Abstract
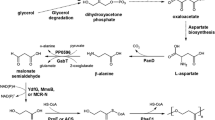
We have previously reported in vivo biosynthesis of polylactic acid (PLA) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-lactate) [P(3HB-co-LA)] employing metabolically engineered Escherichia coli strains by the introduction of evolved Clostridium propionicum propionyl-CoA transferase (Pct Cp ) and Pseudomonas sp. MBEL 6-19 polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) synthase 1 (PhaC1 Ps6-19). Using this in vivo PLA biosynthesis system, we presently report the biosynthesis of PHAs containing 2-hydroxybutyrate (2HB) monomer by direct fermentation of a metabolically engineered E. coli strain. The recombinant E. coli ldhA mutant XLdh strain expressing PhaC1 Ps6-19 and Pct Cp was developed and cultured in a chemically defined medium containing 20 g/L of glucose and varying concentrations of 2HB and 3HB. PHAs consisting of 2HB, 3HB, and a small fraction of lactate were synthesized. Their monomer compositions were dependent on the concentrations of 2HB and 3HB added to the culture medium. Even though the ldhA gene was completely deleted in the chromosome of E. coli, up to 6 mol% of lactate was found to be incorporated into the polymer depending on the culture condition. In order to synthesize PHAs containing 2HB monomer without feeding 2HB into the culture medium, a heterologous metabolic pathway for the generation of 2HB from glucose was constructed via the citramalate pathway, in which 2-ketobutyrate is synthesized directly from pyruvate and acetyl-CoA. Introduction of the Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis Il1403 2HB dehydrogenase gene (panE) into E. coli allowed in vivo conversion of 2-ketobutyrate to 2HB. The metabolically engineered E. coli XLdh strain expressing the phaC1437, pct540, cimA3.7, and leuBCD genes together with the L. lactis Il1403 panE gene successfully produced PHAs consisting of 2HB, 3HB, and a small fraction of lactate by varying the 3HB concentration in the culture medium. As the 3HB concentration in the medium increased the 3HB monomer fraction in the polymer, the polymer content increased. When Ralstonia eutropha phaAB genes were additionally expressed in this recombinant E. coli XLdh strain, P(2HB-co-3HB-co-LA) having small amounts of 2HB and LA monomers could also be produced from glucose as a sole carbon source. The metabolic engineering strategy reported here should be useful for the production of PHAs containing 2HB monomer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atsumi S, Hanai T, Liao JC (2008) Non-fermentative pathways for synthesis of branched-chain higher alcohols as biofuels. Nature 451:86–89
Atsumi S, Liao JC (2008a) Directed evolution of Methanococcus jannaschii citramalate synthase for biosynthesis of 1-propanol and 1-butanol by Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:7802–7808
Atsumi S, Liao JC (2008b) Metabolic engineering for advanced biofuels production from Escherichia coli. Curr Opin Biotechnol 19:414–419
Bernard N, Johnsen K, Ferain T, Garmyn D, Hols P, Holbrook JJ, Delcour J (1994) NAD(+)-dependent d-2-hydroxyisocaproate dehydrogenase of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus. Gene cloning and enzyme characterization. Eur J Biochem 224:439–446
Braunegg G, Sonnleitner B, Lafferty RM (1978) A rapid gas chromatographic method for the determination of poly-β-hydroxybutyric acid in microbial biomass. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 6:29–37
Chambellon E, Rijnen L, Lorquet F, Gitton C, van Hylckama Vlieg JE, Wouters JA, Yvon M (2009) The D-2-hydroxyacid dehydrogenase incorrectly annotated PanE is the sole reduction system for branched-chain 2-keto acids in Lactococcus lactis. J Bacteriol 191:873–881
Datsenko KA, Wanner BL (2000) One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:6640–6645
Fukui T, Yokomizo S, Kobayashi G, Doi Y (1999) Co-expression of polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase and (R)-enoyl-CoA hydratase genes of Aeromonas caviae establishes copolyester biosynthesis pathway in Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett 170:69–75
