Abstract
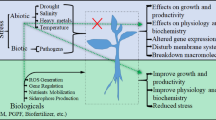
It is consensus that plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPB) be studied extensively in the last two decades, but several of them are not fully investigated/explored especially in arid and semiarid regions worldwide. They have been deployed as potent source of bioactive compounds useful in prospecting of sustainable agricultural. In the present scenario to meet food security, a number of different approaches have been employed to cultivate crops in salt- and drought-prone area. Hence, nowadays, the use of microbial inoculation to alleviate abiotic stress and amelioration of crops could be considered a more cost-effective eco-friendly approach. By keeping current approaches available for plant-microbe interaction, it is needed to pursue prospective research in this area. In the present chapter, authors will emphasize the role of benign PGPB in crop cultivation under stress through produced elicitors/determinants. It is very urgent need to explore this approach for sustainable agriculture grown under stress and also to understand the mutual interactive activities belowground. Therefore, an exploitation of PGPB-plant interactions may be opted in the amelioration of plant health in arid and semiarid area.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albacete A, Ghanem ME, Martínez-Andújar C, Acosta M, Sánchez-Bravo J, Martínez V, Lutts S, Dodd IC, Pérez-Alfocea F (2008) Hormonal changes in relation to biomass partitioning and shoot growth impairment in salinized tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) plants. J Exp Bot 59:4119–4131
Almeida P, Katschnig D, de Boer AH (2013) HKT transporters—state of the art. Int J Mol Sci 14:20359–20385
Apse MP, Aharon GS, Snedden WA, Blumwald E (1999) Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiport in Arabidopsis. Science 285:1256–1258
Bashan Y, de-Bashan LE (2010) How the plant growth-promoting bacterium Azospirillum promotes plant growth-A critical assessment. In: Sparks DL (ed) Advances in agronomy, 108, Elsevier, Academic Press. Adv Agro 108:77–136
Bharti N, Yadav D, Barnawal D, Maji D, Kalra A (2013) Exiguobacterium oxidotolerans, a halotolerant plant growth promoting rhizobacteria, improves yield and content of secondary metabolites in Bacopa monnieri (L.) Pennell under primary and secondary salt stress. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29:379–387
Brini F, Masmoudi K (2012) Ion transporters and abiotic stress tolerance in plants. ISRN Mol Biol. doi:10.5402/2012/927436
Byrt CS, Platten JD, Spielmeyer W, James RA, Lagudah ES, Dennis ES, Tester M, Munns R (2007) HKT1; 5-like cation transporters linked to Na+ exclusion loci in wheat, Nax2 and Kna1. Plant Physiol 143:1918–1928
Chaer GM, Resende AS, de Balieiro FC, Boddey RM (2011) Nitrogen-fixing legume tree species for the reclamation of severely degraded lands in Brazil. Tree Physiol 31:139–149
Chaves MM, Flexas J, Pinheiro C (2009) Photosynthesis under drought and salt stress: regulation mechanisms from whole plant to cell. Ann Bot 103:551–560
Chen L, Dodd IC, Theobald JC, Belimov AA, Davies WJ (2013) The rhizobacterium Variovorax paradoxus 5C-2, containing ACC deaminase, promotes growth and development of Arabidopsis thaliana via an ethylene-dependent pathway. J Exp Bot. doi:10.1093/jxb/ert031
Choudhary DK (2011) Plant growth-promotion (PGP) activities and molecular characterization of rhizobacterial strains isolated from soybean (Glycine max L. Merril) plants against charcoal rot pathogen, Macrophomina phaseolina. Biotechnol Lett 33:2287–2295
da Silva GJ, Costa de Oliveira A (2014) Genes acting on transcriptional control during abiotic stress responses. Adv Agric. doi:10.1155/2014/587070
Duca D, Lorv J, Patten CL, Rose D, Glick BR (2014) Indole-3-acetic acid in plant-microbe interactions. Anton Leeuw 106:85–125
FAO (2013) Climate-smart agriculture sourcebook. FAO, Rome
Figueiredo MV, Burity HA, Martínez CR, Chanway CP (2008) Alleviation of drought stress in the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) by co-inoculation with Paenibacillus polymyxa and Rhizobium tropici. Appl Soil Ecol 40:182–188
