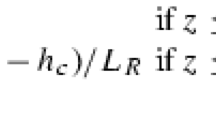Abstract
Horizontal heterogeneity in either the source-sink distribution or the wind field results in streamwise advection of momentum and scalars, which must be accounted for whenever we deduce surface exchange from micrometeorological measurements on flux towers. This Chapter focuses on the second of these causes, addressing scalar advection in topography covered with uniformforest canopies rather than that generated by heterogeneity in the land cover. After defining advection and its relationship with modeling we discuss flow over forested hills by looking first at the wind field, next at the transfer of a generic scalar and finally at the implications for measuring photosynthesis on a two-dimensional ridge. Using analytic approaches as far as is possible, we show that both the turbulent wind field and scalar flow and transport in the canopy on a hill have a two-layer asymptotic structure with an upper canopy layer, coupled by turbulent transfer to the surface-layer flow above, and a lower canopy layer, that is driven by the pressure gradient produced as the wind field is deflected over the hill. The dynamics of these two layers are quite different and their matching through the upper canopy leads to strong modulation of turbulent transport over the hill and substantial advective flux divergence, even on gentle hills. The effect of the hill-induced perturbations on photosynthesis is calculated numerically and is shown to be small, being of order of the hill slope. In contrast, their e ect on the net ecosystem exchange that would be deduced from eddy-flux measurements on a single flux tower is large, being of order one.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aubinet, M., Heinesch, B. Yernaux, M.: 2003, ‘Horizontal and vertical CO2 advection in a sloping forest’ Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 108, 397–417.
Ayotte, K. W., Finnigan, J. J., Raupach, M. R.: 1999, ‘A second-order closure for neutrally stratified vegetative canopy flows’, Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 90, 189–216.
Ayotte, K. W., Davy, R. J., Coppin, P. A.: 2001, ‘A simple temporal and spatial analysis of flow in complex terrain in the context of wind energy modelling’ Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 98, 275–295.
Baldocchi, D. D., Falge, E., Gu, L., Olson, R., Hollinger, D., Running, S., Anthoni, P., Bernhofer, Ch., Davis, K., Evans, R., Fuentes, J., Goldstein, A., Katul, G., Law, B., Lee, X., Malhi, Y., Meyers, T., Munger, W., Oechal, W., Paw U, K. T., Pilegaard, K., Schmid, H. P., Valentini, R., Verma, S., Vesala, T., Wilson, K., Wofsy, S.: 2001, ‘FLUXNET: A new tool to study the temporal and spatial variability of ecosystem-scale carbon dioxide, water vapor and energy flux densities’ Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 82, 2415–2434.
Belcher, S. E., Jerram, N., Hunt, J. C. R.: 2002, ‘Adjustment of a turbulent boundary layer to a canopy of roughness elements’ J. Fluid Mech. 488, 369–398.
Bradley, E. F.: 1968, ‘A micrometeorological study of velocity profiles and surface drag in the region modified by a change in surface roughness’ Q. J. Roy Meteorol. Soc. 94, 361–379.
Campbell, G., Norman, J.: 1998, An Introduction to Environmental Biophysics, Springer, 286pp.
Collatz, G. J., Ball, J. T., Grivet, C., Berry, J. A.: 1991, ‘Physiological and environ-mental regulation of stomatal conductance, photosynthesis and transpiration: A modelthat includes a laminar boundary layer’, Agric. For. Meteorol. 54, 107–136.
Dyer, A. J., Crawford, T. V.: 1965, ‘Observations of climate at a leading edge’ Q. J. Roy Meteorol. Soc. 91, 345–348.
Falk, M. B., Park, Y.-S., Paw U, K. T., Pyles, R. D., Hsiao, T. C., Shaw, R. H., King, T., Matista, A. A., Wahbeh, H.: 2000, ‘A comparison of the carbon and water vapor exchange contributions of mean advection, eddy-covariance, and storage in a tall forest’ 24th Am. Meteorol. Soc. Conf. Agric. For. Meteorol., American Meteorological Society, Boston, Massachusetts.
Farquhar, G. D., Von Caemmerer, S., Berry, J. A.: 1980, ‘A biochemical model of photosynthetic CO2 assimilation in leaves of C3 species’ Planta 149, 78–90.
Finnigan, J. J.: 2004, ‘A re-evaluation of long-term flux measurement techniques. Part II: coordinate systems’ Bound.-Layer Meteorol., in press.
Finnigan, J. J.: 2002, ‘Momentum Transfer to Complex Terrain’ Geophysical Monograph Honouring J R Philip, (Raats, P. A. C, Smiles, D. E., Warrick, A. W. Eds) American Geophysical Union, in press.
Finnigan, J. J.: 2000, ‘Turbulence in plant canopies’ Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 32, 519–571.
Finnigan, J. J., Belcher, S. E.: 2004, ‘Flow over a hill covered with a plant canopy’ Q. J. Roy Meteorol. Soc., in press.
Finnigan, J. J., Clements, R., Malhi, Y., Leuning, R., Cleugh, H.: 2003, ‘A reevaluation of long-term flux measurement techniques. Part I: Averaging and coordinate rotation’ Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 107, 1–48.
