. 95, 185–201 (1974)
Huber, F.: Neural integration (central nervous system). In: M. Rockstein (ed.), The physiology of insecta IV, p. 3–100. New York and London: Acad. Press 1974
Jawlowski, H.: Nerve Tracts in bee (Apis mellifica) running from the light and antennal organs to the brain. Ann. Univ. M. Curie-Sklodowska Sect. D 12, 307–322 (1958)
Kenyon, F. C.: The brain of the bee. A preliminary contribution to the morphology of the nervous system of Arthropoda. J. comp. Neurol. 6, 133–210 (1896)
Mason, C. A.: New features of the brain-retrocerebral neuroendocrine complex of the Locust Schistocerca vaga (Scudder). Z. Zellforsch. 141, 19–32 (1973)
McCann, G. D., Dill, J. C.: Fundamental properties of intensity, form, and motion perception in the visual nervous systems of Calliphora phaenicia and Musca domestica. J. gen. Physiol. 53, 385–414 (1969)
O'Shea, M., Williams, J. L. D.: The anatomy and output connection of a locust visual interneurone; the lobular giant movement detector (LGMD) neurone. J. comp. Physiol. 91, 257–266 (1974)
Palka, J.: Discrimination between movements of eye and object by visual interneurones of crickets. J. exp. Biol. 50, 723–732 (1969)
Pearson, L.: The corpora pedunculata of Sphinx ligustri (L.) and other Lepidoptera: an anatomical study. Phil. Trans. B 259, 477–516 (1971)
Pitman, R. M., Tweedle, C. D., Cohen, M. J.: Branching of central neurons: Intracellular cobalt injection for light and electron microscopy. Science 176, 412–414 (1972)
Politoff, A., Pappas, G. D., Bennett, M. V. L.: Cobalt ions cross an electronic synapse if cytoplasmic concentration is low. Brain Res. 76, 343–346 (1974)
Power, M. E.: The brain of Drosophila melanogaster. J. Morph. 72, 517–559 (1943)
Rowell, C. H. F.: The orthopteran descending movement detector (DMD) neurones: A characterisation and review. Z. vergl. Physiol. 73, 167–194 (1971)
Schürmann, F. W.: Über die Struktur der Pilzkörper des Insektenhirns. III. Die Anatomie der Nervenfasern in den Corpora pedunculata bei Acheta domesticus. Z. Zellforsch. 145, 247–285 (1973)
Schürmann, F. W.: Bemerkungen zur Funktion der Corpora pedunculata im Gehirn der Insekten aus morphologischer Sicht. Exp. Brain Res. 19, 406–432 (1974)
Steiger, U.: Über den Feinbau des Neuropils im Corpus pedunculatum der Waldameise. Elektronenoptische Untersuchungen. Z. Zellforsch. 81, 511–536 (1967)
Strausfeld, N. J.: Variations and invariants of cell arrangements in the nervous systems of insecta. (A review of neuronal arrangements in the visual system and corpora pedunculata). Verh. dtsch. zool. Ges. 64, 97–108 (1970)
Strausfeld, N. J.: Atlas of an insect brain. (In press.) Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1975
Strausfeld, N. J., Blest, A. D.: Golgi studies on insects: Part I. The optic lobes of Lepidoptera. Phil. Trans. B 258, 81–134 (1970)
Truman, J. W., Riddiford, L. M.: Hormonal mechanisms underlying insect behaviour. Adv. Ins. Physiol. 10, 297–352 (1974)
Tyrer, N. M., Altman, J. S.: Motor and sensory flight neurones in a locust demonstrated using cobalt chloride. J. comp. Neurol. 157, 117–138 (1974)
Tyrer, N. M., Bell, E. M.: The intensification of profiles of cobalt-injected neurones in sectioned material. Brain Res. 73, 151–155 (1974)
Zawarzin, A.: Histologische Studien über Insekten. IV Die optischen Ganglien der Aeschna- Larven. Z. wiss. Zool. 108, 175–257 (1913)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Professor B. Rensch on his 75th birthday.
Supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, grant Ho 463/4+7.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Honegger, H.W., Schürmann, F.W. Cobalt sulphide staining of optic fibres in the brain of the cricket, Gryllus campestris . Cell Tissue Res. 159, 213–225 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00219157
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00219157