Abstract
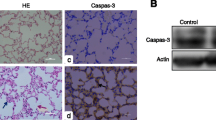
Acute lung injury caused by smoke inhalation is a common severe clinical syndrome. This study aimed to investigate the potential expression of circular RNAs during acute lung injury triggered by smoke inhalation. The acute lung injury rat model was established with smoke inhalation from a self-made smoke generator. The occurrence of acute lung injury was validated by an analysis of the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining of lung tissues. Next-generation sequencing and quantitative PCR were performed to identify the differentially expressed circular RNAs associated with acute lung injury that was caused by smoke inhalation. The circular form of the identified RNAs was finally verified by multiple RT-PCR-based assays. The bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and lung tissue analysis showed that smoke inhalation successfully induced acute injury in rats, as evidenced by the significantly altered cell numbers, including macrophages, neutrophils, and red blood cells, disrupted cell lining, and increased levels of interleukin-1β, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and IL-8 in lung tissues. Ten significantly differentially expressed circular RNAs were identified with next-generation sequencing and RT-PCR. The circular form of these RNAs was verified by multiple RT-PCR-based assays. In conclusion, the identified circular RNAs were prevalently and differentially expressed in rat lungs after acute lung injury caused by smoke inhalation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelmohsen K, Panda AC, De S, Grammatikakis I, Kim J, Ding J, Ji HN, Kim KM, Mattison JA, Cabo RD (2015) Circular RNAs in monkey muscle: age-dependent changes. Aging 7(11):903–910. 10.18632/aging.100834
Chen LL (2016) The biogenesis and emerging roles of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 17(4):205–211. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm.2015.32
Chen LL, Yang L (2015) Regulation of circRNA biogenesis. RNA Biol 12(4):381–388. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2015.1020271
Cheng J, Metge F, Dieterich C (2016) Specific identification and quantification of circular RNAs from sequencing data. Bioinformatics 32(7):1094–1096. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv656
Enkhbaatar P, Traber DL (2004) Pathophysiology of acute lung injury in combined burn and smoke inhalation injury. Clin Sci 107(2):137–143. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20040135
Greene J, Baird AM, Brady L, Lim M, Gray SG, Mcdermott R & Finn SP. (2017). Circular RNAs: biogenesis, function and role in human diseases. Front Mol Biosci. 4:38. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2017.00038
Guo Z, Wen Z, Qin A, Zhou Y, Liao Z, Liu Z, Liang Y, Ren T, Xu L (2013) Antisense oligonucleotide treatment enhances the recovery of acute lung injury through IL-10ق€ secreting M2-like macrophage-induced expansion of CD4+ regulatory T cells. J Immunol 190(8):4337–4348. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1203233
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK, Kjems J (2013) Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 495(7441):384–388. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11993
Johnson ER, Matthay MA (2010) Acute lung injury: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatment. J Aerosol Med Pulmo Drug Delivery 23:243
Khimenko PL, Taylor AE (1999) Segmental microvascular permeability in ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat lung. Am J Physiol 276(6 Pt 1):L958–L960
Ku CM, Lin JY (2015) Farnesol, a sesquiterpene alcohol in herbal plants, exerts anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effects on ovalbumin-sensitized and -challenged asthmatic mice. Ev-Based Complementary Alternat Med 2015(2015–4-19):1–12
Matute-Bello G, Frevert CW, Martin TR (2008) Animal models of acute lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 295:379–399
Petar G, Panagitis P, Nikolaus R (2014) circBase: a database for circular RNAs. Rna-a Publ Rna Soc 20:1666
Pei W, Tao L, Zhang LW, Zhang S, Cao J, Jiao Y, Tong J, Nie J (2017) Circular RNA profiles in mouse lung tissue induced by radon. Environ Health Prev Med 22:36
Sanger HL, Klotz G, Riesner D, Gross HJ, Kleinschmidt AK (1976) Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 73(11):3852–3856. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.73.11.3852
Soejima K, Schmalstieg FC, Sakurai H, Traber LD, Traber DL (2001) Pathophysiological analysis of combined burn and smoke inhalation injuries in sheep. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 280(6):L1233–L1241
Subbiah R, Pattarayan D, R P PSG, Thimmulappa RK (2016) MicroRNA regulation of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Cell Physiol 231(10):2097–106
Tsushima K, King LN (2009) Acute lung injury review. Intern Med 48(9):621–630. https://doi.org/10.2169/internalmedicine.48.1741
Wan L, Zhang L, Fan K, Cheng ZX, Sun QC, Wang JJ Circular RNA-ITCH suppresses lung cancer proliferation via inhibiting the Wnt/خ -catenin pathway. Biomed Res Int 2016, 2016:1–11
Wheeler AP, Bernard GR (2007) Acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome: a clinical review. Lancet 369(9572):1553–1564. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60604-7
Xu Z, Zhang C, Cheng L, Hu M, Tao H, Song L (2014) The microRNA miR-17 regulates lung FoxA1 expression during lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Biochem Biophys Res Communications 445:48–53
You X, Conrad TO (2016) Acfs: accurate circRNA identification and quantification from RNA-Seq data. Sci Rep 6(1):38820. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep38820
Zhang P, Zuo Z, Shang W, Wu A, Bi R, Wu J, Li S, Sun X, Jiang L (2017) Identification of differentially expressed circular RNAs in human colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol J Int Soc Oncodev Biol Med 39:1010428317694546
Zhou T, Garcia JGN, Zhang W (2011) Integrating microRNAs into a system biology approach to acute lung injury. Transl Res J Lab Clin Med 157:180–190
Zhu X, Wang X, Wei S, Chen Y, Chen Y, Fan X, Han S & Wu G. (2017). hsa_circ_0013958: a circular RNA and potential novel biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma. FEBS J 284(14):2170–2182
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Science and Technology Plan Projects of Guangdong Province (Nos. 2014A020212533 and 2014A020212707).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All experiments were authorized by the Animal Care and Ethics Committee of Sun Yat-sen University.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, Z., Liu, X., Yang, Y. et al. The differential expression of novel circular RNAs in an acute lung injury rat model caused by smoke inhalation. J Physiol Biochem 74, 25–33 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-017-0598-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-017-0598-5