Abstract
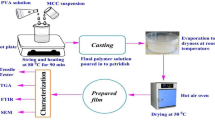
In this study, ultrafine fibers were produced from black bean protein concentrates (BPCs) and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) by electrospinning. The BPC was denatured under acidic (pH 2) or basic (pH 11) conditions. Polymer solutions containing different PVA concentrations (11% or 21%, w/v) and different BPC: PVA ratios (50:50 or 75:25, v/v) were used for fiber production. The electrical conductivity and rheological properties of the fiber-forming solutions were evaluated, as well as the morphology, size distribution, infrared spectrum, and thermal properties of the electrospun fibers. The fibers showed a homogeneous morphology and diameters ranging from 115 to 541 nm. Fibers from the solution containing BPC denatured at pH 11, 11% PVA, and 75:25 (v/v) BPC: PVA presented the lowest diameter, and those from BPC denatured at pH 2 had less beads than the fibers obtained from BPC denatured at pH 11. The solution formulation affected the thermal properties of the fibers, with weight loss increases ranging from 39.0% to 60.9%. The polymeric solutions containing PVA and BPC (whether denatured under basic or acidic conditions) resulted in ultrafine electrospun fibers with highly favorable characteristics that could potentially be used for the encapsulation of bioactive compounds and food applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
FAO, in Italy: FAO Corporate Document Repository. Cereals, pulses, legumes and vegetable proteins. CODEX alimentarius (2007), pp. 1–96
J.A. Evangelho, N.L. Vanier, V.Z. Pinto, J.J.D. Berrios, A.R.G. Dias, E.R. Zavareze, Food Chem. 214, 460–467 (2017)
D. Cho, A.N. Netravali, Y. Lak, Polym. Degrad. Stab. 97(5), 747–754 (2012)
S. Wang, M.F. Marcone, S. Barbut, L. Lim, Food Res. Int. 52(2), 467–472 (2013)
S. Tansaz, L. Liverani, L. Vester, A.R. Boccaccini, Mater. Lett. 199, 143–146 (2017)
A. Baji, Y.W. Mai, S.C. Wong, M. Abtahi, P. Chen, Compos. Sci. Technol. 70(5), 703–718 (2010)
A. Haider, S. Haider, I. Kang, Arab. J. Chem. 15, 1878–5352 (2015)
G. Liu, Z. Gu, Y. Hong, L. Cheng, C. Li, J. Control. Release 252, 95–107 (2017)
J.A. Bhushani, C. Anandharamakrishnan, Trends Food Sci. Technol. 38(1), 21–33 (2014)
M.D.A. Porto, J.P. Santos, H. Hackbart, G.P. Bruni, L.M. Fonseca, E.R. Zavareze, A.R.G. Dias, Int J Biol Macromol 126, 834–841 (2019)
L.M. Fonseca, J.P. Oliveira, P.D. Oliveira, E.R. Zavareze, A.R.G. Dias, L.-T. Lim, Food Res. Int. 116, 1318–1326 (2019)
Y. P. Neo, S. Ray, J. Jin, M. Gizdavic-Nikolaidis, M. K. Nieuwoudt, D. Liu, , S. Y. Quek. Food Chem., 136 , 1013–1021, (2013), 2
H. Wang, W. Wang, S. Jiang, S. Jiang, L. Zhai, Q. Jiang, Iran. Polym. J. 20, 551–558 (2011)
P. Wen, D.H. Zhu, H. Wu, M.H.Z.Y.R. Jing, S.Y. Han, Food Control 59, 366–376 (2016)
V.P. Romani, A.V. Machado, B.D. Olsen, V.G. Martins, Food Hydrocoll. 74, 307–314 (2018)
M.B. Barać, S.P. Pešić, A.Ž. Stanojević, S.B. Kostić, Čabrilo, Acta Period Technol 46, 1–18 (2015)
A. López-Rubio, J.M. Lagaron, Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 13, 200–206 (2012)
A.-C. Vega-Lugo, L.-T. Lim, J. Biobased Mater. Bioenergy 2(3), 223–230 (2008)
F.T. Silva, K.F. Cunha, L.M. Fonseca, M.D. Antunes, S.L.M. Halal, A.M. Fiorentini, E.R. Zavareze, A.R.G. Dias, Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 118(Pt A), 107–115 (2018)
J. Carrasco-Castilla, A. J. Hernández-Álvarez, C. Jiménez-Martínez, C. Jacinto-Hernández, , M. Alaiz, J. Girón-Calle, , J. Vioque, G. Dávila-Ortiz. Food Chem., 135, 1789–1795, (2012), 3
E. Shanesazzadeh, M. Kadivar, M. Fathi, Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 119, 1–7 (2018)
I.B. Ghoran, N. Tucker, Food Hydrocoll. 51, 227–240 (2015)
R. C. Chandan, C. H. White, A. Kilara, Y. H. Hui. (London: Blackwell Publishing Ltd, 2006). p. 364
Z.M. Huang, Y.Z. Zhang, M. Kotaki, S. Ramakrishna, Compos. Sci. Technol. 63(15), 2223–2253 (2003)
N. Bhardwaj, S.C. Kundu, Biotechnol. Adv. 28(3), 325–347 (2010)
S. Ramakrishna, K. Fujihara, W.E. Teo, T.C. Lim, Z. Ma, 5. ed (World Scientific, Cingapura, 2005)
C. Drosou, M. Krokida, C.G. Biliaderis, Food Hydrocoll. 77, 726–735 (2018)
Q. Fang, M. Zhu, S. Yu, G. Sui, X. Yang, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 214, 1–10 (2016)
R. Wongkanya, P. Chuysinuan, C. Pengsuk, J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2(3), 309–316 (2017)
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul (FAPERGS), and Centro de Microscopia Eletrônica do Sul (CEME-SUL) from Universidade Federal do Rio Grande (FURG). This study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior - Brasil (CAPES) - Finance Code 001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 347 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El Halal, S.L.M., Fonseca, L.M., do Evangelho, J.A. et al. Electrospun Ultrafine Fibers from Black Bean Protein Concentrates and Polyvinyl Alcohol. Food Biophysics 14, 446–455 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-019-09594-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-019-09594-y