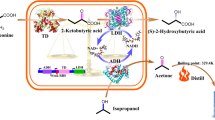
Abstract
The study investigated the enhanced production of 2-hydroxybutyric acid (2-HBA) from threonine using a two-step whole-cell bioconversion by recombinant Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) overexpressing threonine dehydratase and keto-reductase. To address the rate-limiting step posed by NADH regeneration for the keto-reductase reaction converting 2-ketobutyric acid (2-KBA) to 2-HBA, formate dehydrogenase from Candida boidinii was overexpressed under the T7 promoter, resulting in a high titer of 1015 mM and a yield of 0.70 mol/mol. Furthermore, the yield was improved by disrupting three enzymes responsible for the degradation of the intermediate (2-KBA), pyruvate-formate lyase (PflB), pyruvate oxidase (PoxB), and pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDHc), leading to an impressive yield of 0.99 mol/mol, closely approaching the theoretical maximum of 1.00 mol/mol. The triple mutant, designed to prevent 2-KBA degradation, achieved a remarkable titer of 1,400 mM and volumetric productivity of 58 mmol/L/h. To the best of our knowledge, this achievement represents the highest reported titer and yield for 2-HBA production to date.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yamazaki Y, Araki T, Koura M, Shibuya K. Enantioselective synthesis of the PPARa Agonist (R)-K-13675 via (S)-2-hydroxybutyrolactone. Synthesis. 2008;7:1017–22.
Matsumoto K, Terai S, Ishiyama A, Sun J, Kabe T, Song Y, et al. One-pot microbial production, mechanical properties, and enzymatic degradation of isotactic P[( R )-2-hydroxybutyrate] and its copolymer with ( R )-lactate. Biomacromol. 2013;14:1913–8. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm400278j.
Park SJ, Lee TW, Lim S-C, Kim TW, Lee H, Kim MK, et al. Biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates containing 2-hydroxybutyrate from unrelated carbon source by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012;93:273–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3530-x.
Sudo M, Hori C, Ooi T, Mizuno S, Tsuge T, Matsumoto K. Synergy of valine and threonine supplementation on poly(2-hydroxybutyrate-block-3-hydroxybutyrate) synthesis in engineered Escherichia coli expressing chimeric polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase. J Biosci Bioeng. 2020;129:302–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2019.09.018.
Ferrannini E, Natali A, Camastra S, Nannipieri M, Mari A, Adam K-P, et al. Early metabolic markers of the development of dysglycemia and type 2 diabetes and their physiological significance. Diabetes. 2013;62:1730–7. https://doi.org/10.2337/db12-0707.
Gall WE, Beebe K, Lawton KA, Adam K-P, Mitchell MW, Nakhle PJ, et al. α-Hydroxybutyrate is an early biomarker of insulin resistance and glucose intolerance in a nondiabetic population. PLoS ONE. 2010;5: e10883. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0010883.
Sousa AP, Cunha DM, Franco C, Teixeira C, Gojon F, Baylina P, et al. Which role plays 2-hydroxybutyric acid on insulin resistance? Metabolites. 2021;11:835. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11120835.
Kondo S, Hotta K. Semisynthetic aminoglycoside antibiotics: development and enzymatic modifications. J Infect Chemother. 1999;5:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s101560050001.
Zheng N, Gu Y, Hong Y, Sheng L, Chen L, Zhang F, et al. Vancomycin pretreatment attenuates acetaminophen-induced liver injury through 2-hydroxybutyric acid. J Pharm Anal. 2020;10:560–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2019.11.003.
Tsuji H, Okumura A. Stereocomplex formation between enantiomeric substituted poly(lactide)s: blends of poly[(S)-2-hydroxybutyrate] and poly[(R)-2-hydroxybutyrate]. Macromolecules. 2009;42:7263–6. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma9015483.
Chen X, Wu Q, Zhu D. Enzymatic synthesis of chiral 2-hydroxy carboxylic acids. Process Biochem. 2015;50:759–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2015.01.027.
Gao C, Zhang W, Ma C, Liu P, Xu P. Kinetic resolution of 2-hydroxybutanoate racemic mixtures by NAD-independent l-lactate dehydrogenase. Bioresour Technol. 2011;102:4595–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.01.003.
Le T, Park S. Development of efficient microbial cell factory for whole-cell bioconversion of l-threonine to 2-hydroxybutyric acid. Bioresour Technol. 2022;344: 126090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126090.
Tian L, Zhou J, Yang T, Zhang X, Xu M, Rao Z. Cascade biocatalysis for production of enantiopure (S)-2-hydroxybutyric acid using recombinant Escherichia coli with a tunable multi-enzyme-coordinate expression system. Syst Microbiol Biomanuf. 2021;1:234–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43393-020-00021-9.
Yao P, Cui Y, Yu S, Du Y, Feng J, Wu Q, et al. Efficient biosynthesis of (R)- or (S)-2-hydroxybutyrate from l-threonine through a synthetic biology approach. Adv Synth Catal. 2016;358:2923–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.201600468.
Link AJ, Phillips D, Church GM. Methods for generating precise deletions and insertions in the genome of wild-type Escherichia coli: application to open reading frame characterization. J Bacteriol. 1997;179:6228–37. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.179.20.6228-6237.1997.
Stephens PE, Lewis HM, Darlison MG, Guest JR. Nucleotide sequence of the lipoamide dehydrogenase gene of Escherichia coli K12. Eur J Biochem. 1983;135:519–27. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07683.x.
Sumantran VN, Schweizer HP, Datta P. A novel membrane-associated threonine permease encoded by the tdcC gene of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990;172:4288–94. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.172.8.4288-4294.1990.
Khozov AA, Bubnov DM, Plisov ED, Vybornaya TV, Yuzbashev TV, Agrimi G, et al. A study on l-threonine and l-serine uptake in Escherichia coli K-12. Front Microbiol. 2023;14:1151716. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2023.1151716.
Simic P, Sahm H, Eggeling L. l -Threonine Export: Use of Peptides To Identify a New Translocator from Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Bacteriol. 2001;183:5317–24. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.183.18.5317-5324.2001.
Wang Y, Huang Y, Wang J, Cheng C, Huang W, Lu P, et al. Structure of the formate transporter FocA reveals a pentameric aquaporin-like channel. Nature. 2009;462:467–72. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08610.
Wang S, Fang Y, Wang Z, Zhang S, Wang L, Guo Y, et al. Improving l-threonine production in Escherichia coli by elimination of transporters ProP and ProVWX. Microb Cell Factories. 2021;20:58. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-021-01546-x.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (No. NRF-2020R1A5A1019631).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Thai Le: conceptualization, experimentation, data curation. Bassey Friday Bassey: conceptualization, experimentation, data curation and visualization, writing—original draft. Thuan Phu Nguyen-Vo: conceptualization, experimentation, data curation and visualization. Sunghoon Park: conceptualization, funding acquisition, supervision, validation, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationships that could appear to influence the work reported in this paper.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Le, T., Bassey, B.F., Nguyen-Vo, T.P. et al. Achieving high titer and yield in the bioconversion of l-threonine to 2-hydroxybutyric acid with Escherichia coli BL21. Syst Microbiol and Biomanuf 4, 708–715 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43393-023-00224-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43393-023-00224-w