Finnigan, J. J., Brunet, Y.: 1995, ‘Turbulent airflow in forests on flat and hilly terrain’ Wind and Trees, (Coutts M. P., Grace, J. Eds.) Cambridge University Press, UK, 3–40.
Finnigan, J. J., Raupach, M. R.: 1987, ‘Transfer processes in plant canopies in relation to stomatal characteristics’, Stomatal Function (Zeiger, E., Farquar, G. D., Cowan I. R.) Stanford University Press, Stanford, California, 385–429.
Hunt, J. C. R., Leibovich, S., and Richards, K. J.: 1988, ‘Turbulent shear flow over low hills’ Q. J. Roy Meteorol. Soc. 114, 1435–1470.
Jackson, P. S., Hunt, J. C. R.: 1975, ‘Turbulent wind flow over a low hill’, Q. J. Roy Meteorol. Soc. 101 929–956
Katul, G. G., Chang, W. H.: 1999, ‘Principal length scales in second-order closure models for canopy turbulence’ J. Appl. Meteorol. 38, 1631–1643.
Katul, G.G., Finnigan, J. J., Leuning, R., Belcher, S. E.: 2004a, ‘The influence of hilly terrain on canopy-atmosphere carbon dioxide exchange’ Bound.-Layer Meteorol., in review.
Katul, G. G., Finnigan, J. J., Belcher, S. E.: 2004b, ‘Momentum transfer within a canopy situated on complex topography ‘Bound.-Layer Meteorol., in review.
Kaimal J.C., Finnigan J. J.: 1994, Atmospheric BoundaryLayer Flows: Their Structure and Management, Oxford University Press, New York. 289 pp.
Kuo, Y. H., Schlatter, T. W.: 1990, ‘Mesoscale data assimilation’, Notes from an NCAR Summer Colloquium, NCAR, Boulder, Colorado. pp. 644
Lai, C. T, Katul, G., Butnor, J., Ellsworth, D., Oren, R.: 2002, ‘Modelling nighttime ecosystem respiration by a constrained source optimization method’, Global Change Biology 8, 124–141.
Lai, C. T., Katul, G.G., Oren, R., Ellsworth, D., Schafer, K.: 2000, ‘Modeling CO2 and water vapor turbulent flux distributions within a forest canopy’ J. Geophys. Res. 105, 26333–26351.
Lee, X.: 1998, ‘On micrometeorological observations of surface-air exchange over tall vegetation’ Agric. For. Meteorol. 91, 39–49.
Leuning, R.: 1995, ‘A critical appraisal of a combined stomatal-photosynthesis model for C3 plants’ Plant, Cell, and Environment 18, 339–355.
Nastrom, G. D., Gage, K. S.: 1985, ‘A climatology of atmospheric wave number spectra of wind and temperature observed by commercial aircraft’ J. Atmos. Sci. 42, 950–960.
Neff, D.E., Meroney, R.N.: 1998, ‘Wind-tunnel modeling of hill and vegetation influencefon wind-power availability’, J. Wind Eng. Industrial Aerodyn. 74–76, 335–343.
Raupach, M. R., Weng, W. S., Carruthers, D. J., Hunt, J. C. R.: 1992, ‘Temperature and humidity fields and fluxes over low hills’ Q. J. Roy Meteorol. Soc. 118, 191–225.
Raupach, M. R., Finnigan, J. J., Brunet, Y.: 1996, ‘Coherent eddies and turbulence in vegetation canopies: the mixing layer analogy’ Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 78, 351–382.
Rider, N. E., Philip, J. R., Bradley, E. F.: 1963, ‘The horizontal transport of heat and moisture: a micrometeorological study’ Q. J. Roy Meteorol. Soc. 89, 507–531.
Ruck, B., Adams, E.: 1991, ‘Fluid mechanical aspects of the pollutant transport to coniferous trees’ Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 56, 163–195.
Sakai, R. K., Fitzjarrald, D. R., Moore, K. E.: 2001, ‘Importance of fow-frequency contributions to eddy fluxes observed over rough surfaces’ J. Appl. Meteorol. 40, 2178–2192.
Schimel, D. S., Kittel, T. G. F. Running, S., Monson, R., Turnipseed, A., Anderson, D: 2002, ‘Carbon sequestration studied in western US mountains’, EOS 83, 445–449. item Van der Hoven, I.: 1957, ‘Power spectrum of horizontal wind speed in the frequency range from 0.0007 to 900 cycles per hour’ J. Meteorol. 14 160–164.
Van Dyke, 1978: Perturbation Methods in Fluid Mechanics, Parabolic Press, Stanford, pp 271.
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2004 Kluwer Academic Publishers
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Finnigan, J. (2004). Advection and Modeling. In: Lee, X., Massman, W., Law, B. (eds) Handbook of Micrometeorology. Atmospheric and Oceanographic Sciences Library, vol 29. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-2265-4_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-2265-4_10
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-1-4020-2264-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-4020-2265-4
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)