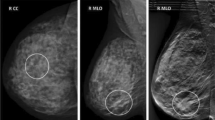
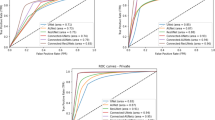
Abstract
Breast cancer is the most ordinary malignant tumor in women worldwide. Early breast cancer screening is the key to reduce mortality. Clinical trials have shown that Computer Aided Design improves the accuracy of breast cancer detection. Segmentation of mammography is a critical step in Computer Aided Design. In recent years, FCN has been applied in the field of image segmentation. Generative Adversarial Networks is also popularized for its ability on generate images which is difficult to distinguish from real images, and have been applied in the image semantic segmentation domain. We apply the Dilated Convolutions to the partial convolutional layer of the Multi-FCN and use the ideas of Generative Adversarial Networks to train and correct our segmentation network. Experiments show that the Dice index of the model D-Multi-FCN-CRF-Adversarial Training on the datasets InBreast and DDSM-BCRP can be increased to 91.15% and 91.8%.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oeffinger, K.C.: Breast cancer screening for women at average risk: 2015 guideline update from the American Cancer Society. JAMA 314(15), 1599–1614 (2015)
Dalmiya, S.: Application of wavelet based k-means algorithm in mammogram segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 52(15), 15–19 (2016)
Cordeiro, F.R.: An adaptive semi-supervised Fuzzy GrowCut algorithm to segment masses of regions of interest of mammographic images. Appl. Soft Comput. 46, 613–628 (2016)
Beller, M., Stotzka, R.: An example-based system to support the segmentation of stellate lesions. In: Meinzer, H.P., Handels, H. (eds.) Bildverarbeitung fur die Medizin 2005, Informatik aktuell, pp. 475–479. Springer, Berlin (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-26431-0_97
Cardoso, J.S.: Closed shortest path in the original coordinates with an application to breast cancer. Int. J. Pattern Recogn. Artif. Intell. 29(1), 1555002 (2015)
Greenspan, H.: Guest editorial deep learning in medical imaging: overview and future promise of an exciting new technique. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 35(5), 1153–1159 (2016)
Kallenberg, M.: Unsupervised deep learning applied to breast density segmentation and mammographic risk scoring. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 35(5), 1322–1331 (2016)
Zhu, W., Lou, Q., Vang, Y.S., Xie, X.: Deep multi-instance networks with sparse label assignment for whole mammogram classification. In: Descoteaux, M., Maier-Hein, L., Franz, A., Jannin, P., Collins, D.L., Duchesne, S. (eds.) MICCAI 2017. LNCS, vol. 10435, pp. 603–611. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66179-7_69
Dhungel, N., Carneiro, G.: Tree RE-weighted belief propagation using deep learning potentials for mass segmentation from mammograms. In: IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, pp. 760–763. IEEE (2015)
Dhungel, N., Carneiro, G.: Deep structured learning for mass segmentation from mammograms. In: IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, pp. 2950–2954. IEEE, Quebec City (2015)
Dhungel, N., Carneiro, G., Bradley, A.P.: Deep learning and structured prediction for the segmentation of mass in mammograms. In: Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F. (eds.) MICCAI 2015. LNCS, vol. 9349, pp. 605–612. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24553-9_74
Zhu, W.: Adversarial deep structural networks for mammographic mass segmentation. CoRR (2016)
Goodfellow, I.J., Pouget-Abadie, J.: Generative adversarial nets. In: International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 2672–2680. MIT Press (2014)
Radford, A.: Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. Computer Science (2015)
Wolterink, J.M.: Generative adversarial networks for noise reduction in low-dose CT. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 36(12), 2536–2545 (2017)
Ganin, Y.: Domain-adversarial training of neural networks. Mach. Learn. Res. 17(1), 2096-2030 (2017)
Kamnitsas, K., et al.: Unsupervised domain adaptation in brain lesion segmentation with adversarial networks. In: Niethammer, M., et al. (eds.) IPMI 2017. LNCS, vol. 10265, pp. 597–609. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59050-9_47
Luc, P.: Semantic segmentation using adversarial networks. CoRR (2016)
Kohl, S.: Adversarial networks for the detection of aggressive prostate cancer. CoRR (2017)
Dai, W.: Scan: structure correcting adversarial network for chest x-rays organ segmentation. CoRR (2017)
Yang, D., et al.: Automatic liver segmentation using an adversarial image-to-image network. In: Descoteaux, M., Maier-Hein, L., Franz, A., Jannin, P., Collins, D.L., Duchesne, S. (eds.) MICCAI 2017. LNCS, vol. 10435, pp. 507–515. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66179-7_58
Moeskops, P., Veta, M., Lafarge, M.W., Eppenhof, K.A.J., Pluim, J.P.W.: Adversarial training and dilated convolutions for brain MRI segmentation. In: Cardoso, M.J., et al. (eds.) DLMIA/ML-CDS -2017. LNCS, vol. 10553, pp. 56–64. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-67558-9_7
Yu, F.: Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions (2015)
Wolterink, J.M., Leiner, T., Viergever, M.A., Išgum, I.: Dilated convolutional neural networks for cardiovascular MR segmentation in congenital heart disease. In: Zuluaga, M.A., Bhatia, K., Kainz, B., Moghari, M.H., Pace, D.F. (eds.) RAMBO/HVSMR-2016. LNCS, vol. 10129, pp. 95–102. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-52280-7_9
Chen, L.C.: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets and fully connected CRFs. Comput. Sci. 4, 357–361 (2014)
Chen, L.C.: DeepLab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 40(4), 834–848 (2016)
Chen, L.C.: Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. CoRR (2017)
Chen, L.C.: Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. CoRR (2018)
Zhu, W.: Co-occurrence feature learning for skeleton based action recognition using regularized deep LSTM networks. In: AAAI, vol. 2 (2016)
Zhu, W., Miao, J.: Hierarchical extreme learning machine for unsupervised representation learning. In: International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, pp. 1–8. IEEE (2015)
Long, J.: Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(4), 640–651 (2014)
Zeiler, M.D., Krishnan, D.: Deconvolutional networks. In: 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2528–2535. IEEE (2010)
Zheng, S.: Conditional Random Fields as Recurrent Neural Networks. CoRR, pp. 1529–1537 (2015)
Chen, L C.: Attention to scale: scale-aware semantic image segmentation. CoRR, pp. 3640–3649 (2015)
Sermanet, P.: OverFeat: integrated recognition, localization and detection using convolutional networks. Eprint Arxiv (2013)
Ines, C.: INbreast: toward a full-field digital mammographic database. Acad. Radiol. 19(2), 236–248 (2012)
Ball, J.E., Bruce, LM.: Digital mammographic computer aided diagnosis (CAD) using adaptive level set segmentation. In: International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine Biology Society. IEEE (2007)
Kingma, D.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. Computer Science (2014)
Szegedy, C.: Intriguing properties of neural networks. Computer Science (2013)
Heath, M., Bowyer, K.: Current status of the digital database for screening mammography. In: Digital mammography, pp. 457–460. Springer, Dordrecht (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-5318-8_75
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 61672181, No. 51679058, Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province under Grant No. F2016005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yin, Q., Pan, H., Yang, B., Bian, X., Chen, C. (2019). Optimizing Breast Mass Segmentation Algorithms with Generative Adversarial Nets. In: Cheng, X., Jing, W., Song, X., Lu, Z. (eds) Data Science. ICPCSEE 2019. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1058. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0118-0_47
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0118-0_47
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-0117-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-0118-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)