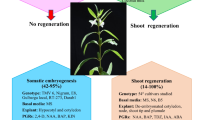
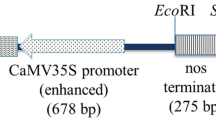
Abstract
Plant tissue culture and genetic transformation are powerful biotechniques for plant genetic improvement. For sesame, in vitro callus induction and differentiation with high efficiency are very difficult because of the specific characters of the species, and employing genetic transformation is too difficult. In the past forty years, many scientists tried a huge number of experiments in order to establish efficient callus induction and plantlet regeneration system in sesame. In this section, we present the history and the main progresses of sesame tissue culture and gene transformation research. Several successful examples for plant regeneration and gene transformation in sesame are listed. In addition, the main factors influencing the efficiency of tissue culture, plantlet regeneration, and gene transformation are discussed. The application prospect of tissue culture and gene transformation in sesame genetics and breeding research is also introduced.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdellatef E, Ahmed MMM, Daffalla HM, Khalafalla MM (2010) Enhancement of adventitious shoot regeneration in sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) cultivar promo KY using ethylene inhibitors. J Phytol 2:61–67
Ahmed MMM, Abdellatef E, Khalafalla MM (2008) In vitro multiple shoot induction and plant regeneration in elite Sudanese sesame cultivars (Sesamum indicum L.). Amer-Euras J Sustain Agri 2:308–314
An JW, Miao HM, Wei SL, Guo WZ, Zhang HY (2011) Study on Induced factors affecting adventitious bud formation from cotyledon in sesame. J Henan Agric Sci 10:44–47
An (2009) adventitious shoot induction and plant regeneration from cotyledon of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Thesis, Nanjing agriculture university, Nanjing, China
Bangaremma SW, Lokesha R, Gayatree GS, Sharanamma, (2013) Sesame shoot regeneration using different combinations of growth regulators. Mol Plant Breed 4:267–269
Baskaran P, Jayabalan N (2006) In vitro mass propagation and diverse callus orientation on Sesamum indicum L.- an important oil plant. J Agri Technol 2:259–269
Bhattacharyya J, Chakraborty A, Mitra J, Chakraborty S, Pradhan S et al (2015) Genetic transformation of cultivated sesame (Sesamum indicum L. cv Rama) through particle bombardment using 5-day-old apical, meristematic tissues of germinating seedlings. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 123:455–466
Breitler JC, Labeyrie A, Meynard D, Legavre T, Guiderdoni E (2002) Efficient microprojectile bombardment-mediated transformation of rice using gene cassettes. Theor Appl Genet 104:709–719
Charaborti P, Ghosh A (2009) Variation in callus induction and root-shoot bud formation depend on seed coat of sesame genotypes. Res J Bot 5:14–19
Chattopadhyaya B, Banerjee J, Basu A, Sen SK, Maiti MK (2010) Shoot induction and regeneration using internodal transverse thin cell layer culture in Sesamum indicum L. Plant Biotechnol Rep 4:173–178
Chen ZK, Wang JL, Zhi YB, Yi ML (1994) Study of multiple bud induction and shoot regeneration in sesame. Henan Agric Sci 11:10–12
Chen Z, Zhi Y, Yi M, Wang J, Liang X et al (1996) Transformation of engineered male sterile gene and establishment of transgenic plants in sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Acta Agri Bor-Sin 11(4):33–38
Chowdhury S, Basu A, Kundu S (2014) A new high-frequency Agrobacterium-mediated transformation technique for Sesamum indicum L. using de-embryonated cotyledon as explant. Protoplasma 251:1–16
Chowdhury S, Basu A, Kundu S (2017) Overexpression of a new osmotin-Like protein gene (SindOLP) confers tolerance against biotic and abiotic stresses in sesame. Front Plant Sci 8:410
Christou P (1995) Strategies for variety-independent genetic transformation of important cereals, legumes and woody species utilizing particle bombardment. Euphytica 85:13–27
Cui YH, Sun Y, Liu WP (2010) Study on in vitro culture of hypocotyl of black sesame. Chin J Guizhou Sci 28:67–72
Gangopadhyay G, Poddar R, Gupta S (1998) Micropropagation of sesame (Sesamum indicum) by in vitro multiple shoot production from nodal explants. Phytomorphology 48:83–90
George L, Bapat VA, Rao PS (1987) In vitro multiplication of sesame (Sesamum indicum) through tissue culture. Ann Bot-London 60:17–21
George L, Bapat VA, Rao PS (1989) Plant regeneration in vitro, in different cultivars of sesame ( Sesamum indicum, L.). Proc Plant Sci 99:135–137
Honnale HN (2011) Callus induction and organogenesis in Sesamum indicum L. CV E8. Curr Trends Biotechnol Pharmacy 6:1330–1332
