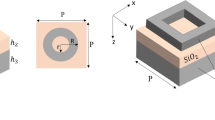
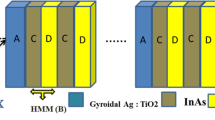
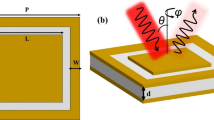
Abstract
This paper suggests a broadband nano-ring chromium metasurface absorbers model in the shape of a square hole and circle hole which covers an extensive wavelength spectrum by introducing an equivalent circuit. So as to confirm the proposed equivalent circuit method, metamaterial absorbers were simulated and detailed. The final results of the circuit model highly match the outcomes of full-wave numerical simulations done primarily based on the finite element method (FEM). Moreover, the circuit model reduces computation time and it needs less storage versus full-wave simulations. As a result, it is easier to investigate the effects of different parameters on the performance of the suggested devices and to determine the appropriate structures. Nano-ring chromium with a square-hole absorber registers a peak absorbance (i.e., more than 99.99%) at 448 nm and minimum absorption rate (i.e., 90.35%) at 580 nm. The Nano-ring chromium with circle hole absorber recorded a peak absorbance of more than 99% and higher than 98% absorbance from 430 to 552 nm and from 626 to 728 nm, respectively. The suggested approach is easy yet general. This method can be adopted to design and simulate other subwavelength structures in a wide frequency range, such as terahertz and visible light.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statements
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
References
S. L. Mortazavifar, M. R. Salehi, M. Shahraki, E. Abiri, Optimization of light absorption in ultrathin elliptical silicon nanowire arrays for solar cell applications. J. Mod. Opt. 69(7), 368–380 (2022)
S. L. Mortazavifar, M. R. Salehi, M. Shahraki, E. Abiri, Ultra-thin broadband solar absorber based on stadium-shaped silicon nanowire arrays. Front. Optoelectron. 15(1), 1–13 (2022)
S. L. Mortazavifar, M. R. Salehi, M. Shahraki, E. Abiri, Absorption improvement of a-Si/c-Si rectangular nanowire arrays in ultrathin solar cells. J. Photonics Energy 11(1), 014502 (2021)
M. Gil, J. Bonache, F. Martin, Metamaterial filters: a review. Metamaterials 2(4), 186–197 (2008)
Z. Wang, F. Cheng, T. Winsor, Y. Liu, Optical chiral metamaterials: a review of the fundamentals, fabrication methods and applications. Nanotechnology 27(41), 412001 (2016)
J. Sun, L. Liu, G. Dong, J. Zhou, An extremely broad band metamaterial absorber based on destructive interference. Opt. Express 19(22), 21155–21162 (2011)
B. Choudhury, R. Jha, A review of metamaterial invisibility cloaks. Comput. Mater. Continua 33(3), 275–303 (2013)
M.K. Hedayati, F. Faupel, M. Elbahri, Review of plasmonic nanocomposite metamaterial absorber. Materials 7(2), 1221–1248 (2014)
Y. Zhi Cheng, Y. Wang, Y. Nie, R. Zhou Gong, X. Xiong, X. Wang, Design, fabrication and measurement of a broadband polarization-insensitive metamaterial absorber based on lumped elements. J. Appl. Phys. 111(4), 044902 (2012)
V.J. Gokhale, O.A. Shenderova, G.E. McGuire, M. Rais-Zadeh, Infrared absorption properties of carbon nanotube/nanodiamond based thin film coatings. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 23(1), 191–197 (2013)
X. Duan, S. Chen, W. Liu, H. Cheng, Z. Li, J. Tian, Polarization-insensitive and wide-angle broadband nearly perfect absorber by tunable planar metamaterials in the visible regime. J. Opt. 16(12), 125107 (2014)
S. Ogawa, M. Kimata, Metal-insulator-metal-based plasmonic metamaterial absorbers at visible and infrared wavelengths: a review. Materials 11(3), 458 (2018)
Y. Liu, S. Gu, C. Luo, X. Zhao, Ultra-thin broadband metamaterial absorber. Appl. Phys. A 108(1), 19–24 (2012)
Q. Zhou et al., Optically transparent and flexible broadband microwave metamaterial absorber with sandwich structure. Appl. Phys. A 125(2), 1–8 (2019)
D. Shreiber et al., Tunable metamaterial device for THz applications based on BaSrTiO3 thin film. Thin Solid Films 660, 282–286 (2018)
B.-X. Wang, L.-L. Wang, G.-Z. Wang, W.-Q. Huang, X.-F. Li, X. Zhai, A broadband, polarisation-insensitive and wide-angle coplanar terahertz metamaterial absorber. Eur. Phys. J. B 87(4), 1–6 (2014)
H.T. Yudistira, K. Kananda, Design of wideband single-layer metamaterial absorber in the S-band and C-band spectrum. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 136(5), 1–7 (2021)
