Abstract
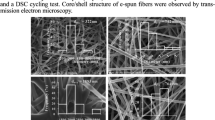
In this work, shape-stabilized solid-solid phase change materials (PCMs) were fabricated by simply electrospinning polyethylene glycol (PEG) and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA). Owing to the strong hydrogen bonds and entanglement between those molecular chains of PEG and PVA, PEG was packaged by PVA. The morphological structures, thermal stability and thermal energy storage properties of those fibers were investigated. SEM results showed that those electrospun PVA/PEG composite membranes hold a three-dimensional nonwoven web structure even the content of PEG as high as 70%. The thermal energy storage ability of those composite fibers increased with the increase of the content of PEG. The heat enthalpies of PEG/PVA = 7/3 were as high as 78.806 J/g. Moreover, those composite fibers had excellent thermal stability. After 100 heating and cooling cycles, there was almost no obvious change in the melting enthalpy and crystallization enthalpy. Those fibers still maintained good thermal regulation. The simple preparation process, low cost of raw materials and excellent stability endow the PCMs great utilization potentiality in smart textile and energy storage systems.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang D, Zhou J, Wu K, Li Z. Granular phase changing composites for thermal energy storage. Sol Energy. 2005;78:471–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2004.04.022.
Karaipekli A, Sari A. Capric-myristic acid/vermiculite composite as form-stable phase change material for thermal energy storage. Sol Energy. 2009;83:323–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2008.08.012.
Shao C, Kim HY, Gong J, Ding B, Lee DR, Park SJ. Fiber mats of poly(vinyl alcohol)/silica composite via electrospinning. Mater Lett. 2003;57:1579–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-577X(02)01036-4.
Kou Y, Wang S, Luo J, Sun K, Zhang J, Tan Z, Shi Q. Thermal analysis and heat capacity study of polyethylene glycol (PEG) phase change materials for thermal energy storage applications. J Chem Thermodyn. 2019;128:259–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jct.2018.08.031.
Zhang Y, Wang J, Qiu J, Jin X, Umair MM, Lu R, Zhang S, Tang B. Ag-graphene/PEG composite phase change materials for enhancing solar-thermal energy conversion and storage capacity. Appl Energy.2019;237:83–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.12.075.
Qiu J, Huo D, Xue J, Zhu G, Liu H, Xia Y. Encapsulation of a phase-change material in nanocapsules with a well-defined Hole in the wall for the controlled release of drugs, angew. Chemie Int Ed. 2019;58:10606–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201904549.
Alva G, Lin Y, Fang G. An overview of thermal energy storage systems. Energy. 2018;144:341–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.12.037.
Pielichowski K, Flejtuch K. Differential scanning calorimetric studies on poly(ethylene glycol) with different molecular weights for thermal energy storage materials. Polym Advan Technol. 2002;13:690–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.276.
Alkan C, Sarı A, Uzun O. Poly (ethylene glycol)/acrylic polymer blends for latent heat thermal energy storage. AIChE J. 2006;52:3310–4. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.10928.
Cao R, Li X, Chen S, Yuan H, Zhang X. Fabrication and characterization of novel shape-stabilized synergistic phase change materials based on PHDA/GO composites. Energy. 2017;138:157–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.07.049.
Han N, Li Z, Zhang X, Yu W, Chen X, Wang D, Li J. Synthesis and characterization of cellulose-g-polyoxyethylene (2) hexadecyl ether solid–solid phase change materials. Cellulose. 2016;23:1663–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0901-6.
Hawlader MNA, Uddin MS, Mya M. Microencapsulated PCM thermal-energy storage system. Appl Energy. 2003;74:195–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0306-2619(02)00146-0.
Barba A, Spiga M. Discharge mode for encapsulated PCMs in storage tanks. Sol Energy. 2003;74:141–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-092X(03)00117-8.
Zhang HL, Baeyens J, Degrève J, Cáceres G, Segal R, Pitié F. Latent heat storage with tubular-encapsulated phase change materials (PCMs). Energy. 2014;76:66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2014.03.067.
Schossig P, Henning H, Gschwander S. Micro-encapsulated phase-change materials integrated into construction materials. Sol Energ Mat Sol C. 2005;89:297–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2005.01.017.
Fang G, Li H, Yang F, Liu X, Wu S. Preparation and characterization of nano-encapsulated n-tetradecane as phase change material for thermal energy storage. Chem Eng J. 2009;153:217–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.06.019.
Onder E, Sarier N, Cimen E. Encapsulation of phase change materials by complex coacervation to improve thermal performances of woven fabrics. Thermochim Acta. 2008;467:63–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2007.11.007.
Loke G, Yan W, Khudiyev T, Noel G, Fink Y. Recent progress and perspectives of thermally drawn multimaterial fiber electronics. Adv Mater. 2019;32:1904911. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201904911.
