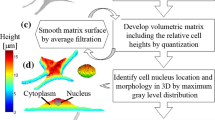
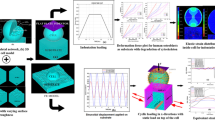
Abstract
The mechanical and biological response of cells to various loading regimes is a subject of great interest in the research field of biomechanics. Extensive utilization of different cellular mechanics experimental designs has been made over the years in order to provide better insight regarding the mechanical behavior of cells, and the mechanisms underlying the transduction of the applied loads into biological reactions. These experimental protocols have limited ability in directly measuring different mechanical parameters (e.g. internal cellular strains and stresses). In addition, they are very costly and involve highly complex apparatuses and experimental designs. Thus, further understating of cellular response can be achieved by means of computational models, such as the finite element (FE) method. FE modeling of cells is an emerging direction in the research field of cellular mechanics. Its application has been rapidly growing over the last decade due to its ability to quantify deformations, strains and stresses in and around cells, thus providing basic understating of the mechanical state of cells and allowing identification of mechanical properties of cells and cellular organelles when coupled with appropriate experiments. In this chapter, we review the two-dimensional (2D) and three-dimensional (3D) reported cell models of various cell types, subjected to different applied mechanical stimuli, e.g. compression, micropipette aspiration, indentation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baaijens, F.P., Trickey, W.R., Laursen, T.A., Guilak, F.: Large deformation finite element analysis of micropipette aspiration to determine the mechanical properties of the chondrocyte. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 33, 494–501 (2005)
Bursa, J., Fuis, V.: Finite element simulation of mechanical tests of individual cells. In: IFMBE Proceedings WC 2009, pp. 16–19 (2009)
Bursa, J., Lebis, R., Janicek, P.: FE models of stress–strain states in vascular smooth muscle cells. Technol. Health Care 14, 311–320 (2006)
Caille, N., Thoumine, O., Tardy, Y., Meister, J.J.: Contribution of the nucleus to the mechanical properties of endothelial cells. J. Biomech. 35, 177–187 (2002)
Dailey, H.L., Ricles, L.M., Yalcin, H.C., Ghadiali, S.N.: Image-based finite element modeling of alveolar epithelial cell injury during airway reopening. J. Appl. Physiol. 106, 221–232 (2009)
De Santis, G., Boschetti, F., Lennon, A. B., Prendergast, P.J., Verdonck, P., Verhegghe, B.: How an eukaryotic cell senses the substrate stiffness? An extrapolation using a finite element model with cytoskeleton modelled as tensegrity structure. In: Proceedings of the ASME 2009 Summer Bioengineering Conference, Resort at Squaw Creek, Lake Tahoe, CA, USA, 17–21 June 2009
Deguchi, S., Fukamachi, H., Hashimoto, K., Lio, K., Tsujioka, K.: Measurements and finite element modeling of the force balance in the vertical section of adhering vascular endothelial cells. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2, 173–185 (2009)
Ferko, M.C., Bhatnagar, A., Garcia, M.B., Butler, P.J.: Finite-element stress analysis of a multi-component model of sheared and focally-adhered endothelial cells. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 35, 208–223 (2007)
Ferko, M.C., Pattersom, B.P., Butler, P.J.: High-resolution solid modeling of biological samples imaged with 3D fluorescence microscopy. Microsc. Res. Tech. 69, 648–655 (2006)
Frisch, T., Thoumine, O.: Predicting the kinetics of cell spreading. J. Biomech. 35, 1137–1141 (2002)
Gladilin, E., Micoulet, A., Hisseini, B., Rohr, K., Spatz, J., Elis, R.: 3D finite element analysis of uniaxial cell stretching: from image to insight. Phys. Biol. 4, 104–113 (2007)
Huang, W., Anvari, B., Torres, J., Lebaron, R., Athanasiou, K.: Temporal effects of cell adhesion on mechanical characteristics of the single chondrocyte. J. Orthop. Res. 21, 88–95 (2003)
Jean, R.P., Gray, D.S., Spector, A.A., Chen, C.S.: Characterization of the nuclear deformation caused by changes in endothelial cell shape, J. Biomech. Eng. 126(5): 552–558 (2004)
