Abstract
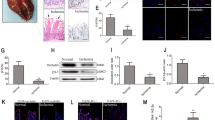
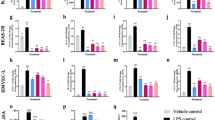
The apoptosis and inflammation of pulmonary epithelial cells are important pathogenic factors of sepsis-induced acute lung injury (ALI). Upregulation of circPalm2 (circ_0001212) expression levels has been previously detected in the lung tissue of ALI rats. Herein, the biological significance and detailed mechanism of circPalm2 in ALI pathogenesis were investigated. In vivo models of sepsis-induced ALI were established by treating C57BL/6 mice with cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) surgery. Murine pulmonary epithelial cells (MLE-12 cells) were stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to establish in vitro septic ALI models. MLE-12 cell viability and apoptosis were evaluated by CCK-8 assay and flow cytometry analysis, respectively. The pathological alterations of the lung tissue were analysed based on hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) staining. Cell apoptosis in the lung tissue samples was examined by TUNEL staining assay. LPS administration suppressed the viability and accelerated the inflammation and apoptotic behaviours of MLE-12 cells. CircPalm2 displayed high expression in LPS-stimulated MLE-12 cells and possessed circular characteristics. The silencing of circPalm2 impeded apoptosis and inflammation in LPS-stimulated MLE-12 cells. Mechanistically, circPalm2 bound with miR-376b-3p, which targeted MAP3K1. In rescue assays, MAP3K1 enhancement reversed the repressive effects of circPalm2 depletion on LPS-triggered inflammatory injury and MLE-12 cell apoptosis. Furthermore, the lung tissue collected from CLP model mice displayed low miR-376b-3p expression and high levels of circPalm2 and MAP3K1. CircPalm2 positively regulated MAP3K1 expression by downregulating miR-376b-3p in murine lung tissues. Importantly, circPalm2 knockdown attenuated CLP-induced inflammation, apoptosis, and pathological alterations in lung tissues collected from mice. Silenced circPalm2 inhibits LPS-induced pulmonary epithelial cell dysfunction and mitigates abnormalities in lung tissues collected from CLP-stimulated mice via the miR-376b-3p/MAP3K1 axis in septic ALI.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Uhle F, Lichtenstern C, Brenner T, Weigand MA (2015) [Pathophysiology of sepsis]. Anasthesiol Intensivmed Notfallmed Schmerzther 50:114–122. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0041-100391
Napolitano LM (2018) Sepsis 2018: definitions and guideline changes. Surg Infect (Larchmt) 19:117–125. https://doi.org/10.1089/sur.2017.278
Aziz M, Ode Y, Zhou M, Ochani M, Holodick NE, Rothstein TL, Wang P (2018) B-1a cells protect mice from sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Mol Med 24:26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10020-018-0029-2
Li R, Ren T, Zeng J (2019) Mitochondrial coenzyme Q protects sepsis-induced acute lung injury by activating PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β/mTOR pathway in rats. Biomed Res Int 2019:5240898. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5240898
Park I, Kim M, Choe K, Song E, Seo H, Hwang Y, Ahn J, Lee SH, Lee JH, Jo YH, Kim K, Koh GY, Kim P (2019) Neutrophils disturb pulmonary microcirculation in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Eur Respir J 53:1800786. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.00786-2018
Ling L, Tong J, Zeng L (2020) [Paeoniflorin improves Acute Lung Injury in Sepsis by activating Nrf2/Keap1 signaling pathway]. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 51:664–669. https://doi.org/10.12182/20200960201
Xu Q, Wang J (2020) IGFBP7 aggravates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by activating the ERK1/2 pathway. Folia Histochem Cytobiol 58:247–254. https://doi.org/10.5603/FHC.a2020.0028
Martin TR, Nakamura M, Matute-Bello G (2003) The role of apoptosis in acute lung injury. Crit Care Med 31:S184–S188. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.Ccm.0000057841.33876.B1
Parsons PE, Eisner MD, Thompson BT, Matthay MA, Ancukiewicz M, Bernard GR, Wheeler AP (2005) Lower tidal volume ventilation and plasma cytokine markers of inflammation in patients with acute lung injury. Crit Care Med 33:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ccm.0000149854.61192.dc
Meduri GU, Kohler G, Headley S, Tolley E, Stentz F, Postlethwaite A (1995) Inflammatory cytokines in the BAL of patients with ARDS. Persistent elevation over time predicts poor outcome. Chest 108:1303–1314. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.108.5.1303
