Abstract
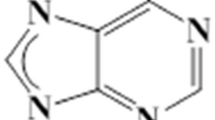
Structural polymeric nanohybrids is presently a popular topic and can be conceived for numerous functional applications, including the pH-sensitive oral colon-targeted drug-delivery system. In this paper, a brand-new Janus core@shell (JCS) nanostructure was fabricated using a trifluid electrospinning, in which three polymers and a model drug 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) were elaborately and intentionally positioned. In the structural hybrids, the pH-sensitive polymer hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose acetate succinate was located in the common shell layer, and the 5-FU-loaded ethyl cellulose (EC) and polyethylene oxide (PEO) were organized in a side-by-side manner in the core sections. The JCS fiber had a fine linear morphology with a multiple-chamber structure and a shell thickness of about 24 nm. The drug presented in the fibers in an amorphous state, owing to the secondary intermolecular interactions between EC and 5-FU. The ex vivo adhesion experiments suggested that the JCS fibers could stick firmly to the intestine membranes. In vitro dissolution tests showed the JCS fibers released only 7.8% ± 3.5% of the loaded 5-FU in an acid condition. In vivo gavage administration verified that the JCS fibers effectively promoted the absorbance of 5-FU in a synergistic manner, better than the double-layer core–shell and Janus nanofibers, and near fourfold than the drug solutions as a control. The present protocol opens a new way for developing novel multifunctional nanomaterials with the JCS nanostructure as a powerful supporting platform.
Graphical abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data presented in the study are included, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
References
Xing C, Zhu H, Dou X, Gao L, Baddi S, Zou Y, Zhao C, Peng Y, Fang Y, Feng CL (2023) Infected diabetic wound regeneration using peptide-modified chiral dressing to target revascularization. ACS Nano 17(7):6275–6291. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.2c10039
Zhu H, Wang Y, Qu M, Pan Y, Zheng G, Dai K, Huang M, Alhadhrami A, Ibrahim MM, El-Bahy ZM, Liu C, Shen C, Liu X (2022) Electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol)/silica film for radiative cooling. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5(3):1966–1975. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00529-9
Mhetre H, Kanse Y, Chendake Y (2023) Influence of electrospinning voltage on the diameter and properties of 1-dimensional zinc oxide nanofiber. ES Mater Manuf 20:838. https://doi.org/10.30919/esmm5f838
Shen Y, Yu X, Cui J, Yu F, Liu M, Chen Y, Wu J, Sun B, Mo X (2022) Development of biodegradable polymeric stents for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Biomolecules 12(9):1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12091245
Jiang W, Du Y, Ji Y, Zhou Y, Zhao P, Yu D G (2022) Modernization of traditional chinese condiments via electrospun polymeric nanocomposites. ES Food Agrofor 8:47–56. https://doi.org/10.30919/esfaf738
Yu DG, Zhao P (2022) The key elements for biomolecules to biomaterials and to bioapplications. Biomolecules 12(9):1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12091234
Song W, Zhang Y, Tran CH, Choi HK, Yu DG, Kim I (2023) Porous organic polymers with defined morphologies: synthesis, assembly, and emerging applications. Prog Polym Sci 142:101691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2023.101691
Xiao L, Xu W, Huang L, Liu J, Yang G (2023) Nanocomposite pastes of gelatin and cyclodextrin-grafted chitosan nanoparticles as potential postoperative tumor therapy. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 6(1):15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00575-3
Wang Z, Li R, Zhang J (2022) On-demand drug delivery of triptolide and celastrol by poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticle/triglycerol monostearate-18 hydrogel composite for rheumatoid arthritis treatment. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5(4):2921–2935. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00493-4
Wang X, Qi Y, Hu Z, Jiang L, Pan F, Xiang Z, Xiong Z, Jia W, Hu J, Lu W (2022) Fe3O4@PVP@DOX magnetic vortex hybrid nanostructures with magnetic-responsive heating and controlled drug delivery functions for precise medicine of cancers. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5(3):1786–1798. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00433-2
