Abstract
-
1.
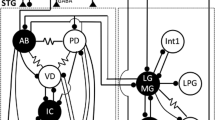
The neurons of the pyloric network of the lobster (Panulirus interruptus) stomatogastric ganglion organize their rhythmic motor output using both chemical and electrical synapses. The 6 electrical synapses within this network help set the firing phases of the pyloric neurons during each rhythmic cycle. We examined the modulatory effects of the amines dopamine (DA), serotonin (5HT) and octopamine (Oct) on coupling at all the electrical synapses of the pyloric network.
-
2.
Electrical coupling within the pacemaker group [anterior burster (AB) to pyloric dilator (PD), and PD-
-
3.
Dopamine decreased or increased the coupling strength of all the pyloric electrical synapses: the sign of the effect depended upon which neuron was the target of current injection. For example, DA decreased AB→ PD coupling (i.e., when current was injected into the AB) but increased coupling in the other direction, PD→ AB. Dopamine decreased AB to VD coupling when current was injected into either neuron. Serotonin also had mixed effects; it enhanced PD→AB coupling but decreased AB to VD and PD to VD coupling in both directions. Octopamine's only effect was to reduce PD→ VD coupling. li]4.
-
5.
The characteristic modulation of electrical coupling by each amine may contribute to the unique motor pattern that DA, 5HT and Oct each elicit from the pyloric motor network.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AB:
-
anterior burster
- CPG:
-
central pattern generator
- DA:
-
dopamine
- GSP:
-
graded synaptic potential
- 5HT:
-
serotonin
- IC:
-
inferior cardiac
- I/O:
-
input/output
- LP:
-
lateral pyloric
- Oct:
-
octopamine
- PD:
-
pyloric dilator
- PTX:
-
picrotoxin
- PY:
-
pyloric constrictor
- Rin :
-
input resistance
- R1, R2 :
-
soma resistance
- R1A, R2A :
-
axial resistance
- R1D, R2D :
-
dendrite resistance
- RJ :
-
junctional resistance
- STG:
-
stomatogastric ganglion
- TTX:
-
tetrodotoxin
- VD:
-
ventral dilator
References
Anwyl R (1991) Modulation of vertebrate neuronal calcium channels by transmitters. Brain Res Rev 16:265–281
Barker DL, Kushner PD, Hooper NK (1979) Synthesis of dopamine and octopamine in the crustacean stomatogastric nervous system. Brain Res 161:99–113
Beltz B, Eisen J, Flamm R, Harris-Warrick RM, Hooper S, Marder E (1984) Serotonergic innervation and modulation of the stomatogastric ganglion of three decapod crustaceans (Panulirus interruptus, Homarus americanus and Cancer irroratus). J Exp Biol 109:35–54
Bennett MVL (1977) Electrical transmission: a functional analysis and comparison to chemical transmission. In: Kandel ER (ed) Cellular biology of neurons, vol. 1, Sect. 1, Handbook of physiology, The nervous system. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 357–416
Berry MS, Cottrell GA (1979) Ionic basis of different synaptic potentials mediated by identified dopamine-containing neuron in Planorbis. Proc R Soc Lond B 203:417–444
Berry MS, Pentreath VW (1977) The integrative properties of electrotonic synapses. Comp Biochem Physiol 57A: 289–295
Bidaut M (1980) Pharmacological dissection of the pyloric network of the lobster stomatogastric ganglion using picrotoxin. J Neurophysiol 44:1089–1101
Carew TJ, Kandel ER (1976) Two functional effects of decreased conductance EPSPs: synaptic augmentation and increased electrotonic coupling. Science 192:150–153
Colombaioni L, Brunelli M (1988) Neurotransmitter-induced modulation of an electrotonic synapse in the CNS of Hirudo medicinalis. Exp Biol 47:139–144
Dowling JE (1991) Retinal neuromodulation: the role of dopamine. Visual Neurosci 7:87–97
Edwards DH, Heitler WJ, Leise EM, Fricke RA (1991) Postsynaptic modulation of rectifying electrical synaptic inputs to the LG escape command neuron in crayfish. J Neurosci 11:2117–2129
Eisen JS, Marder E (1982) Mechanisms underlying pattern generation in lobster stomatogastric ganglion as determined by selective inactivation of identified neurons. III. Synaptic connections of electrically coupled pyloric neurons. J Neurophysiol 48:1392–1415