Patop IL, Wüst S, Kadener S (2019) Past, present, and future of circRNAs. EMBO J 38:e100836. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2018100836
Yu T, Wang Y, Fan Y, Fang N, Wang T, Xu T, Shu Y (2019) CircRNAs in cancer metabolism: a review. J Hematol Oncol 12:90. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-019-0776-8
Altesha MA, Ni T, Khan A, Liu K, Zheng X (2019) Circular RNA in cardiovascular disease. J Cell Physiol 234:5588–5600. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27384
Cao Q, Guo Z, Du S, Ling H, Song C (2020) Circular RNAs in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Life Sci 255:117837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117837
Beltrán-García J, Osca-Verdegal R, Nacher-Sendra E, Pallardó FV, García-Giménez JL (2020) Circular RNAs in sepsis: biogenesis, function, and clinical significance. Cells 9:1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061544
Zang J, Lu D, Xu A (2020) The interaction of circRNAs and RNA binding proteins: an important part of circRNA maintenance and function. J Neurosci Res 98:87–97. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.24356
Yuan C, Gu J, Wu J, Yin J, Zhang M, Miao H, Li J (2020) Circular RNA expression in the lungs of a mouse model of sepsis induced by cecal ligation and puncture. Heliyon 6:e04532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04532
Yang CL, Yang WK, He ZH, Guo JH, Yang XG, Li HB (2021) Quietness of circular RNA circ_0054633 alleviates the inflammation and proliferation in lipopolysaccharides-induced acute lung injury model through NF-κB signaling pathway. Gene 766:145153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2020.145153
Bao X, Zhang Q, Liu N, Zhuang S, Li Z, Meng Q, Sun H, Bai J, Zhou X, Tang L (2019) Characteristics of circular RNA expression of pulmonary macrophages in mice with sepsis-induced acute lung injury. J Cell Mol Med 23:7111–7115. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14577
Ma K, Wang W, Gao C, He J (2021) The role of circTMOD3 in regulating LPS-induced acute inflammation and injury in human lung fibroblast WI-38 cells. Exp Lung Res 47:311–322. https://doi.org/10.1080/01902148.2021.1940376
Zou Z, Wang Q, Zhou M, Li W, Zheng Y, Li F, Zheng S, He Z (2020) Protective effects of P2X7R antagonist in sepsis-induced acute lung injury in mice via regulation of circ_0001679 and circ_0001212 and downstream pln, Cdh2, and Nprl3 expression. J Gene Med 22:e3261. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgm.3261
Chen LL (2020) The expanding regulatory mechanisms and cellular functions of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 21:475–490. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-020-0243-y
Zhu J, Zhang X, Gao W, Hu H, Wang X, Hao D (2019) lncRNA/circRNA–miRNA–mRNA ceRNA network in lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Mol Med Rep 20:3160–3174. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.10569
Correia de Sousa M, Gjorgjieva M, Dolicka D, Sobolewski C, Foti M (2019) Deciphering miRNAs’ action through miRNA editing. Int J Mol Sci 20:6249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20246249
Jiang WY, Ren J, Zhang XH, Lu ZL, Feng HJ, Yao XL, Li DH, Xiong R, Fan T, Geng Q (2020) CircC3P1 attenuated pro-inflammatory cytokine production and cell apoptosis in acute lung injury induced by sepsis through modulating miR-21. J Cell Mol Med 24:11221–11229. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15685
Zhao D, Wang C, Liu X, Liu N, Zhuang S, Zhang Q, Bao X, Xu S, Zhou X, Meng Q, Li S, Tang L (2021) CircN4bp1 facilitates sepsis-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome through mediating macrophage polarization via the miR-138-5p/EZH2 axis. Mediators Inflamm 2021:7858746. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/7858746
Lin Q, Liang Q, Qin C, Li Y (2021) CircANKRD36 Knockdown suppressed cell viability and migration of LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells by sponging MiR-330. Inflammation 44:2044–2053. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-021-01480-5
Ji Q, Sun Z, Yang Z, Zhang W, Ren Y, Chen W, Yao M, Nie S (2021) Protective effect of ginsenoside Rg1 on LPS-induced apoptosis of lung epithelial cells. Mol Immunol 136:168–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2018.11.003
Lipner MB, Peng XL, Jin C, Xu Y, Gao Y, East MP, Rashid NU, Moffitt RA, Herrera Loeza SG, Morrison AB, Golitz BT, Vaziri C, Graves LM, Johnson GL, Yeh JJ (2020) Irreversible JNK1-JUN inhibition by JNK-IN-8 sensitizes pancreatic cancer to 5-FU/FOLFOX chemotherapy. JCI Insight 5:2. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.129905