Franche C, Lindström K, Elmerich C (2009) Nitrogen-fixing bacteria associated with leguminous and non-leguminous plants. Plant Soil 321:35–59
Fujita Y, Fujita M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2011) ABA-mediated transcriptional regulation in response to osmotic stress in plants. J Plant Res 124:509–525
Gabrijel O, Davor R, Zed R, Marija R, Monika Z (2009) Cadmium accumulation by muskmelon under salt stress in contaminated organic soil. Sci Total Environ 407:2175–2182
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:909–930
Glick BR (2012) Plant growth-promoting bacteria: mechanisms and applications. Scientifica. doi:10.6064/2012/963401
Huang GT, Ma SL, Bai LP, Zhang L, Ma H, Jia P, Liu J, Zhong M, Guo ZF (2012) Signal transduction during cold, salt, and drought stresses in plants. Mol Biol Rep 39:969–987
Jaleel CA, Riadh K, Gopi R, Manivannan P, Inès J, Al-Juburi HJ, Chang-Xing Z, Hong-Bo S, Panneerselvam R (2009) Antioxidant defense responses: physiological plasticity in higher plants under abiotic constraints. Acta Physiol Plant 31:427–436
Kang SM, Khan AL, Waqas M, You YH, Kim JH, Kim JG, Hamayun M, Lee IJ (2014) Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria reduce adverse effects of salinity and osmotic stress by regulating phytohormones and antioxidants in Cucumis sativus. J Plant Interact 9:673–682
Kasotia A, Choudhary DK (2014a) Induced inorganic phosphate solubilization through N-Methyl-N′-Nitro-N-Nitrosoguanidine treated mutants of Pseudomonas koreensis strain AK-1 (MTCC Number 12058) under polyethylene glycol. Proc Natl Acad Sci, India, Sect B Biol Sci 86:115–123
Kasotia A, Choudhary DK (2014b) Pseudomonas-mediated mitigation of salt stress and growth promotion in Glycine max L. Merrill Agric Res. doi:10.1007/s40003-014-0139-1
Khan AA, Jilani G, Akhtar MS, Naqvi SS, Rasheed M (2009) Phosphorus solubilizing bacteria: occurrence, mechanisms and their role in crop production. J Agric Biol Sci 1:48–58
Kim MC, Chung WS, Yun D-J, Cho MJ (2009) Calcium and calmodulin-mediated regulation of gene expression in plants. Mol Plant 2:13–21
Kintu K, Dave BP, Dube HC (2001) Detection and chemical characterization of siderophores produced by certain fungi. Indian J Microbiol 41:87–91
Kochar M, Upadhyay A, Srivastava S (2011) Indole-3-acetic acid biosynthesis in the biocontrol strain Pseudomonas fluorescens Psd and plant growth regulation by hormone overexpression. Res Microbiol 162:426–435
Kohler J, Hernandez JA, Caravaca F, Roldàn A (2008) Plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi modify alleviation biochemical mechanisms in water-stressed plants. Funct Plant Biol 35:141–151
Li B, Sang T, He L, Sun J, Li J, Guo S (2013) Exogenous spermidine inhibits ethylene production in leaves of cucumber seedlings under NaCl stress. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 138:108–113
Liu F, Xing S, Ma H, Du Z, Ma B (2013) Cytokinin-producing, plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria that confer resistance to drought stress in Platycladus orientalis container seedlings. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:9155–9164
López-Otín C, Overall CM (2002) Protease degradomics: a new challenge for proteomics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:509–519
Miller GAD, Susuki N, Ciftci-Yilmaz S, Mittler RON (2010) Reactive oxygen species homeostasis and signalling during drought and salinity stresses. Plant Cell Environ 33:453–467
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681
Nakashima K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2014) The transcriptional regulatory network in the drought response and its crosstalk in abiotic stress responses including drought, cold, and heat. Front Plant Sci. doi:10.3389/fpls.2014.00170
Nawaz K, Hussain K, Majeed A, Khan F, Afghan S, Ali K (2013) Fatality of salt stress to plants: morphological, physiological and biochemical aspects. Afr J Biotechnol 9:5475–5480