Chen R, Shi J, Liu C, Li J, Cao S (2022) In situ self-assembly of gold nanorods with thermal-responsive microgel for multi-synergistic remote drug delivery. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5(3):2223–2234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00306-0
Wang H, Lu Y, Yang H, Yu DG, Lu X (2023) The influence of the ultrasonic treatment of working fluids on electrospun amorphous solid dispersions. Front Mol Biosci 10:1184767. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2023.1184767
Ji Y, Zhao H, Liu H, Zhao P, Yu DG (2023) Electrosprayed stearic-acid-coated ethylcellulose microparticles for an improved sustained release of anticancer drug. Gels 9(9):700. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9090700
Yu D G, Zhou J (2023) How can electrospinning further service well for pharmaceutical researches? J Pharm Sci S0022354923003337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xphs.2023.08.017
Wen P, Feng K, Yang H, Huang X, Zong MH, Lou WY, Li N, Wu H (2017) Electrospun core-shell structured nanofilm as a novel colon-specific delivery system for protein. Carbohydr Polym 169:157–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.03.082
Awad A, Madla CM, McCoubrey LE, Ferraro F, Gavins FKH, Buanz A, Gaisford S, Orlu M, Siepmann F, Siepmann J, Basit AW (2022) Clinical translation of advanced colonic drug delivery technologies. Adv Drug Delivery Rev 181:114076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2021.114076
Cui M, Zhang M, Liu K (2021) Colon-targeted drug delivery of polysaccharide-based nanocarriers for synergistic treatment of inflammatory bowel disease: a review. Carbohydr Polym 272:118530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118530
Zhang Z, Wells CJR, King AM, Bear JC, Davies GL, Williams GR (2020) pH-responsive nanocomposite fibres allowing MRI monitoring of drug release. J Mater Chem B 8(32):7264–7274. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0TB01033B
Cai X, Wang X, He M, Wang Y, Lan M, Zhao Y, Gao F (2021) Colon-targeted delivery of tacrolimus using pH-responsive polymeric nanoparticles for murine colitis therapy. Int J Pharm 606:120836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.120836
Situ W, Li X, Liu J, Chen L (2015) Preparation and characterization of glycoprotein-resistant starch complex as a coating material for oral bioadhesive microparticles for colon-targeted polypeptide delivery. J Agric Food Chem 63(16):4138–4147. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b00393
Zhao P, Xia X, Xu X, Leung KKC, Rai A, Deng Y, Yang B, Lai H, Peng X, Shi P, Zhang H, Chiu PWY, Bian L (2021) Nanoparticle-assembled bioadhesive coacervate coating with prolonged gastrointestinal retention for inflammatory bowel disease therapy. Nat Commun 12(1):7162. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-27463-6
Xu YJ, Wei K, Zhao P, Feng Q, Choi CKK, Bian L (2016) Preserving the adhesion of catechol-conjugated hydrogels by thiourea–quinone coupling. Biomater Sci 4(12):1726–1730. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6BM00434B
Akl MA, Kartal-Hodzic A, Suutari T, Oksanen T, Montagner IM, Rosato A, Ismael HR, Afouna MI, Caliceti P, Yliperttula M, Samy AM, Mastrotto F, Salmaso S, Viitala T (2019) Real-time label-free targeting assessment and in vitro characterization of curcumin-loaded poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid nanoparticles for oral colon targeting. ACS Omega 4(16):16878–16890. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b02086
Maroni A, Zema L, Del Curto MD, Foppoli A, Gazzaniga A (2012) Oral colon delivery of insulin with the aid of functional adjuvants. Adv Drug Delivery Rev 64(6):540–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2011.10.006
Varum FJO, Veiga F, Sousa JS, Basit AW (2011) Mucoadhesive platforms for targeted delivery to the colon. Int J Pharm 420(1):11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.08.006
Lin WC, Pan WY, Liu CK, Huang WX, Song HL, Chang KS, Li MJ, Sung HW (2018) In situ self-spray coating system that can uniformly disperse a poorly water-soluble H2S donor on the colorectal surface to treat inflammatory bowel diseases. Biomaterials 182:289–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.07.044