Sun H, Hu H, Xu X, Fang M, Tao T, Liang Z (2021) Protective effect of dexmedetomidine in cecal ligation perforation-induced acute lung injury through HMGB1/RAGE pathway regulation and pyroptosis activation. Bioengineered 12:10608–10623. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2021.2000723
Zhang J, Zheng Y, Wang Y, Wang J, Sang A, Song X, Li X (2022) YAP1 alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting ferritinophagy-mediated ferroptosis. Front Immunol 13:884362. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.884362
Qiu N, Xu X, He Y (2020) LncRNA TUG1 alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by targeting miR-34b-5p/GAB1. BMC Pulm Med 20:49. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-020-1084-3
Matute-Bello G, Downey G, Moore BB, Groshong SD, Matthay MA, Slutsky AS, Kuebler WM (2011) An official american thoracic society workshop report: features and measurements of experimental acute lung injury in animals. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 44:725–738. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2009-0210ST
Nagura-Ikeda M, Imai K, Tabata S, Miyoshi K, Murahara N, Mizuno T, Horiuchi M, Kato K, Imoto Y, Iwata M, Mimura S, Ito T, Tamura K, Kato Y (2020) Clinical evaluation of self-collected saliva by quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (RT-qPCR), direct RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification, and a rapid antigen test to diagnose COVID-19. J Clin Microbiol 58:e01438–20. https://doi.org/10.1128/jcm.01438-20
Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu LH, Yang JH (2014) starBase v2.0: decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D92–D97. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1248
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120:15–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2004.12.035
Ye Z, Liu X, Yang Y, Zhang X, Yu T, Li S, Feng Y, Luo G (2018) The differential expression of novel circular RNAs in an acute lung injury rat model caused by smoke inhalation. J Physiol Biochem 74:25–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-017-0598-5
Ren Y, Li L, Wang M, Yang Z, Sun Z, Zhang W, Cao L, Nie S (2022) Knockdown of circRNA paralemmin 2 ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced murine lung epithelial cell Injury by sponging mir-330-5p to reduce ROCK2 expression. Immunol Invest 51:1707–1724. https://doi.org/10.1080/08820139.2022.2027961
Cheng N, Liang Y, Du X, Ye RD (2018) Serum amyloid A promotes LPS clearance and suppresses LPS-induced inflammation and tissue injury. EMBO Rep 19:e45517. https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.201745517
Chang Y, Yan W, Sun C, Liu Q, Wang J, Wang M (2017) Mir-145-5p inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the JNK signaling pathway by targeting MAP3K1 in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncol Lett 14:6923–6928. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.7092
Pham TT, Angus SP, Johnson GL (2013) MAP3K1: genomic alterations in Cancer and function in promoting cell survival or apoptosis. Genes Cancer 4:419–426. https://doi.org/10.1177/1947601913513950
Parker A, Cross SH, Jackson IJ, Hardisty-Hughes R, Morse S, Nicholson G, Coghill E, Bowl MR, Brown SD (2015) The goya mouse mutant reveals distinct newly identified roles for MAP3K1 in the development and survival of cochlear sensory hair cells. Dis Model Mech 8:1555–1568. https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.023176
Hui Z, Jie H, Fan GH (2021) Expression of DUSP12 reduces lung vascular endothelial cell damage in a murine model of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via the apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1)-Jun N-Terminal kinase activation (JNK) pathway. Med Sci Monit 27:e930429. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.930429
Wang WB, Li JT, Hui Y, Shi J, Wang XY, Yan SG (2022) Combination of pseudoephedrine and emodin ameliorates LPS-induced acute lung injury by regulating macrophage M1/M2 polarization through the VIP/cAMP/PKA pathway. Chin Med 17:19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13020-021-00562-8
Chen Q, Shao X, He Y, Lu E, Zhu L, Tang W (2021) Norisoboldine attenuates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by modulating macrophage polarization via PKM2/HIF-1α/PGC-1α pathway. Biol Pharm Bull 44:1536–1547. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.b21-00457
