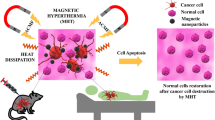
Abstract
Precise magnetic hyperthermia/chemo synergistic therapy has attracted great attention as a promising cancer therapy. However, how to improve the hyperthermia efficiency and precisely control the drug release in vivo are still challenging issues associated with the clinical precision medicine of cancers. To solve these problems, magnetic vortex Fe3O4@PVP@DOX nanostructures with magneto-triggered on-demand hyperthermia, magnetic responsive controllable drug delivery functions, and MRI T2-weighted signal enhancement were successfully developed for the hyperthermia and chemotherapy synergetic theranostic of cancers. This strategy utilizes the advantage of magnetic field stimulus which can be on-demand applied to any organ without taking account of the depth. In vitro experiments reveal the excellent on-demand heating efficiency, magnetic-responsive drug release, high MRI T2 signals and low cytotoxicity. More importantly, the results of in vivo animal experiments show that the magnetic vortex nanoplatform can effectively perform magnetic response on-demand heat therapy, and DOX drug release in the presence of a magnetic field, leading to an efficient synergistic effect in inhibiting tumor growth without any side effect. Therefore, these magnetic-responsive magnetic vortex nanostructures provide us a new strategy for the development of next-generation stimuli-responsive multifunctional theranostic platform for the clinical precision medicine of cancers.
Graphical abstract

The multifunctional nanoplatform with an excellent heating efficiency was successfully developed for synergetic theranostic with enhanced MRI contrast.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gao F, Zhang T, Liu X, Ghosal A, Zhao L (2019) Non-magnetic hypertonic saline based implant for breast cancer postsurgical recurrence prevention by magnetic field/pH-driven thermochemotherapy. Acs Appl Mater Interfaces 11:10597–10607
Fan W, Yung B, Huang P, Chen X (2017) Nanotechnology for multimodal synergistic cancer therapy. Chem Rev 117:13566–13638
Ghosh SG, Pramanik S, N. (2020) Bio-evaluation of doxorubicin (DOX)-incorporated hydroxyapatite (HAp)-chitosan (CS) nanocomposite triggered on osteosarcoma cells. Adv Compos Hybrid Ma 3:303–314
Jia W, Qi Y, Hu Z, Xiong Z, Luo Z, Xiang Z, Hu J, Lu W (2021) Facile fabrication of monodisperse CoFe2O4 nanocrystals@dopamine@DOX hybrids for magnetic-responsive on-demand cancer theranostic applications. Adv Compos Hybrid Ma 4:989–1001
Liu X, Zheng J, Sun W, Zhao X, Li Y, Gong N, Wang Y, Ma X, Zhang T, Zhao L-Y (2019) Ferrimagnetic vortex nanoring-mediated mild magnetic hyperthermia imparts potent immunological effect for treating cancer metastasis. ACS Nano 13:8811–8825
Zhou P, Zhao H, Wang Q, Zhou Z, Wang J, Deng G, Wang X, Liu Q, Yang H, Yang S (2018) Photoacoustic-enabled self-guidance in magnetic-hyperthermia Fe@Fe3 O4 nanoparticles for theranostics in vivo. Adv Healthc Mater 7:e1701201
Hijnen N, Kneepkens E, de Smet M, Langereis S, Heijman E, Grull H (2017) Thermal combination therapies for local drug delivery by magnetic resonance-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:E4802–E4811
lian Y, Wang L, Cao J, Liu T, Xu Z, Yang B, Huang T, Jiang X, Wu N, (2021) Recent advances on the magnetic nanoparticle–based nanocomposites for magnetic induction hyperthermia of tumor: a short review. Adv Compos Hybrid Ma 4:925–937