Qi J, Hu M, Li H, Jing R, Shen G (2018) A novel method of synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots for supersensitive and selective detection of cancer markers. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 18(12):8085–8093. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2018.16403
Bie P, Chen L, Li X, Li L (2016) Characterization of concanavalin a-conjugated resistant starch acetate bioadhesive film for oral colon-targeting microcapsule delivery system. Ind Crops Prod 84:320–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.02.023
Ziyadi H, Baghali M, Bagherianfar M, Mehrali F, Faridi-Majidi R (2021) An investigation of factors affecting the electrospinning of poly (vinyl alcohol)/kefiran composite nanofibers. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 4(3):768–779. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00230-3
Li Z, Xie W, Yao F, Du A, Wang Q, Guo Z, Gu H (2022) Comprehensive electrocatalytic degradation of tetracycline in wastewater by electrospun perovskite manganite nanoparticles supported on carbon nanofibers. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5(3):2092–2105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00550-y
Long Z, Yuan L, Shi C, Wu C, Qiao H, Wang K (2022) Porous Fe2O3 nanorod-decorated hollow carbon nanofibers for high-rate lithium storage. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5(1):370–382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00397-9
Zhang Z, Zhao Y, Li Z, Zhang L, Liu Z, Long Z, Li Y, Liu Y, Fan R, Sun K, Zhang Z (2022) Synthesis of carbon/SiO2 core-sheath nanofibers with Co-Fe nanoparticles embedded in via electrospinning for high-performance microwave absorption. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5(1):513–524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00350-w
Liu S, Du H, Liu K, Ma MG, Kwon YE, Si C, Ji XX, Choi SE, Zhang X (2021) Flexible and porous Co3O4-carbon nanofibers as binder-free electrodes for supercapacitors. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 4(4):1367–1383. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00344-8
Yang S, Shi C, Qu K, Sun Z, Li H, Xu B, Huang Z, Guo Z (2023) Electrostatic self-assembly cellulose nanofibers/MXene/nickel chains for highly stable and efficient seawater evaporation and purification. Carbon Lett. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42823-023-00540-0
Zhou J, Wang P, Yu DG, Zhu Y (2023) Biphasic drug release from electrospun structures. Expert Opin Drug Delivery 20(5):621–640. https://doi.org/10.1080/17425247.2023.2210834
Wang Y, Yu DG, Liu Y, Liu YN (2022) Progress of electrospun nanofibrous carriers for modifications to drug release profiles. J Func Biomater 13(4):289. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb13040289
Wang Q, Zeng J, Li J, Yu S, Innocent MT, Li M, Ma W, Xiang H, Zhu M (2023) Multifunctional fiber derived from wet spinning combined with UV photopolymerization for human motion and temperature detection. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 6(1):26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00583-3
Han W, Wang L, Li Q, Ma B, He C, Guo X, Nie J, Ma G (2022) A review: current status and emerging developments on natural polymer-based electrospun fibers. Macromol Rapid Commun 43(21):2200456. https://doi.org/10.1002/marc.202200456
Kose MD, Ungun N, Bayraktar O (2022) Eggshell membrane based turmeric extract loaded orally disintegrating films. Curr Drug Deliv 19(5):547–559. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567201818666210708123449
Ejeta F, Gabriel T, Joseph NM, Belete A (2022) Formulation, optimization and in vitro evaluation of fast disintegrating tablets of salbutamol sulphate using a combination of superdisintegrant and subliming agent. Curr Drug Deliv 19(1):129–141. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567201818666210614094646
He H, Wu M, Zhu J, Yang Y, Ge R, Yu DG (2022) Engineered spindles of little molecules around electrospun nanofibers for biphasic drug release. Adv Fiber Mater 4(2):305–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-021-00112-9
Tabakoglu S, Kolbuk D, Sajkiewicz P (2022) Multifluid electrospinning for multi-drug delivery systems: pros and cons, challenges, and future directions. Biomater Sci 11(1):37–61. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2bm01513g
Yang Y, Chen W, Wang M, Shen J, Tang Z, Qin Y, Yu DG (2023) Engineered shellac beads-on-the-string fibers using triaxial electrospinning for improved colon-targeted drug delivery. Polymers 15(10):2237. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15102237