Baradaran Rahimi V, Rakhshandeh H, Raucci F, Buono B, Shirazinia R, Samzadeh Kermani A, Maione F, Mascolo N, Askari VR (2019) Anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant activity of Portulaca oleracea extract on LPS-induced rat lung injury. Molecules 24:139. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24010139
Sakhatskyy P, Wang Z, Borgas D, Lomas-Neira J, Chen Y, Ayala A, Rounds S, Lu Q (2017) Double-hit mouse model of cigarette smoke priming for acute lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 312:L56. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00436.2016
Mu Q, Zhang C, Li R, Guo Z (2022) CircPalm2 knockdown alleviates LPS-evoked pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell apoptosis and inflammation via miR-450b-5p/ROCK1 axis. Int Immunopharmacol 113:109199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109199
Tay Y, Rinn J, Pandolfi PP (2014) The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature 505:344–352. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12986
Gao M, Yu T, Liu D, Shi Y, Yang P, Zhang J, Wang J, Liu Y, Zhang X (2021) Sepsis plasma-derived exosomal mir-1-3p induces endothelial cell dysfunction by targeting SERP1. Clin Sci (Lond) 135:347–365. https://doi.org/10.1042/cs20200573
Jiao Y, Zhang T, Zhang C, Ji H, Tong X, Xia R, Wang W, Ma Z, Shi X (2021) Exosomal miR-30d-5p of neutrophils induces M1 macrophage polarization and primes macrophage pyroptosis in sepsis-related acute lung injury. Crit Care 25:356. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-021-03775-3
Lin J, Lin Z, Lin L (2021) MiR-490 alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by targeting MRP4 in new-born mice. Acta Biochim Pol 68:151–158. https://doi.org/10.18388/abp.2020_5397
Tomofuji T, Yoneda T, Machida T, Ekuni D, Azuma T, Kataoka K, Maruyama T, Morita M (2016) MicroRNAs as serum biomarkers for periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol 43:418–425. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.12536
Yang B, Gao X, Sun Y, Zhao J, Chen J, Gao L, Zhao L, Li Y (2020) Dihydroartemisinin alleviates high glucose-induced vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation and inflammation by depressing the miR-376b-3p/KLF15 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 530:574–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.07.095
Morrell ED, O’Mahony DS, Glavan BJ, Harju-Baker S, Nguyen C, Gunderson S, Abrahamson A, Radella F 2, Rona G, Black RA, Wurfel MM (2018) Genetic variation in MAP3K1 associates with ventilator-free days in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 58:117–125. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2017-0030OC
Zhao Y, Zou M, Sun Y, Zhang K, Peng X (2019) Gga-miR-21 modulates Mycoplasma gallisepticum (HS strain)-Induced inflammation via targeting MAP3K1 and activating MAPKs and NF-κB pathways. Vet Microbiol 237:108407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2019.108407
Li G, Qi W, Li X, Zhao J, Luo M, Chen J (2021) Recent advances in c-Jun N-Terminal kinase (JNK) inhibitors. Curr Med Chem 28:607–627. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867327666200210144114
Kim EK, Choi EJ (2010) Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1802:396–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2009.12.009
Lou L, Hu D, Chen S, Wang S, Xu Y, Huang Y, Shi Y, Zhang H (2019) Protective role of JNK inhibitor SP600125 in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 12:528–538
Du J, Wang G, Luo H, Liu N, Xie J (2021) JNK-IN-8 treatment alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via suppression of inflammation and oxidative stress regulated by JNK/NF–κB signaling. Mol Med Rep 23:150. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2020.11789
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The work was supported by Huaian Health and Health Research Project (approval number: HAWJ202108) and Science and Technology Development Foundation of Nanjing Medical University (approval number: NMUB20210135).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PG designed this study. WD collected and analyzed the data. HS drafted the manuscript. QW interpreted the data and revised the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, P., Duan, W., Shi, H. et al. Silencing circPalm2 inhibits sepsis-induced acute lung injury by sponging miR-376b-3p and targeting MAP3K1. Toxicol Res. 39, 275–294 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43188-022-00169-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43188-022-00169-7