Han X, Satoh Y, Satoh T, Matsumoto K, Kakuchi T, Taguchi S, Dairi T, Munekata M, Tajima K (2011) Chemo-enzymatic synthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) incorporating 2-hydroxybutyrate by wild-type class I PHAsynthase from Ralstonia eutropha. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. doi:10.1007/s00253-011-3362-8
Hein S, Sohling B, Gottschalk G, Steinbüchel A (1997) Biosynthesis of poly(4-hydroxybutyric acid) by recombinant strains of Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett 153:411–418
Hong SH, Lee SY (2001) Metabolic flux analysis for succinic acid production by recombinant Escherichia coli with amplified malic enzyme activity. Biotechnol Bioeng 74:89–95
Jacquel N, Lo CW, Wei YH, Wu HS, Wang SS (2008) Isolation and purification of bacterial poly (3-hydroxyalkanoates). Biochem Eng J 39:15–27
Jung YK, Kim TY, Park SJ, Lee SY (2010) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of polylactic acid and its copolymers. Biotechnol Bioeng 105:161–171
Jung YK, Lee SY (2011) Efficient production of polylactic acid and its copolymers by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 151:94–101
Kim J, Darley D, Buckel W (2005) 2-Hydroxyisocaproyl-CoA dehydratase and its activator from Clostridium difficile. FEBS J 272:550–561
Kovach ME, Elzer PH, Hill DS, Robertson GT, Farris MA, Roop RM II, Peterson KM (1995) Four new derivatives of the broad-host-range cloning vector pBBR1MCS, carrying different antibiotic-resistance cassettes. Gene 166:175–176
Lee SH, Park SJ, Lee SY, Hong SH (2008) Biosynthesis of enantiopure (S)-3-hydroxybutyric acid in metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79:633–641
Lee SY (1996) Bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Biotechnol Bioeng 49:1–14
Lim SC, Kim SW, Jung MH, Cho MK, Kim JH, Cho HS, Ok JH (2008) Complete NMR spectral assignments of siloxanol based copolycarbonate including the configurational copolymer structure and the determination of each monomer conversion. J Mol Struct 886:166–174
Liu SJ, Steinbüchel A (2000) A novel genetically engineered pathway for synthesis of poly(hydroxyalkanoic acids) in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:739–743
Liu T, Simmons TL, Bohnsack DA, Mackay ME, Smith MR, Baker GL (2007) Synthesis of polymandelide: a degradable polylactide derivative with polystyrene-like properties. Macromolecules 40:6040–6047
Lütke-Eversloh T, Fischer A, Remminghorst U, Kawada J, Marchessault RH, Bögershausen A, Kalwei M, Eckert H, Reichelt R, Liu SJ, Steinbüchel A (2002) Biosynthesis of novel thermoplastic polythioesters by engineered Escherichia coli. Nat Mater 1:236–240
Madison LL, Huisman GW (1999) Metabolic engineering of poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates): from DNA to plastic. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63:21–53
Park SJ, Choi J, Lee SY (2005) Engineering of Escherichia coli fatty acid metabolism for the production of polyhydroxyalkanoates. Enzyme Microb Technol 36:579–588
Park SJ, Yang TH, Kang HO, Lee EJ, Lee SH, Kim TW, Lee SY (2008a) Copolymer containing 3-hydroxyalkanoate unit and lactate unit, and its manufacturing method. WO08/062996
Park SJ, Yang TH, Kang HO, Lee EJ, Lee SH, Kim TW, Lee SY (2008b) Copolymer containing 4-hydroxybutyrate unit and lactate unit, and its manufacturing method. WO08/062995
Rasal RM, Janorkar AV, Hirt DE (2010) Poly(lactic acid) modifications. Prog Polym Sci 35:338–356
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning—A laboratory manual. 3rd edn. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press
Shen CR, Liao JC (2008) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for 1-butanol and 1-propanol production via the keto-acid pathways. Metab Eng 10:312–320