Jin UH, Chun JA, Han MO, Li JW, Yi YB et al (2005) Sesame hairy root cultures for extra-cellular production of a recombinant fungal phytase. Process Biochem 40:3754–3762
Joshi AB (1961) Sesamum. Indian Central Oilseed Committee Hyderabad, India, p 109
Kwon TH, Abe T, Sasahara T (1993) Efficient callus induction and plant regeneration in Sesamum species. Plant Tissue Cult Lett 10:260–266
Li B, Chen R (1990) Tissue culture and plantlet regeneration of sesame. J Shanxi Univ 13:307–310
Li M, Zhang J, Wang Q, Yang YW, Wang ZS (1996) Callus induction and organogenesis of Sesamum indicum L. hypocotyl. J Henan Normal Uni 1:61–64
Li X, An SJ, Shao TM, Chai XQ, Liu P et al (2016) Insulin gene transformation into sesame via pollen-tube pathway. Chin J Jiangsu J Agr Sci 32(5):1013–1017
Liu M (1986) Preliminary report on tissue culture experiment of sesame. Chin J Henan Agric Sci 2:15–16
Liu M (1990) Anther culture of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Henan Sci 2:55–61
Liu SL, Wang YD, Luo S, Zhang J, Han BW (1994) Somatic embryogenesis from hypocotyl culture of sesame and changes of endogenous hormones and soluble proteins during embryogenesis. J Agric Biotechnol 2:44–49
Lokesha R, Shashidhara N, Janagoudar BS (2007) Callus induction and plant regeneration in sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) through direct seeding. Plant Cell Biotechnol Mol Biol 8:85–88
Lokesha R, Rahaminsab J, Ranganatha ARG, Dharmataj P (2012) Whole plant regeneration via adventitious shoot formation from de-embryonated cotyledon explants of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). World J Nuclear Sci Technol 2:47–51
Malaghan S, Lokesha R, Savitha R, Ranganatha A (2013) Adventitious shoot regeneration in Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) (Pedaliaceae) via deembryonated cotyledonary explants. Res J Biol 1:31–35
Malaghan S, Lokesha R, Revadi S (2016) Whole plant regeneration through direct organogenesis in sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Green Farming 7:1034–1039
Mary RJ, Jayabalan N (1997) Influence of growth regulators on somatic embryogenesis in sesame. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 49:67–70
Miao HM, Ju M, Wei LB, Ma Q, Zhang HY (2012) Establishment of sesame callus induction and shoot regeneration system. Chin Bull Bot 47:162-170
Mitsuma S, Ishigaki E, Sugiyama R, Tetsuya A, Kuoji Y et al (2004) Activation of phenylpropanoid metabolism in sesame by over-expression of carrot calmodulin gene. Biol Pharm Bull 27:1621–1625
Mukherji S (1947) Relation of total soluble solids in the cell sap of Sesamum species to the degree of susceptibility and resistance to Antigastra (Lepidoptera–Pyralidæ) attack. Nature 160:95–96
Nimmakayala P, Perumal R, Mulpuri S, Reddy UK (2011) Sesamum. In: Kole C (ed) Wild crop relatives: genomic and breeding resources. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 261–273
Pratik P, Shilpa B, Kokiladevi E (2016) Efficacy of plant growth hormones for shoot induction and regeneration in Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Res J Biotechnol 11(10):27–30
Qu Z, Wu XY, Xia FJ (1994) Embryo rescue and plant regeneration of inerspecific hybridization between S. indicum and a wild specie S. schizinixianum. Chin J Oil Crops 1:33–35
Raja A, Jayabalan N (2010) Callus induction and plantlet regeneration from leaf explants of Sesame (Sesamumindicum L. cv. SVPR - 1). J Swamy Bot Club 27:93–98
Raja A, Jayabalan N (2011) In vitro shoot regeneration and flowering of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) cv. SVPR-1. J Agri Technol 7:1089–1096
Rao KR, Vaidyanath K (1997) Induction of multiple shoots from seedling shoot tips of different varieties of Sesamum. Indian J Plant Physiol 2:257–261
Saravanan S, Nadarajan N (2005) Effect of media supplements on in vitro response of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) genotypes. Res J Agric Biol Sci 1:98–100
Seo HY, Kim YJ, Park TI, Kim HS, Yun SJ et al (2007) High-frequency plant regeneration via adventitious shoot formation from deembryonated cotyledon explants of Sesamum indicum L. Vitro Cell Dev Biol 43:209–214
Shashidhara N, Santosh D, Ravikumar H, Ashoka N, Dhanalakshmi T et al (2011) Exogeneous and endogeneous contaminations in sesame tissue culture—Boon or Bane. Intl J Agric Environ Biotechnol 4:103–106
Shi SW, Cai M (1986) Presentation of plant regeneration of the stem segment culture in wild sesame Congo. Chi J Oil Crops 4:67–68
Shi SW, Cai M (1989) Callus induction and plantlet regeneration from hypocotyls of Sesamum indicum. J Plant Physiol 04:40