Weng W, Yang J, Zhang Y, Li Y, Yang S, Zhu L, Zhu M. A route toward smart system integration: from fiber design to device construction. Adv Mater. 2019;32:1902301. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201902301.
Shi J, Liu S, Zhang L, Yang B, Shu L, Yang Y, Ren M, Wang Y, Chen J, Chen W, Chai Y, Tao X. Smart textile-integrated microelectronic systems for wearable applications. Adv Mater. 2019;32:1901958. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201901958.
Yan W, Page A, Nguyen-Dang T, Qu Y, Sordo F, Wei L, Sorin F. Advanced multimaterial electronic and optoelectronic fibers and textiles. Adv Mater. 2019;31:1–28. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201802348.
Chen C, Wang L, Huang Y. Electrospinning of thermo-regulating ultrafine fibers based on polyethylene glycol/cellulose acetate composite. Polymer. 2007;48:5202–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2007.06.069.
Venugopal J, Ma LL, Yong T, Ramakrishna S. In vitro study of smooth muscle cells on polycaprolactone and collagen nanofibrous matrices. Cell Biol Int. 2005;29:861–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellbi.2005.03.026.
Cao Q, Liu P. Hyperbranched polyurethane as novel solid–solid phase change material for thermal energy storage. Eur Polym J. 2006;42:2931–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2006.07.020.
Karaman S, Karaipekli A, Sar A, Biçer A. Polyethylene glycol (PEG)/diatomite composite as a novel form-stable phase change material for thermal energy storage. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells. 2011;95:1647–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2011.01.022.
El Halal SLM, Fonseca LM, do Evangelho JA, Bruni GP, dos Santos Hackbart HC, da Rosa Zavareze E, Dias ARG,. Electrospun ultrafine fibers from black bean protein concentrates and polyvinyl alcohol. Food Biophys. 2019; 14:446–455. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-019-09594-y.
dos Santos JP, E da R Zavareze, Dias ARG, Vanier NL,. Immobilization of xylanase and xylanase–β-cyclodextrin complex in polyvinyl alcohol via electrospinning improves enzyme activity at a wide pH and temperature range. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;118:1676–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.07.014.
Porto MDA, dos Santos JP, Hackbart H, Bruni GP, Fonseca LM, da Rosa Zavareze E, Dias ARG. Immobilization of α-amylase in ultrafine polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) fibers via electrospinning and their stability on different substrates. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;126:834–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.12.263.
Koski A, Yim K, Shivkumar S. Effect of molecular weight on fibrous PVA produced by electrospinning. Mater Lett. 2004;58:493–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-577X(03)00532-9.
Awadhia A, Patel SK, Agrawal SL. Dielectric investigations in PVA based gel electrolytes. Prog Cryst Growth Charact Mater. 2006;52:61–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcrysgrow.2006.03.009.
Wali A, Zhang Y, Sengupta P, Higaki Y, Takahara A, Badiger MV. Electrospinning of non-ionic cellulose ethers/polyvinyl alcohol nanofibers: characterization and applications. Carbohydr Polym. 2018;181:175–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.10.070.
Fu X, Xiao Y, Hu K, Wang J, Lei J, Zhou C. Thermosetting solid–solid phase change materials composed of poly(ethylene glycol)-based two components: flexible application for thermal energy storage. Chem Eng J. 2016;291:138–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.01.096.
Lin WJ, Flanagan DR, Linhardt RJ. A novel fabrication of poly(ε-caprolactone) microspheres from blends of poly(ε-caprolactone) and poly(ethylene glycol)s. Polymer. 1999;40:1731–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-3861(98)00378-4.
Hamdy S, Elamanchili P, Alshamsan A, Molavi O, Satou T, Samuel J. Enhanced antigen-specific primary CD4+ and CD8+ responses by codelivery of ovalbumin and toll-like receptor ligand monophosphoryl lipid A in poly (D, L-lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2007;81:652–62. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.31019.
Fong H, Chun I, Reneker DH. Beaded nanofibers formed during electrospinning. Polymer. 1999;40:4585–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-3861(99)00068-3.
Ke G, Wang X, Pei J. Fabrication and properties of electrospun PAN/LA–SA/TiO2 composite phase change fiber, polym-plast. Technol Eng. 2018;57:958–64. https://doi.org/10.1080/03602559.2017.1370101.
Ke H. Electrospun methyl stearate/PET form-stable phase change composite nanofibres for storage and retrieval of thermal energy. Mater Res Innov. 2018;22:150–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/14328917.2016.1266203.
Wu Y, Chen C, Jia Y, Wu J, Huang Y, Wang L. Review on electrospun ultrafine phase change fibers (PCFs) for thermal energy storage. Appl Energy. 2018;210:167–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.11.001.