Shozui F, Matsumoto K, Nakai T, Yamada M, Taguchi S (2010) Biosynthesis of novel terpolymers poly(lactate-co-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)s in lactate-overproducing mutant Escherichia coli JW0885 by feeding propionate as a precursor of 3-hydroxyvalerate. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:949–954
Simmons TL, Baker GL (2001) Poly(phenyllactide): synthesis, characterization, and hydrolytic degradation. Biomacromolecules 2:658–663
Taguchi S, Yamada M, Matsumoto K, Tajima K, Satoh Y, Munekata M, Ohno K, Kohda K, Shimamura T, Kambe H, Obata S (2008) A microbial factory for lactate-based polyesters using a lactate-polymerizing enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:17323–17327
Tsuji H, Okumura A (2009) Stereocomplex formation between enantiomeric substituted poly(lactide)s: blends of poly[(S)-2-hydroxybutyrate] and poly[(R)-2-hydroxybutyrate]. Macromolecules 42:7263–7266
Valentin HE, Mitsky TA, Mahadeo DA, Tran M, Gruys KJ (2000) Application of a propionyl coenzyme A synthetase for poly(3-hydroxypropionate-co-3-hydroxybutyrate) accumulation in recombinant Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:5253–5258
Yamada M, Matsumoto K, Nakai T, Taguchi S (2009) Microbial production of lactate-enriched poly[(R)-lactate-co-(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate] with novel thermal properties. Biomacromolecules 10:677–681
Yamada M, Matsumoto K, Shimizu K, Uramoto S, Nakai T, Shozui F, Taguchi S (2010) Adjustable mutations in lactate (LA)-polymerizing enzyme for the microbial production of LA-based polyesters with tailor-made monomer composition. Biomacromolecules 11:815–819
Yamada M, Matsumoto K, Uramoto S, Motohashi R, Abe H, Taguchi S (2011) Lactate fraction dependent mechanical properties of semitransparent poly(lactate-co-3-hydroxybutyrate)s produced by control of lactyl-CoA monomer fluxes in recombinant Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2011.05.011
Yang TH, Kim TW, Kang HO, Lee SH, Lee EJ, Lim SC, Oh SO, Song AJ, Park SJ, Lee SY (2010) Biosynthesis of polylactic acid and its copolymers using evolved propionate CoA transferase and PHA synthase. Biotechnol Bioeng 105:150–160
Yang TH, Jung YK, Kang HO, Kim TW, Park SJ, Lee SY (2011) Tailor-made type II Pseudomonas PHA synthases and their use for the biosynthesis of polylactic acid and its copolymer in recombinant Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90:603–614
Yuan W, Jia Y, Tian J, Snell KD, Muh U, Sinskey AJ, Lambalot RH, Walsh CT, Stubbe J (2001) Class I and III polyhydroxyalkanoate synthases from Ralstonia eutropha and Allochromatium vinosum: characterization and substrate specificity studies. Arch Biochem Biophys 394:87–98
Zhang S, Kamachi M, Takagi Y, Lenz RW, Goodwin S (2001) Comparative study of the relationship between monomer structure and reactivity for two polyhydroxyalkanoate synthases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56:131–136
Zhang X, Jantama K, Shanmugam KT, Ingram LO (2009) Reengineering Escherichia coli for succinate production in mineral salts medium. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7807–7813
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Korean Systems Biology Research Project (20090065571) of the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (MEST) through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea. Further support by World Class University program (R32-2008-000-10142-0) and by the Advanced Biomass R&D Center of Korea (ABC-2010-0029799) through the Global Frontier Research Program of MEST is appreciated. B.K.S, S.H.L, and S.J.P appreciate the financial supports from the R&D Program of MKE/KEIT (10032001) and KRICT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, S.J., Lee, T.W., Lim, SC. et al. Biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates containing 2-hydroxybutyrate from unrelated carbon source by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93, 273–283 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3530-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3530-x