Z. Zhang et al., Broadband metamaterial absorber for low-frequency microwave absorption in the S-band and C-band. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 497, 166075 (2020)
Y. Lee, S.-J. Kim, H. Park, B. Lee, Metamaterials and metasurfaces for sensor applications. Sensors 17(8), 1726 (2017)
J. Zhao, Y. Cheng, Ultrabroadband microwave metamaterial absorber based on electric SRR loaded with lumped resistors. J. Electron. Mater. 45(10), 5033–5039 (2016)
W. Wang, A.V. Amirkhizi, Exceptional points and scattering of discrete mechanical metamaterials. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 137(4), 1–15 (2022)
P. Singh, S.K. Ameri, L. Chao, M.N. Afsar, S. Sonkusale, Broadband millimeterwave metamaterial absorber based on embedding of dual resonators. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 142, 625–638 (2013)
A. Sellier, T.V. Teperik, A. de Lustrac, Resonant circuit model for efficient metamaterial absorber. Opt. Express 21(106), A997–A1006 (2013)
H. Heidari, A. Afifi, Design and fabrication of an energy-harvesting device using vibration absorber. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 132(5), 1–11 (2017)
V. Dave, V. Sorathiya, T. Guo, S.K. Patel, Graphene based tunable broadband far-infrared absorber. Superlattices Microstruct. 124, 113–120 (2018)
M. Zhang, J.T. Yeow, Nanotechnology-based terahertz biological sensing: a review of its current state and things to come. IEEE Nanatechnol. Mag. 10(3), 30–38 (2016)
E. Zarepour, M. Hassan, C.T. Chou, A.A. Adesina, Energy-harvesting nanosensor networks: efficient event detection. IEEE Nanatechnol. Mag. 10(4), 4–12 (2016)
S. Behura et al., WS2\/Silicon heterojunction solar cells: a CVD process for the fabrication of WS2 Films on p-Si substrates for photovoltaic and spectral responses. IEEE Nanatechnol. Mag. 11(2), 33–38 (2017)
C.M. Watts, X. Liu, W.J. Padilla, Metamaterial electromagnetic wave absorbers. Adv. Mater. 24(23), OP98–OP120 (2012)
Y. Li et al., Wideband radar cross section reduction using two-dimensional phase gradient metasurfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 104(22), 221110 (2014)
C. Cao, Y. Cheng, A broadband plasmonic light absorber based on a tungsten meander-ring-resonator in visible region. Appl. Phys. A 125(1), 1–8 (2019)
N. Yu, F. Capasso, Flat optics with designer metasurfaces. Nat. Mater. 13(2), 139–150 (2014)
H.-L. Huang, H. Xia, Z.-B. Guo, D. Xie, H.-J. Li, Design of broadband metamaterial absorbers for permittivity sensitivity and solar cell application. Chin. Phys. Lett. 34(11), 117801 (2017)
J.A. Bossard, L. Lin, S. Yun, L. Liu, D.H. Werner, T.S. Mayer, Near-ideal optical metamaterial absorbers with super-octave bandwidth. ACS Nano 8(2), 1517–1524 (2014)
H. Deng et al., Broadband perfect absorber based on one ultrathin layer of refractory metal. Opt. Lett. 40(11), 2592–2595 (2015)
I. Kim, S. So, A.S. Rana, M.Q. Mehmood, J. Rho, Thermally robust ring-shaped chromium perfect absorber of visible light. Nanophotonics 7(11), 1827–1833 (2018)
Q. Wang et al., Design, fabrication, and modulation of THz bandpass metamaterials. Laser Photonics Rev. 13(11), 1900071 (2019)
K. Mohamed, 2.16 Nanoimprint Lithography for Nanomanufacturing, in Comprehensive Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2nd edn., (Academic Press, Oxford, 2019), pp. 357–386.
R.T. Ako, A. Upadhyay, W. Withayachumnankul, M. Bhaskaran, S. Sriram, Dielectrics for terahertz metasurfaces: material selection and fabrication techniques. Adv. Opt. Mater. 8(3), 1900750 (2020)
J.B. Khurgin, A. Boltasseva, Reflecting upon the losses in plasmonics and metamaterials. MRS Bull. 37(8), 768–779 (2012)
N. W. Ashcroft, N. D. Mermin, Solid state physics, in Holt, Rinehart and Winston, (New york London, 1976)
J.-S.G. Bouillard, W. Dickson, D.P. O’Connor, G.A. Wurtz, A.V. Zayats, Low-temperature plasmonics of metallic nanostructures. Nano Lett. 12(3), 1561–1565 (2012)
R. Cohen, G. Cody, M. Coutts, B. Abeles, Optical properties of granular silver and gold films. Phys. Rev. B 8(8), 3689 (1973)
B. Kramer, Advances in solid state physics (Springer, Berlin, 2007)
O. Heavens, Optical properties of thin films. Rep. Prog. Phys. 23(1), 1 (1960)
L. Kazmerski, D.M. Racine, Growth, environmental, and electrical properties of ultrathin metal films. J. Appl. Phys. 46(2), 791–795 (1975)
P. Clegg, The optical constants of thin metallic films deposited by evaporation. Proc. Phys. Soc. Sect. B 65(10), 774 (1952)
K.H. Park, J.S. Ha, E.H. Lee, Uniform Ag thin film growth on an Sb-terminated Si (111) Surface. ETRI J. 19(2), 71–81 (1997)
