Summary
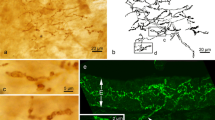
The distribution of substance P (SP) — and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) — containing nerve fibers in the rat larynx was studied using immunohistochemistry. Double-labeling studies revealed a high degree of co-existence of SP- and CGRP-like immunoreactivity (LI) in the nerve fibers in the larynx. There was a considerable regional difference in the number of immunoreactive nerve fibers in the epithelium and lamina propria. Richly supplied sites were the laryngeal side of the epiglottis and the ventral recess, whilst there was no evidence of nerve fibers in the squamous epithelium of the vocal cords. However, where the squamous epithelium of the vocal cords changed into a cuboidal epithelium, a moderate number of nerve fibers was present, and a large number of fibers was seen where the squamous epithelium of the cords was in close contact with cartilage. Nerve fibers showing SP- and CGRP-LI were also observed close to the acini and ducts of the glands, in the blood vessel walls, close to the perichondrium of all the cartilages, and outside the cricothyroid and cricoarytenoid joints. CGRP-LI was detected in epithelial cells facing the lumen of the airway and in cells in the acini and ducts of glands in the subglottic region and trachea. Unilateral sympathectomy did not affect the pattern of SP- and CGRP-innervation in the larynx, whereas after vagotomy, the SP- and CGRP-innervation almost disappeared ipsilaterally in the upper parts of the epiglottis and aryepiglottic folds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amara SG, Jonas V, Rosenfeld MG, Ong ES, Evans RM (1982) Alternative RNA processing in calcitonin gene expression generates mRNAs encoding different polypeptide products. Nature 298:240–244
Cadieux A, Springall DR, Mulderry PK, Rodrigo J, Ghatei MA, Terenghi G, Bloom SR, Polak JM (1986) Occurrence, distribution and ontogeny of CGRP immunoreactivity in the rat lower respiratory tract: effect of capsaicin treatment and surgical denervations. Neuroscience 19:605–627
Dey RD, Altemus JB, Zervos I, Hoffpauir J (1990) Origin and colocalization of CGRP- and SP-reactive nerves in cat airway epithelium. J Appl Physiol 68:770–778
Dubowitz V, Brooke HM (1973) Muscle biopsy: A modern approach. Saunders, London, pp 20–23
Gamse R, Saria A (1985) Potentiation of tachykinin-induced plasma protein extravasation by calcitonin gene-related peptide. Eur J Pharmacol 114:61–66
Ghatei MA, Sheppard MN, O'Shaughnessy DJ, Adrian TE, McGregor GP, Polak JM, Bloom SR (1982) Regulatory peptides in the mammalian respiratory tract. Endocrinology 111:1248–1254
Gracheva MS (1963) Sensory innervation of locomotor apparatus of the larynx. Fed Proc 22:T1120–1123
Grunditz T, Håkansson R, Sundler F, Udman R (1988) Neuronal pathways to the rat thyroid revealed by retrograde tracing and immunocytochemistry. Neuroscience 24:321–335
Hebel R, Stromberg MW (1986) Anatomy and embryology of the laboratory rat. BioMed, Wörthsee, pp 58–64
Hisa Y, Sato F, Fukui K, Ibata Y, Mizukoshi O (1985) Substance P nerve fibres in the canine larynx by PAP immunohistochemistry. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 100:128–133
Johnson DE, Wobken JD (1987) Calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in airway epithelial cells of the human fetus and infant. Cell Tissue Res 250:579–583
Katz DM, Karten HJ (1980) Substance P in the vagal sensory ganglia: localization in cell bodies and pericellular arborizations. J Comp Neurol 193:549–564
Koizumi H (1953) On sensory innervation of larynx in dog. Tohoku J Exp Med 58:199–210
Kurita S, Nagata K, Hirano M (1983) A comparative study of the layer structure of the vocal fold. In: Bless DM, Abbs JH (eds) Vocal fold physiology: contemporary research and clinical issues. College-Hill Press, San Diego, pp 3–21
Lauweryns JM, van Ranst L (1987) Calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in rat lung: light and electron microscopic study. Thorax 42:183–189
Le Greves P, Nyberg F, Terenius L, Hökfelt T (1985) Calcitonin gene-related peptide is a potent inhibitor of substance P degradation. Eur J Pharmacol 115:309–311
Lewis DJ, Prentice DE (1980) The ultrastructure of rat laryngeal epithelia. J Anat 130:617–632
Lundberg JM, Saria A (1982) Capsaicin-sensitive vagal neurons involved in control of vascular permeability in rat trachea. Acta Physiol Scand 115:521–523
Lundberg JM, Saria A (1983) Capsaicin-induced desensitization of airway mucosa to cigarette smoke, mechanical and chemical irritants. Nature 302:251–253
Lundberg JM, Hökfelt T, Nilsson G, Terenius L, Rehfeld JF, Elde R, Said S (1978) Peptide neurons in the vagus, splanchnic and sciatic nerves. Acta Physiol Scand 104:499–501
Lundberg JM, Martling C-R, Saria A, Folkers K, Rosell S (1983a) Cigarette smoke-induced airway oedema due to activation of capsaicin-sensitive vagal afferents and substance P release. Neuroscience 10:1361–1368