Shi SW, Cai M (1989) Effect on inducing factors on pollen callus formation of in vitro cultured anthers in sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Chin J Oil Crops 2:45–49
Singh KD, Shagufta K (2011) In vitro regeneration of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) – —an important medicinal oil crop. Crop Res 42(1 to 3):125–130
Singh RP, Singh SP, Pransad BK, Singh BD (2006) Multiple plantlets regeneration in tissue culture of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Res Crops 7:760–764
Subramanian M (2003) Wide crosses and chromosome behavior in Sesamum. Madras Agric J 90:1–15
Sudhaker D, SreeRangasamy SR, Liang GQ (1990) Sesame seed embryo culture. Chin J Oil Crops 3:102
Taskin KM, Turgut K (1997) In vitro regeneration of Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) Turk J Bot 21:15–18
Taskin KM, Ercan AG, Turgut K (1999) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Turk J Bot 23:291–296
Tiwari S, Kumar S, Gontia I (2011) Mini review: biotechnological approaches for sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) and niger (Guizotia abyssinica L. f. Cass). Asia Pac J Mol Biol Biotechnol 19:2–9
Wadeyar BS (2013) Sesame shoot regeneration-using different combinations of growth regulators. Mol Plant Breed 4:267–269
Wadeyar BS, Lokesha R (2011) Studies on high frequency shoot regeneration in sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Plant Tiss Cult Biotechnol 21:45–52
Wei SL, Zhang HY, Zheng YZ, Zhang TD, Mei HX et al (2007) Study on callus induction in cotyledon and hypocotyl of sesame. J Henan Agric Sci 2:41–45
Were BA (2006) Genetic improvement of oil quality in sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Thesis, Swedish University of Agricultural Science, Uppsala, Swedish
Were BA, Gudu S, Onkware AO, Carlsson AS, Welander M (2006) In vitro regeneration of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) from seedling cotyledon and hypocotyl explants. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 85:235–239
Xu ZQ, Jia JF, Hu ZD (1997) Somatic Embryogenesis in Sesamum indicum L. cv. Nigrum. J Plant Physiol 150:755–758
Yadav M, Chaudhary D, Sainger M, Jaiwal PK (2010) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated genetic transformation of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 103:377–386
Yang M, Liu H, Zhou T, Qu H, Yang Y et al (2017) Production and identification of F1 interspecific hybrid between Sesamum indicum and wild relative S. indicatum. Sci Agri Sin 50(10):1763–1771
Yi Y, Zhang H, Zuo T, Wang ZZ (1997) Study on the culture of different explants of black seedcoat seame in vitro. Acta Agri Bor-Occiden Sin 6(4):26–29
Yifter M, Sbhatu DB, Mekbib F, Abraha E (2013) In vitro regeneration of four Ethiopian varieties of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) using anther culture. Asian J Plant Sci 12:214–218
Yu ZG (2005) Study on callus inducement and differentiation of black sesame seed. J Yangtze Univ Agric Sci 2:73–75
Zhang HY, Miao HM, Zhang TD, Wei LB, Li C et al (2013) Biological characters of interspecific hybrid progenies between Sesamum indicum L. and wild relatives (Sesamum schinzianum Asch, Sesamum radiatum Schum & Thonn). Sci Agri Sin 46(19):3965–3977
Zhang HY, Miao HM, Ju M (2019) Potential for adaptation to climate change through genomic breeding in sesame. In: Kole C (ed) Genomic designing of climate-smart oilseed crops. Springer, Cham, Switzerland, pp 374–376
Zhao RH, Miao HM, Ma Q, Chen CB, Song WQ et al (2018) Karyotype comparison analysis of the wild species Sesamum alatum and the cultivated sesame. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Nankaiensis 5(05):27–36
Zhen ZG, Duan Y, Wang XL, Cui XH, Sun MY et al (2004) Breeding of sesame lines with high resistance introduced with foreign DNA by pollen tubes path. Chin J Oil Crop Sci 26:31–34
Zhi YB, Jiang WS, Yi ML, Chen ZK (1998) Study on influence of regeneration frequency of in vitro culture of cotyledon of sesame. Chin J Xinyang Agric College 8:12–15
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Miao, H., Ju, M., Wang, H., Zhang, H. (2021). Tissue Culture and Genetic Transformation in Sesame. In: Miao, H., Zhang, H., Kole, C. (eds) The Sesame Genome. Compendium of Plant Genomes. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-98098-0_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-98098-0_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-98097-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-98098-0
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)