Summary
The possible presence of a direct nervous projection from the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) of the hypothalamus to the pineal gland of the rat was investigated by means of the anterograde neuron-tracing method using horseradish peroxidase. The tracer was injected unilaterally into the PVN and the animals were allowed to survive between 12 and 26 h.
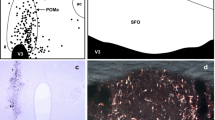
Numerous peroxidase-positive fibers were observed, ipsilateral to the injection site, in the stria medullaris thalami and could be followed into the medial habenular nucleus and the habenular commissure. From there, fibers penetrated into the deep pineal gland (lamina intercalaris), and further into the pineal stalk. These data support results of previous investigations describing retrograde labeling of the PVN following intrapineal injections of horseradish peroxidase and are in accordance with recent experiments demonstrating an influence of the PVN on electrical and biochemical activity of the pineal gland.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buijs RM, Pévet P (1980) Vasopressin- and oxytocin-containing fibers in the pineal gland and subcommissural organ of the rat. Cell Tissue Res 205:11–17
Guérillot C, Pfister A, Müller J, DaLage C (1982) Recherche de l'origine des fibres nerveuses extraorthosympathiques innervant l'épiphyse du rat (étude du transport retrograde de la peroxydase de raifort). Reprod Nutr Dev 22:371–378
Klein DC, Smoot R, Weller JL, Higa S, Markey SP, Creed GJ, Jacobowitz DM (1983) Lesions in the paraventricular nucleus area of the hypothalamus disrupt the suprachiasmatic-spinal cord circuit in the melatonin rhythm generating system. Brain Res Bull 10:647–652
Korf H-W, Møller M (1984) The innervation of the mammalian pineal gland with special reference to central pinealopetal projections. In: Reiter RJ (ed) Pineal research reviews, vol 2, Alan R. Liss, Inc, New York, pp 41–86
Korf H-W, Møller M (1985) The central innervation of the mammalian pineal organ. In: Mess B, Ruzsàs C, Tima L, Pévet P (eds) The pineal gland. Akadémiai Kiado, Budapust, pp 48–69
Korf H-W, Wagner U (1980) Evidence for a nervous connection between the brain and the pineal organ in the guinea pig. Cell Tissue Res 209:505–510
Luo ZR, Schultz RL, Whitter EF, Vollrath L (1984) The ultrastructure of the nerve fibers and pinealocytes in the rat pineal stalk. J Pineal Res 1:323–337
Mesulam M-M (1978) Tetramethyl benzidine for horseradish peroxidase neurohistochemistry: a non-carcinogenic blue reactionproduct with superior sensitivity for visualizing neural afferents and efferents. J Histochem Cytochem 26:106–117
Mesulam M-M, Mufson EJ (1980) The rapid anterograde transport of horseradish peroxidase. Neuroscience 5:1277–1286
Mikkelsen JD, Fahrenkrug J, Møller M (unpublished) Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) in the hypothalamic-pituitary system of the Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus). An immunohistochemical and receptor-autoradiographic study
Møller M (1985) Non-sympathetic synaptic innervation of the pinealocyte of the Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus): an electron microscopic study. J Neurocytol 14:541–550
Møller M, Korf H-W (1983) The origin of central pinealopetal nerve fibers in the Mongolian gerbil as demonstrated by the retrograde transport of horseradish peroxidase. Cell Tissue Res 230:273–287
Møller M, Mikkelsen JD, Fahrenkrug J, Korf HW (1985) The presence of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP)-like immunoreactive nerve fibers and VIP-receptors in the pineal gland of the Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus): an immunohistochemical and receptor-autoradiographic study. Cell Tissue Res 241:333–340
Møller M, Reuss S, Olcese J, Stehle J, Vollrath L (submitted), Experientia Central neural control of pineal melatonin synthesis in rats
Nürnberger F, Korf HW (1981) Oxytocin- and vasopressin-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the pineal gland of the hedgehog, Erinaceus europaeus L. Cell Tissue Res 220:87–97
Paxinos G, Watson C (1982) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, London
Reuss S, Semm P, Vollrath L (1984) Electrophysiological investigations on the central innervation of the rat and guinea-pig pineal gland. J Neural Transm 60:31–43
Reuss S, Olcese J, Vollrath L (1985) Electrical stimulation of the hypothalamic paraventricular nuclei inhibits pineal melatonin synthesis in male rats. Neuroendocrinology 41:192–196
Reuss S, Møller M, Stehle J, Vollrath L (unpublished) Hypothalamo-pineal pathways: An electrophysiological study
Rønnekleiv OK, Kelly MJ, Wuttke W (1980) Single unit recordings in the rat pineal gland: evidence for habenulo-pineal neural connections. Exp Brain Res 39:187–192
Semm P (1981) Electrophysiological aspects of the mammalian pineal gland. In: Oksche A, Pévet P (eds) The pineal organ: Photobiology — Biochronometry — Endocrinology. Biomedical Press, Elsevier, pp 81–96
Semm P, Schneider T, Vollrath L (1981) Morphological and electrophysiological evidence for habenular influence on the guinea-pig pineal gland. J Neural Transm 50:247–266
Swanson LW, Sawchenko PE (1980) Paraventricular nucleus: A site for the intergration of neuroendocrine and autonomic mechanisms. Neuroendocrinology 31:410–417
Swanson LW, Sawchenko PE (1983) Hypothalamic integration: organization of the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei. Ann Rev Neurosa 6:269–324
Uddman R, Alumets J, Hakanson R, Lorén L, Sundler F (1980) Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) occurs in nerves of the pineal gland. Experientia 36:1119–1120
Vollrath L (1981) The pineal organ. In: Handbuch der mikroskopischen Anatomie des Menschen VI/7. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 1–665
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reuss, S., Møller, M. Direct projections to the rat pineal gland via the stria medullaris thalami. Cell Tissue Res. 244, 691–694 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00212551
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00212551