Rosu D, Tudorachi N, Rosu L. Investigations on the thermal stability of a MDI based polyurethane elastomer. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2010;89:152–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2010.07.004.
Chen C, Liu W, Wang H, Peng K. Synthesis and performances of novel solid–solid phase change materials with hexahydroxy compounds for thermal energy storage. Appl Energy. 2015;152:198–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.12.004.
Fu X, Kong W, Zhang Y, Jiang L, Wang J, Lei J. Novel solid–solid phase change materials with biodegradable trihydroxy surfactants for thermal energy storage. RSC Adv. 2015;5:68881–9. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra11842e.
Zhou D, Zhao CY, Tian Y. Review on thermal energy storage with phase change materials (PCMs) in building applications. Appl Energy. 2012;92:593–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2011.08.025.
Radhakrishnan R, Gubbins KE. Free energy studies of freezing in slit pores: an order-parameter approach using Monte Carlo simulation. Mol Phys. 1999;96:1249–67. https://doi.org/10.1080/00268979909483070.
Abdalkarim SYH, Yu HY, Song ML, Zhou Y, Yao J, Ni QQ. In vitro degradation and possible hydrolytic mechanism of PHBV nanocomposites by incorporating cellulose nanocrystal-ZnO nanohybrids. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;176:38–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.08.051.
Abdalkarim SYH, Yu HY, Wang D, Yao J. Electrospun poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxy-valerate)/cellulose reinforced nanofibrous membranes with ZnO nanocrystals for antibacterial wound dressings. Cellulose. 2017;24:2925–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1303-0.
Abdalkarim SYH, Yu HY, Wang C, Yang L, Guan Y, Huang L, Yao J. Sheet-like cellulose nanocrystal-ZnO nanohybrids as multifunctional reinforcing agents in biopolyester composite nanofibers with ultrahigh UV-shielding and antibacterial performances. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2018;1:714–27. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.8b00188.
Abdalkarim SYH, Yu H, Wang C, Chen Y, Zou Z, Han L, Yao J, Tam KC. Thermo and light-responsive phase change nanofibers with high energy storage efficiency for energy storage and thermally regulated on–off drug release devices. Chem Eng J. 2019;375:121979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.121979.
Petrović ZS, Zavargo Z, Flyn JH, Macknight WJ. Thermal degradation of segmented polyurethanes. J Appl Polym Sci. 1994;51:1087–95. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.1994.070510615.
Matthews JA, Wnek GE, Simpson DG, Bowlin GL. Electrospinning of collagen nanofibers. Biomacromolecules. 2002;3:232–8. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm015533u.
Karaipekli A, Sari A. Capric acid and palmitic acid eutectic mixture applied in building wallboard for latent heat thermal energy storage. J Sci Ind Res (India). 2007;66:470–6.
Li H, Liu X, Fang G. Preparation and characteristics of n-nonadecane/cement composites as thermal energy storage materials in buildings. Energ Build. 2010;42:1661–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2010.04.009.
Li C, Xie B, Chen J, He Z, Chen Z, Long Y. Emerging mineral-coupled composite phase change materials for thermal energy storage. Energ Convers Manage. 2019;183:633–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2019.01.021.
Lu Y, Xiao X, Fu J, Huan C, Qi S, Zhan Y, Zhu Y, Xu G. Novel smart textile with phase change materials encapsulated core-sheath structure fabricated by coaxial electrospinning. Chem Eng J. 2019;355:532–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.189.
Feng D, Feng Y, Li P, Zang Y, Wang C, Zhang X. Modified mesoporous silica filled with PEG as a shape-stabilized phase change materials for improved thermal energy storage performance. Micropor Mesopor Mat. 2020;292:109756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.109756.
Zhou S, Hu R, Luo X. Thermal illusion with twinborn-like heat signatures. Int J Heat Mass Trans. 2018;27:607–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.07.034.
Cui Y, Gong H, Wang Y, Li D, Bai H. A thermally insulating textile inspired by polar bear hair. Adv Mater. 2018;30:1706807. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201706807.
Acknowledgements
The project was supported by international cooperation of Prof. Jaromir Marek and Key Program for International S &T Innovation Cooperation Projects of China [2016YFE0131400]. This project was supported by the Scientific Research Project of Department of Education of Zhejiang Province [19010035-F]. This work was supported by Science Foundation of Zhejiang Sci-Tech University (ZSTU) under Grant No. 19012393-Y.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written with contributions from all the authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, J., Yu, H., Abdalkarim, S.Y.H. et al. Electrospun Polyethylene Glycol/Polyvinyl Alcohol Composite Nanofibrous Membranes as Shape-Stabilized Solid–Solid Phase Change Materials. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2, 167–177 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-020-00038-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-020-00038-8