V. Logeeswaran et al., Ultra-smooth metal surfaces generated by pressure-induced surface deformation of thin metal films. Appl. Phys. A 87(2), 187–192 (2007)
W. Chen, M.D. Thoreson, S. Ishii, A.V. Kildishev, V.M. Shalaev, Ultra-thin ultra-smooth and low-loss silver films on a germanium wetting layer. Opt. Express 18(5), 5124–5134 (2010)
D. Pashley, The preparation of smooth single crystal surfaces of silver by an evaporation technique. Phil. Mag. 4(39), 316–323 (1959)
P. Palmberg, T. Rhodin, C. Todd, Epitaxial growth of gold and silver on magnesium oxide cleaved in ultrahigh vacuum. Appl. Phys. Lett. 11(2), 33–35 (1967)
W. Kraus, G.C. Schatz, Plasmon resonance broadening in small metal particles. J. Chem. Phys. 79(12), 6130–6139 (1983)
H. Hövel, S. Fritz, A. Hilger, U. Kreibig, M. Vollmer, Width of cluster plasmon resonances: bulk dielectric functions and chemical interface damping. Phys. Rev. B 48(24), 18178 (1993)
V.P. Drachev, U.K. Chettiar, A.V. Kildishev, H.-K. Yuan, W. Cai, V.M. Shalaev, The Ag dielectric function in plasmonic metamaterials. Opt. Express 16(2), 1186–1195 (2008)
D. Smith, D. Vier, T. Koschny, C. Soukoulis, Electromagnetic parameter retrieval from inhomogeneous metamaterials. Phys. Rev. E 71(3), 036617 (2005)
D.M. Pozar, Microwave engineering (Wiley, New York, 2011)
G. Shen, M. Zhang, Y. Ji, W. Huang, H. Yu, J. Shi, Broadband terahertz metamaterial absorber based on simple multi-ring structures. AIP Adv. 8(7), 075206 (2018)
J.-Y. Jung et al., Infrared broadband metasurface absorber for reducing the thermal mass of a microbolometer. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 1–8 (2017)
A.K. Azad et al., Metasurface broadband solar absorber. Sci. Rep. 6(1), 1–6 (2016)
Z.H. Jiang et al., Broadband and wide field-of-view plasmonic metasurface-enabled waveplates. Sci. Rep. 4(1), 1–8 (2014)
D. Katrodiya, C. Jani, V. Sorathiya, S.K. Patel, Metasurface based broadband solar absorber. Opt. Mater. 89, 34–41 (2019)
W. Li et al., Refractory plasmonics with titanium nitride: broadband metamaterial absorber. Adv. Mater. 26(47), 7959–7965 (2014)
E.D. Palik, Handbook of optical constants of solids (Academic press, Cambridge, 1998)
W.L. Barnes, Surface plasmon–polariton length scales: a route to sub-wavelength optics. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Opt. 8(4), S87 (2006)
M. Olsen et al., A high-temperature, high-efficiency solar thermoelectric generator prototype. Energy Procedia 49, 1460–1469 (2014)
M. Lobet, M. Lard, M. Sarrazin, O. Deparis, L. Henrard, Plasmon hybridization in pyramidal metamaterials: a route towards ultra-broadband absorption. Opt. Express 22(10), 12678–12690 (2014)
D. Ji et al., Broadband absorption engineering of hyperbolic metafilm patterns. Sci. Rep. 4(1), 1–7 (2014)
S. Mahmud, S.S. Islam, K. Mat, M.E. Chowdhury, H. Rmili, M.T. Islam, Design and parametric analysis of a wide-angle polarization-insensitive metamaterial absorber with a star shape resonator for optical wavelength applications. Results Phys. 18, 103259 (2020)
M.L. Hakim et al., Wide-oblique-incident-angle stable polarization-insensitive ultra-wideband metamaterial perfect absorber for visible optical wavelength applications. Materials 15(6), 2201 (2022)
X. Zhang, Y. Fan, L. Qi, H. Li, Broadband plasmonic metamaterial absorber with fish-scale structure at visible frequencies. Opt. Mater. Express 6(7), 2448–2457 (2016)
D. Hu, H.-Y. Wang, Q.-F. Zhu, Design of an ultra-broadband and polarization-insensitive solar absorber using a circular-shaped ring resonator. J. Nanophotonics 10(2), 026021 (2016)
P. Wu, C. Zhang, Y. Tang, B. Liu, L. Lv, A perfect absorber based on similar fabry-perot four-band in the visible range. Nanomaterials 10(3), 488 (2020)
F. Xu et al., Broadband Solar Absorber Based on Square Ring cross Arrays of ZnS. Micromachines 12(8), 909 (2021)
Funding
No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors (L. Mortazavifar, M. Salehi, M. Shahraki) contributed equally to the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We have no conflict of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mortazavifar, S.L., Salehi, M.R. & Shahraki, M. Ultrathin nano-ring metasurface absorber in visible regime based on circuit model. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 137, 1072 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-03272-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-03272-8