Flamm RE, Harris-Warrick RM (1986a) Aminergic modulation in lobster stomatogastric ganglion. I. Effects on motor pattern and activity of neurons within the pyloric circuit. J Neurophysiol 55:847–865
Flamm RE, Harris-Warrick RM (1986b) Aminergic modulation in lobster stomatogastric ganglion. II. Target neurons of dopamine, octopamine and serotonin within the pyloric circuit. J Neurophysiol 55:866–881
Friesen WO (1985) Neuronal control of leech swimming movements: interactions between cell 60 and previously described oscillator neurons. J Comp Physiol A 156:231–242
Furshpan EJ, Potter DD (1959) Transmission at the giant motor synapses of the crayfish. J Physiol (Lond) 145:289–325
Getting P (1988) Comparative analysis of invertebrate central pattern generators. In: Cohen AH, Rosignol S, Grillner S (eds) Neural control of rhythmic movements. John Wiley, New York, pp 101–128
Giaume C, Kado RT, Korn H (1987) Voltage-clamp analysis of a crayfish rectifying synapse. J Physiol (Lond) 386:91–112
Gola M, Selverston AI (1981) Ionic requirements for bursting activity in lobster stomatogastric neurons. J Comp Physiol 145:191–207
Graubard K, Hartline DK (1987) Full wave rectification from a mixed electrical-chemical synapse. Science 237:535–537
Hall DH, Marder E, Bennett MVL (1985) Interneuronal and interglial gap junctions in the stomatogastric ganglion of the rock crab. Neurosci Abstr 11:506
Hampson ECGM, Vaney DI, Weiler R (1992) Dopaminergic modulation of gap junction permeability between amacrine cells in mammalian retina. J Neurosci 12:4911–4922
Harris-Warrick RM (1988) Chemical modulation of central pattern generators. In: Cohen AH, Rosignol S, Grillner S (eds) Neural control of rhythmic movements. John Wiley, New York, pp 285–331
Harris-Warrick RM, Flamm RE (1987) Multiple mechanisms of bursting in a conditional burster neuron. J Neurosci 7:2113–2128
Harris-Warrick RM, Marder E (1991) Modulation of neural networks for behavior. Annu Rev Neurosci 14:39–57
Harris-Warrick RM, Nagy F, Nusbaum MP (1992) Neuromodulation of stomatogastric networks by identified neurons and transmitters. In: Harris-Warrick RM, Marder E, Selverston AI, Moulins M (eds) Dynamic biological networks: the stomatogastric nervous system. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 87–137
Hartline DK, Graubard K (1992) Cellular and synaptic properties in the crustacean stomatogastric nervous system. In: HarrisWarrick RM, Marder E, Selverston AI, Moulins M (eds) Dynamic biological networks: the stomatogastric nervous system. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 31–85
Hartline DK, Gassie DV, Sirchia CD (1987) PY cell types in the stomatogastric ganglion of Panulirus. In: Selverston AI, Moulins M (eds) The crustacean stomatogastric system. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 75–77
Hartline DK, Russell DF, Raper JA, Graubard K (1988) Special cellular and synaptic mechanisms in motor pattern generation. Comp Biochem Physiol 91C: 115–131
Heitler WJ, Fraser K, Edwards DH (1991) Different types of rectification at electrical synapses made by a single crayfish neurone investigated experimentally and by computer simulation. J Comp Physiol A 169:707–718
Hermann A (1979) Generation of a fixed motor pattern I. Details of synaptic interactions of pyloric neurons in the stomatogastric ganglion of the crab, Cancer pagurus. J Comp Physiol 130:221–228
Hooper SL, Marder E (1987) Modulation of a central pattern generator by the peptide, proctolin. J Neurosci 7:2097–2112
Johnson BR, Harris-Warrick RM (1990) Aminergic modulation of graded synaptic transmission in the lobster stomatogastric ganglion. J Neurosci 10:2066–2076
Johnson BR, Hooper SL (1992) Overview of the stomatogastric nervous system. In: Harris-Warrick RM, Marder E, Selverston AI, Moulins M (eds) Dynamic biological networks: the stomatogastric nervous system. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 1–30