Nishiyama R, Watanabe Y, Fujita Y, Le DT, Kojima M, Werner T, Vankovad R, Yamaguchi-Shinozakib K, Shinozakia K, Kakimoto T, Sakakibara H, Schmülling T, Tran LSP (2011) Analysis of cytokinin mutants and regulation of cytokinin metabolic genes reveals important regulatory roles of cytokinins in drought, salt and abscisic acid responses, and abscisic acid biosynthesis. Plant Cell 23:2169–2183
Nunkaew T, Kantachote D, Nitoda T, Kanzaki H, Ritchie RJ (2014) Characterization of exopolymeric substances from selected Rhodopseudomonas palustris strains and their ability to adsorb sodium ions. Carbohydr Polym 115:334–341
Paul D (2013) Osmotic stress adaptations in rhizobacteria. J Basic Microbiol 53:101–110
Paul D, Nair S (2008) Stress adaptations in a plant growth promoting rhizobacterium (PGPR) with increasing salinity in the coastal agricultural soils. J Basic Microbiol 48:378–384
Pérez-Alfocea F, Ghanem ME, Gómez-Cadenas A, Dodd IC (2011) Omics of root-to-shoot signaling under salt stress and water deficit. Omics J Integr Biol 15:893–901
Reddy AA, Bantilan MCS, Mohan G (2013) Pulses production scenario: policy and technological options. Policy Brief 26, International Crop Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics
Richardson AE, Simpson RJ (2011) Soil microorganisms mediating phosphorus availability update on microbial phosphorus. Plant Physiol 156:989–996
Saibo NJM, Lourenςo T, Oliveira MM (2009) Transcription factors and regulation of photosynthetic and related metabolism under environmental stresses. Ann Bot 103:609–623
Sandhya V, Ali SZ, Grover M, Reddy G, Venkateswarlu B (2009) Alleviation of drought stress effects in sunflower seedlings by exopolysaccharides producing Pseudomonas putida strain P45. Biol Fertil Soils 46:17–26
Santi C, Bogusz D, Franche C (2013) Biological nitrogen fixation in non-legume plants. Ann Bot 111:743–767
Shi H, Lee BH, Wu SJ, Zhu JK (2002) Overexpression of a plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter gene improves salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Biotechnol 21:81–85
Singh A, Nath Panda S, Flugel WA, Krause P (2012) Waterlogging and farmland salinisation: causes and remedial measures in an irrigated semi‐arid region of India. Irrig Drain 61:357–365
Suzuki N, Rivero RM, Shulaev V, Blumwald E, Mittler R (2014) Abiotic and biotic stress combinations. New Phytol 203:32–43
Wood JM (2011) Bacterial osmoregulation: a paradigm for the study of cellular homeostasis. Annu Rev Microbiol 65:215–238
Yang SF, Hoffman NE (1984) Ethylene biosynthesis and its regulation in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 35:155–189
Yang J, Kloepper JW, Ryu C-M (2009) Rhizosphere bacteria help plants tolerate abiotic stress. Trends Plant Sci 14:1–4
Zhang H, Kim MS, Sun Y, Dowd SE, Shi H, Paré PW (2008a) Soil bacteria confer plant salt tolerance by tissue-specific regulation of the sodium transporter HKT1. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 21:737–744
Zhang H, Xie X, Kim MS, Kornyeyev DA, Holaday S, Pare PW (2008b) Soil bacteria augment Arabidopsis photosynthesis by decreasing glucose sensing and abscisic acid levels in planta. Plant J 65:264–273
Zhang T, Zeng S, Gao Y, Ouyang Z, Li B (2011) Assessing impact of land uses on land salinization in the Yellow River Delta, China using an integrated and spatial statistical model. Land Use Policy 28:857–866
Acknowledgments
In the present review, some of the research has been partially supported by DBT and SERB grant no. BT/PR1231/AGR/021/340/2011 and SR/FT/LS-129/2012, respectively, to DKC. Authors would also like to acknowledge UGC-RGNF fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Kasotia, A., Varma, A., Tuteja, N., Choudhary, D.K. (2016). Microbial-Mediated Amelioration of Plants Under Abiotic Stress: An Emphasis on Arid and Semiarid Climate. In: Choudhary, D., Varma, A., Tuteja, N. (eds) Plant-Microbe Interaction: An Approach to Sustainable Agriculture. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-2854-0_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-2854-0_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-2853-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-2854-0
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)