Huang H, Song Y, Zhang Y, Li Y, Li J, Lu X, Wang C (2022) Electrospun nanofibers: current progress and applications in food systems. J Agric Food Chem 70(5):1391–1409. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.1c05352
Yu DG, Huang C (2023) Electrospun biomolecule-based drug delivery systems Biomolecules 13(7):1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13071152
Du Y, Yang Z, Kang S, Yu DG, Chen X, Shao J (2023) A sequential electrospinning of a coaxial and blending process for creating double-layer hybrid films to sense glucose. Sensors 23(7):3685. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23073685
Huang X, Jiang W, Zhou J, Yu DG, Liu H (2022) The applications of ferulic-acid-loaded fibrous films for fruit preservation. Polymers 14(22):4947. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14224947
Wang ML, Yu DG, Bligh SWA (2023) Progress in preparing electrospun janus fibers and their applications. Appl Mater Today 31:101766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2023.101766
Guler E, Hazar-Yavuz AN, Tatar E, Haidari MM, Ozcan GS, Duruksu G, Graca MPF, Kalaskar DM, Gunduz O, Cam ME (2023) Oral empagliflozin-loaded tri-layer core-sheath fibers fabricated using tri-axial electrospinning: enhanced in vitro and in vivo antidiabetic performance. Int J Pharm 635:122716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2023.122716
Liu H, Wang H, Lu X, Murugadoss V, Huang M, Yang H, Wan F, Yu DG, Guo Z (2022) Electrospun structural nanohybrids combining three composites for fast helicide delivery. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5(2):1017–1029. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00478-3
Song W, Tang Y, Qian C, Kim BJ, Liao Y, Yu DG (2023) Electrospinning spinneret: a bridge between the visible world and the invisible nanostructures. Innovation 4(2):100381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xinn.2023.100381
Wen X, Deng Z, Xu Y, Yan G, Deng X, Wu L, Liang Q, Fang F, Feng X, Yu M, He J (2021) Preparation and in vitro/in vivo evaluation of orally disintegrating/modified-release praziquantel tablets. Pharmaceutics 13(10):1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13101567
Mudie D, Stewart A, Rosales J, Adam M, Morgen M, Vodak D (2021) In vitro-in silico tools for streamlined development of acalabrutinib amorphous solid dispersion tablets. Pharmaceutics 13(8):1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13081257
Jede C, Wagner C, Kubas H, Weigandt M, Weber C, Lecomte M, Badolo L, Koziolek M, Weitschies W (2019) Improved prediction of in vivo supersaturation and precipitation of poorly soluble weakly basic drugs using a biorelevant bicarbonate buffer in a gastrointestinal transfer model. Mol Pharmaceutics 16(9):3938–3947. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b00534
Jermain SV, Lowinger MB, Ellenberger DJ, Miller DA, Su Y, Williams RO (2020) In vitro and in vivo behaviors of KinetiSol and spray-dried amorphous solid dispersions of a weakly basic drug and ionic polymer. Mol Pharmaceutics 17(8):2789–2808. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c00108
Zema L, Loreti G, Melocchi A, Maroni A, Palugan L, Gazzaniga A (2013) Gastroresistant capsular device prepared by injection molding. Int J Pharm 440(2):264–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2012.05.071
Darbasizadeh B, Mortazavi SA, Kobarfard F, Jaafari MR, Hashemi A, Farhadnejad H, Feyzi-Barnaji B (2021) Electrospun doxorubicin-loaded PEO/PCL core/sheath nanofibers for chemopreventive action against breast cancer cells. J Drug Delivery Sci Technol 64:102576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2021.102576
Kaseem M, Choe HC (2021) Acceleration of bone formation and adhesion ability on dental implant surface via plasma electrolytic oxidation in a solution containing bone ions. Metals 11(1):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11010106
Li G, Chen Y, Hu J, Wu X, Hu J, He X, Li J, Zhao Z, Chen Z, Li Y, Hu H, Li Y, Lan P (2013) A 5-fluorouracil-loaded polydioxanone weft-knitted stent for the treatment of colorectal cancer. Biomaterials 34(37):9451–9461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.08.055
Parodi B, Russo E, Gatti P, Cafaggi S, Bignardi G (1999) Development and in vitro evaluation of buccoadhesive tablets using a new model substrate for bioadhesion measures: the eggshell membrane. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 25(3):289–295. https://doi.org/10.1081/DDC-100102173