Johnson BR, Peck JH, Harris-Warrick RM (1991) Temperature sensitivity of graded synaptic transmission in the lobster stomatogastric ganglion. J Exp Biol 156:267–285
Johnson BR, Peck JH, Harris-Warrick RM (1992a) Amine modulation of mixed chemical-electrical synapses in the pyloric network of the lobster stomatogastric ganglion. Neurosci Abstr 18:1055
Johnson BR, Peck JH, Harris-Warrick RM (1992b) Elevated temperature alters the ionic dependence of amine-induced pacemaker activity in a conditional burster neuron. J Comp Physiol A 170:201–209
Katz PS, Eigg MH, Harris-Warrick RM (1989) Serotonergic/cholinergic muscle receptor cells in the crab stomatogastric nervous system: I. Identification and characterization of the gastro-pyloric receptor cells. J Neurophysiol 62:558–570
Kravitz EA (1988) Hormonal control of behavior: amines and the biasing of behavioral output in lobsters. Science 241:1775–1781
Marder E (1984) Roles for electrical coupling in neural circuits as revealed by selective neuronal deletions. J Exp Biol 112:147–167
Marder E, Eisen JS (1984) Transmitter identification of pyloric neurons: electrically coupled neurons use different transmitters. J Neurophysiol 51:1345–1361
Miller JP (1980) Mechanisms underlying pattern generation in the lobster stomatogastric ganglion. PhD thesis, University of California, San Diego, CA
Miller JP (1987) Pyloric mechanisms. In: Selverston AI, Moulins M (eds) The crustacean stomatogastric system. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 109–136
Miller JP, Selverston AI (1979) Rapid killing of single neurons by irradiation of intracellularly injected dye. Science 206:702–704
Mulloney B (1987) Neural circuits. In: Selverston AI, Moulins M (eds) The crustacean stomatogastric system. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 57–77
Mulloney B, Selverston AI (1974) Organization of the stomatogastric ganglion of the spiny lobster. I. Neurons driving the lateral teeth. J Comp Physiol 91:1–32
Nagy F, Miller JP (1987) Pyloric pattern generation in Panulirus interruptus is terminated by blockade of activity through the stomatogastric nerve. In: Selverston AI, Moulins M (eds) The crustacean stomatogastric system. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 136–139
Ramon F, Rivera A (1986) Gap junction channel modulation a physiological viewpoint. Prog Biophys Molec Biol 48:127–153
Raper JA (1979) Non-impulse mediated synaptic transmission in the stomatogastric ganglion of the spiny lobster. PhD thesis, University of California, San Diego, CA
Russell DF (1979) CNS control of pattern generation in the lobster stomatogastric ganglion. Brain Res 177:598–602
Selverston AI (1987) Gastric mill mechanisms. In: Selverston AI, Moulins M (eds) The crustacean stomatogastric system. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 147–171
Selverston AI, Russell DF, Miller JP, King DG (1976) The stomatogastric nervous system: structure and function of a small neural network. Prog Neurobiol 7:215–289
Spira ME, Spray DC, Bennett MVL (1980) Synaptic organization of expansion motoneurons of Navanax inermis. Brain Res 195:241–269
Spray DC, Bennett MVL (1985) Physiology and pharmacology of gap junctions. Annu Rev Physiol 47:281–303
Spray DC, White RL, Verselis V, Bennett MVL (1985) General and comparative physiology of gap junction channels. In: Bennett MVL, Spray DC (eds) Gap junctions. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, pp 139–153
Zipser B (1979) Voltage-modulated membrane resistance in coupled leech neurons. J Neurophysiol 42:465–475
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnson, B.R., Peck, J.H. & Harris-Warrick, R.M. Amine modulation of electrical coupling in the pyloric network of the lobster stomatogastric ganglion. J Comp Physiol A 172, 715–732 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00195397
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00195397