Lundberg JM, Brodin E, Saria A (1983b) Effects and distribution of vagal capsaicin-sensitive substance P neurons with special reference to the trachea and lungs. Acta Physiol Scand 119:243–252
Lundberg JM, Hökfelt T, Martling C-R, Saria A, Cuello C (1984) Substance P-immunoreactive sensory nerves in the lower respiratory tract of various mammals including man. Cell Tissue Res 235:251–261
Lundblad L, Lundberg JM, Brodin E, Änggård A (1983a) Origin and distribution of capsaicin-sensitive substance P-immunoreactive nerves in the nasal mucosa. Acta Otolaryngol 96:485–493
Lundblad L, Änggård A, Lundberg JM (1983b) Effects of antidromic trigeminal nerve stimulation in relation to parasympathetic vasodilation in cat nasal mucosa. Acta Physiol Scand 119:7–13
Luts A, Sundler F (1989) Peptide-containing nerve fibers in the respiratory tract of the ferret. Cell Tissue Res 258:259–267
Luts A, Uddman R, Sundler F (1989) Neuronal galanin is widely distributed in the chicken respiratory tract and co-exists with multiple neuropeptides. Cell Tissue Res 256:95–103
Martling C-R, Saria A, Fischer JA, Hökfelt T, Lundberg JM (1988) Calcitonin gene-related peptide and the lung: neuronal coexistence with substance P, release by capsaicin and vasodilatory effect. Regul Pept 20:125–139
Martling C-R, Matran R, Alving K, Hökfelt T, Lundberg JM (1990) Innervation of lower airways and neuropeptide effects on bronchial and vascular tone in the pig. Cell Tissue Res 260:223–233
Nilsson G, Dahlberg K, Brodin E, Sundler F, Strandberg K (1977) Distribution and constrictor effect of substance P in guinea pig tracheobronchial tissue. In: von Euler US, Pernow B (eds) Substance P, Raven Press, New York, pp 75–81
Rosenfeld MG, Mermod J-J, Amara SG, Swanson LW, Sawchenko PE, Rivier J, Vale WW, Evans RM (1983) Production of a novel neuropeptide encoded by the calcitonin gene via tissue-specific RNA processing. Nature 304:129–135
Scheuermann DW, Timmermans J-P, Adriaensen D, De Groodt-Lasseel MHA (1987) Immunoreactivity for calcitonin gene-related peptide in neuroepithelial bodies of the newborn cat. Cell Tissue Res 249:337–340
Shin T, Watanabe S, Wada S, Maeyama T (1987a) Sensory nerve endings in the mucosa of the epiglottis. Morphologic investigations with silver impregnation, immunohistochemistry, and electron microscopy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 96:55–62
Shin T, Wada S, Maeyama T, Watanabe S (1987b) Substance P immunoreactive nerve fibers of the canine laryngeal mucosa. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 97:39–46
Smith G (1977) Structure of the normal rat larynx. Lab Anim 11:223–228
Springall DR, Cadieux A, Oliveira H, Su H, Royston D, Polak JM (1987) Retrograde tracing shows that CGRP-immunoreactive nerves of rat trachea and lung originate from vagal and dorsal root ganglia. J Autonom Nerv Syst 20:155–166
Stjärne P, Lundblad L, Änggård A, Hökfelt T, Lundberg JM (1989) Tachykinins and calcitonin gene-related peptide: co-existence in sensory nerves o the nasal mucosa and effects on blood flow. Cell Tissue Res 256:439–446
Terenghi G, Polak JM, Rodrigo J, Mulderry PK, Bloom SR (1986) Calcitonin gene-related peptide-immunoreactive nerves in the tongue, epiglottis and pharynx of the rat: occurrence, distribution and origin. Brain Res 365:1–14
Tramu G, Pillez A, Leonardelli J (1978) An efficient method of antibody elution for the successive or simultaneous localization of two antigens by immunocytochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem 26:322–324
Uddman R, Sundler F (1987) Sites and synthesis. Neuropeptides in the airways: a review. Am Rev Respir Dis 136:S3-S8
Uddman R, Malm L, Sundler F (1981) Peptide containing nerves in the nasal mucosa. Rhinology 19:75–79
Uddman R, Malm L, Sundler F (1983) Substance-P-containing nerve fibers in the nasal mucosa. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 238:9–16
Uddman R, Luts A., Sundler F (1985) Occurrence and distribution of calcitonin gene-related peptide in the mammalian respiratory tract and middle ear. Cell Tissue Res 241:551–555
Wharton J, Polak JM, Bloom SR, Will JA, Brown MR, Pearse GE (1979) Substance P-like immunoreactive nerves in mammalian lung. Invest Cell Pathol 2:3–10
Yoshida Y, Tanaka Y, Mitsumasu T, Hirano M, Kanaseki T (1986) Peripheral course and intramucosal distribution of the laryngeal sensory nerve fibers of cats. Brain Res Bull 17:95–105
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Domeij, S., Dahlqvist, Å. & Forsgren, S. Regional differences in the distribution of nerve fibers showing substance P- and calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity in the rat larynx. Anat Embryol 183, 49–56 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00185834
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00185834