Wang M, Ge RL, Zhang F, Yu DG, Liu ZP, Li X, Shen H, Williams GR (2023) Electrospun fibers with blank surface and inner drug gradient for improving sustained release. Biomaterials Adv 150:213404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioadv.2023.213404
Liu C, Liu S-l, Bian J-f, Geng Z, Lu Y, Hu H-y (2001) A simple and rapid HPLC determination of 5-Fluorouracil in human serum. Chinese J Pharm Anal 21(2):96–98. https://doi.org/10.16155/j.0254-1793.2001.02.008
Yao L, Sun C, Lin H, Li G, Lian Z, Song R, Zhuang S, Zhang D (2023) Electrospun bi-decorated BixTiyOz/TiO2 flexible carbon nanofibers and their applications on degradating of organic pollutants under solar radiation. J Mater Sci Technol 150:114–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2022.07.066
Cao X, Chen W, Zhao P, Yang Y, Yu DG (2022) Electrospun porous nanofibers: pore-forming mechanisms and applications for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants in wastewater. Polymers 14(19):3990. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14193990
Bai Y, Liu Y, Lv H, Shi H, Zhou W, Liu Y, Yu DG (2022) Processes of electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride-based nanofibers, their piezoelectric properties, and several fantastic applications. Polymers 14(20):4311. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204311
Zhou J, Wang L, Gong W, Wang B, Yu DG, Zhu Y (2023) Integrating chinese herbs and western medicine for new wound dressings through handheld electrospinning. Biomedicines 11(8):2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11082146
Qian C, Liu Y, Chen S, Zhang C, Chen X, Liu Y, Liu P (2023) Electrospun core–sheath PCL nanofibers loaded with nHA and simvastatin and their potential bone regeneration applications. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 11:1205252. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2023.1205252
Zhou J, Dai Y, Fu J, Yan C, Yu DG, Yi T (2023) Dual-step controlled release of berberine hydrochloride from the trans-scale hybrids of nanofibers and microparticles. Biomolecules 13(6):1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13061011
Xu L, He H, Du Y, Zhang S, Yu DG, Liu P (2023) Electrosprayed core (cellulose acetate)–shell (polyvinylpyrrolidone) nanoparticles for smart acetaminophen delivery. Pharmaceutics 15(9):2314. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15092314
Yu DG, Xu L (2023) Impact evaluations of articles in current drug delivery based on web of science. Curr Drug Deliv 21(3):360–367. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567201820666230508115356
Lv H, Liu Y, Bai Y, Shi H, Zhou W, Chen Y, Liu Y, Yu DG (2023) Recent combinations of electrospinning with photocatalytic technology for treating polluted water. Catalysts 13(4):758. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13040758
Arun A, Malrautu P, Laha A, Ramakrishna S (2021) Gelatin nanofibers in drug delivery systems and tissue engineering. Eng Sci 16(0):71–81. https://doi.org/10.30919/es8d527
Bhardwaj A K, Pandit A K, Rehalia A, Singh V, Sharma R (2023) A review on nanomaterials for drug delivery systems and application of carbon based nanomaterials. ES Mater Manuf 21:824. https://doi.org/10.30919/esmm5f824
Song N, Ren S, Zhang Y, Wang C, Lu X (2022) Confinement of prussian blue analogs boxes inside conducting polymer nanotubes enables significantly enhanced catalytic performance for water treatment. Adv Funct Mater 32(34):2204751. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202204751
Chen X, Yan S, Wen S, Chen J, Xu J, Wang C, Lu X (2023) Chelating adsorption-engaged synthesis of ultrafine iridium nanoparticles anchored on N-doped carbon nanofibers toward highly efficient hydrogen evolution in both alkaline and acidic media. J Colloid Interface Sci 641:782–790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2023.03.097
Kang S, Hou S, Chen X, Yu DG, Wang L, Li X, Williams RG (2020) Energy-saving electrospinning with a concentric teflon-core rod spinneret to create medicated nanofibers. Polymers 12(10):2421. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102421
Jiang W, Zhang X, Liu P, Zhang Y, Song W, Yu DG, Lu X (2022) Electrospun healthcare nanofibers from medicinal liquor of phellinus igniarius. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5(4):3045–3056. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00551-x