Jean, R.P., Chen, C.S., Spector, A.A.: Finite-element analysis of the adhesion–cytoskeleton–nucleus mechanotransduction pathway during endothelial cell rounding: axisymmetric model. J. Biomech. Eng. 127, 594–600 (2005)
Leipzig, N.D., Athanasiou, K.A.: Static compression of single chondrocytes catabolically modifies single-cell gene expression. Biophys. J. 94, 2412–2422 (2008)
Lenaerts, L., van Lenthe, G.H.: Multi-level patient-specific modeling of the proximal femur. A promising tool to quantify the effect of osteoporosis treatment. Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 367, 2079–2093 (2009)
Linder-Ganz, E., Shabshin, N., Itzchak, Y., Gefen, A.: Assessment of mechanical conditions in sub-dermal tissues during sitting: a combined experimental-MRI and finite element approach. J. Biomech. 40, 1443–1454 (2007)
McGarry, J.P.: Characterization of cell mechanical properties by computational modeling of parallel plate compression. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 37, 2317–2375 (2009)
McGarry, J.G., Prendergast, P.J.: A three-dimensional finite element model of an adherent eukaryotic cell. Eur. Cell Mater. 16, 27–34 (2004)
Mijailovich, S.M., Kojic, M., Zivkovic, M., Fabry, B., Fredberg, J.J.: A finite element model of cell deformation during magnetic bead twisting. J. Appl. Physiol. 93, 1429–1436 (2002)
Miyazaki, H., Hasegawa, Y., Hayashi, K.: Tensile properties of contractile and synthetic vascular smooth muscle cells. JSME Int. J. 45, 870–879 (2002)
Ofek, G., Natoli, R.M., Athanasiou, K.A.: In situ mechanical properties of the chondrocyte cytoplasm and nucleus. J. Biomech. 42, 873–877 (2009)
Ohayon, J., Tracqui, P.: Computation of adherent cell elasticity for critical cell-bead geometry in magnetic bead twisting. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 33, 131–141 (2005)
Peeters, E.A.G., Oomens, C.W.J., Boute, C.V.C., Bader, D.L., Baaijens, F.P.T.: Mechanical and failure properties of single attached cells under compression. J. Biomech. 38, 1685–1693 (2005)
Pistoia, W., van Rietbergen, B., Lochmuller, E.M., Lill, C.A., Eckstein, F., Ruegsegger, P.: Image-based micro-finite-element modeling for improved distal radius strength diagnosis: moving from bench to bedside. J. Clin. Densitom. 7, 153–160 (2004)
Portnoy, S., Yizhar, Z., Shabshin, N., Itzchak, Y., Kristal, A., Dotan-Marom, Y., Siev-Ner, I., Gefen, A.: Internal mechanical conditions in the soft tissues of a residual limb of a trans-tibial amputee. J. Biomech. 41, 1897–1909 (2008)
Salvi, J.D., Lim, J.Y., Donahue, H.J.: Finite element analyses of fluid flow conditions in cell culture. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 16(4): 661–670 (2010)
Slomka, N., Gefen, A.: Confocal microscopy-based three-dimensional cell-specific modeling for large deformation analyses in cellular mechanics. J. Biomech. (2010). doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2010.02.011
Slomka, N., Or-Tzadikario, S., Sassun, D., Gefen, A.: Membrane-stretch-induced-cell death in deep tissue injury: computer model studies. Cell Mol. Bioeng. 2, 118–132 (2009)
Zhao, R., Wyss, K., Simmons, C.A.: Comparison of analytical and inverse finite element approaches to estimate cell viscoelastic properties by micropipette aspiration. J. Biomech. 42, 2768–2773 (2009)
Zeng, D., Juzkiw, T., Read, A.T., Chan, D.W., Glucksberg, M.R., Ethier, C.R., Johnson, M.: Young’s modulus of elasticity of Schlemm’s canal endothelial cells. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 9, 19–33 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Slomka, N., Gefen, A. (2010). Finite Element Modeling of Cellular Mechanics Experiments. In: Gefen, A. (eds) Cellular and Biomolecular Mechanics and Mechanobiology. Studies in Mechanobiology, Tissue Engineering and Biomaterials, vol 4. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/8415_2010_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/8415_2010_31
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-14217-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-14218-5
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)