Wang M, Hou J, Yu DG, Li S, Zhu J, Chen Z (2020) Electrospun tri-layer nanodepots for sustained release of acyclovir. J Alloy Compd 846:156471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156471
Liu H, Dai Y, Li J, Liu P, Zhou W, Yu DG, Ge R (2023) Fast and convenient delivery of fluidextracts liquorice through electrospun core-shell nanohybrids. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 11:1172133. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2023.1172133
Peppas NA (1985) Analysis of fickian and non-fickian drug release from polymers. Pharm Acta Helv 60(4):110–111. PMID:4011621
Bahaar H, Reddy SG, Kumar BS et al (2023) Modified layered double hydroxide – PEG magneto-sensitive hydrogels with suitable ligno-alginate green polymer composite for prolonged drug delivery applications. Eng Sci 24:914. https://doi.org/10.30919/es914
Meng X, Li Y, AlMasoud N, Wang W, Alomar TS, Li J, Ye X, Algadi H, Seok I, Li H, Xu BB, Lu N, El-Bahy ZM, Guo Z (2023) Compatibilizing and toughening blends of recycled acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene/recycled high impact polystyrene blends via styrene-butadiene-glycidyl methacrylate terpolymer. Polymer 272:125856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2023.125856
Li T, Wei H, Zhang Y, Wan T, Cui D, Zhao S, Zhang T, Ji Y, Algadi H, Guo Z, Chu L, Cheng B (2023) Sodium alginate reinforced polyacrylamide/xanthan gum double network ionic hydrogels for stress sensing and self-powered wearable device applications. Carbohyd Polym 309:120678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.120678
Gao F, Liu Y, Jiao C, El‐Bahy SM, Shao Q, El‐Bahy ZM, Li H, Wasnik P, Algadi H, Xu BB, Wang N, Yuan Y, Guo Z (2023) Fluorine-phosphate copolymerization waterborne acrylic resin coating with enhanced anticorrosive performance. J Polym Sci Pol 20230108. https://doi.org/10.1002/pol.20230108
Dong N, Liu Z, He H, Lu Y, Qi J, Wu W (2023) “Hook&Loop” multivalent interactions based on disk-shaped nanoparticles strengthen active targeting. J Controlled Release 354:279–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.01.022
Zhang T, Li L, Chunta S, Wu W, Chen Z, Lu Y (2023) Enhanced oral bioavailability from food protein nanoparticles: a mini review. J Controlled Release 354:146–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.12.043
Man F, Yang Y, He H, Qi J, Wu W, Lu Y (2023) Establishment of in vitro dissolution based on similarity with in vivo dissolution: a case study on aripiprazole. Mol Pharmaceutics 20(5):2579–2588. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.3c00014
Wang X, Feng C (2023) Chiral fiber supramolecular hydrogels for tissue engineering. Wiley Wires Nanomed Nanobi 15(2):e1847. https://doi.org/10.1002/wnan.1847
Acknowledgements
Mr. Yingfu Bai’s precious help on the investigations are highly appreciated.
Funding
Shanghai Natural Science Foundation (nos. 21ZR1459500 and 20ZR1439000), the Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning Foundation of Shanghai (no. 202140413), the Medical Health Science and Technology Innovation Plan of Jinan (nos. 202019202 and 202134037), the Science and technology innovation project of Medical staff in Shandong Province, the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (nos. ZR2020QH264 and ZR2021MH129), the Science and Technology Development Fund of Macao Special Administrative Region (0061/2023/RIA1), and the Macao Polytechnic University Research Fund (RP/FCSD-01/2023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Jianfeng Zhou, Tao Yi, Zhiyuan Zhang and Liangzhe Wang. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Jianfeng Zhou and Tao Yi, and all authors commented on the previous versions of the manuscript. Jianfeng Zhou, Tao Yi, and Zhiyuan Zhang contributed to the data curation and the preparation of figures. Tao Yi, Deng-Guang Yu, and Ping Liu acquired the funding. Ping Liu, Liangzhe Wang, and Yuanjie Zhu edited and proofread the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Yi, T., Zhang, Z. et al. Electrospun Janus core (ethyl cellulose//polyethylene oxide) @ shell (hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose acetate succinate) hybrids for an enhanced colon-targeted prolonged drug absorbance. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 6, 189 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-023-00766-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-023-00766-6