Hu Q, Zhou J, Qiu B, Wang Q, Song G, Guo Z (2021) Synergistically improved methane production from anaerobic wastewater treatment by iron/polyaniline composite. Adv Compos Hybrid Ma 4:265–273
Zhang M, Du H, Liu K, Nie S, Xu T, Zhang X, Si C (2021) Fabrication and applications of cellulose-based nanogenerators. Adv Compos Hybrid Ma 4:865–884
Noh SH, Moon SH, Shin TH, Lim Y, Cheon J (2017) Recent advances of magneto-thermal capabilities of nanoparticles: From design principles to biomedical applications. Nano Today 13:61–76
Hayashi K, Nakamura M, Miki H, Ozaki S, Abe M, Matsumoto T, Sakamoto W, Yogo T, Ishimura K (2014) Magnetically responsive smart nanoparticles for cancer treatment with a combination of magnetic hyperthermia and remote-control drug release. Theranostics 4:834–844
Oh Y, Lee N, Kang HW, Oh J (2016) In vitro study on apoptotic cell death by effective magnetic hyperthermia with chitosan-coated MnFe(2)O(4). Nanotechnology 27:115101
Pereira C, Pereira AM, Fernandes C, Rocha M, Mendes R, Fernández-García MP, Guedes A, Tavares PB, Grenèche J-M, Araújo JP, Freire C (2012) Superparamagnetic MFe2O4 (M = Fe Co, Mn) nanoparticles: tuning the particle size and magnetic properties through a novel one-step coprecipitation route. Chem Mater 24:1496–1504
Tong S, Quinto CA, Zhang L, Mohindra P, Bao G (2017) Size-dependent heating of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. ACS Nano 11:6808–6816
Lee JH, Jang JT, Choi JS, Moon SH, Noh SH, Kim JW, Kim JG, Kim IS, Park KI, Cheon J (2011) Exchange-coupled magnetic nanoparticles for efficient heat induction. Nat Nanotechnol 6:418–422
Johannsen M, Gneveckow U, Thiesen B, Taymoorian K, Cho CH, Waldofner N, Scholz R, Jordan A, Loening SA, Wust P (2007) Thermotherapy of prostate cancer using magnetic nanoparticles: feasibility, imaging, and three-dimensional temperature distribution. Eur Urol 52:1653–1661
Guo Y, Zhang Y, Ma J, Li Q, Li Y, Zhou X, Zhao D, Song H, Chen Q, Zhu X (2018) Light/magnetic hyperthermia triggered drug released from multi-functional thermo-sensitive magnetoliposomes for precise cancer synergetic theranostics. J Control Release 272:145–158
Xu C, Feng Q, Yang H, Wang G, Huang L, Bai Q, Zhang C, Wang Y, Chen Y, Cheng Q, Chen M, Han Y, Yu Z, Lesniak MS, Cheng Y (2018) A Light-triggered mesenchymal stem cell delivery system for photoacoustic imaging and chemo-photothermal therapy of triple negative breast cancer. Adv Sci 5:1800382
Xiang Z, Shi Y, Zhu X, Cai L, Lu W (2021) Flexible and waterproof 2D/1D/0D construction of MXene-based nanocomposites for electromagnetic wave absorption, emi shielding, and photothermal conversion. Nanomicro Lett 13:150
Zhang Y, Ruan K, Gu J (2021) Flexible sandwich-structured electromagnetic interference shielding nanocomposite films with excellent thermal conductivities. Small 17:e2101951
Park J, Aryal M, Vykhodtseva N, Zhang YZ, McDannold N (2017) Evaluation of permeability, doxorubicin delivery, and drug retention in a rat brain tumor model after ultrasound-induced blood-tumor barrier disruption. J Control Release 250:77–85
Xiang Z, Wang X, Zhang X, Shi Y, Cai L, Zhu X, Dong Y, Lu W (2022) Self-assembly of nano/microstructured 2D Ti3CNTx MXene-based composites for electromagnetic pollution elimination and Joule energy conversion application. Carbon 189:305–318
Xiang Z, Huang C, Song Y, Deng B, Zhang X, Zhu X, Batalu D, Tutunaru O, Lu W (2020) Rational construction of hierarchical accordion-like Ni@porous carbon nanocomposites derived from metal-organic frameworks with enhanced microwave absorption. Carbon 167:364–377
Zhang TT, Xu CH, Zhao W, Gu Y, Li XL, Xu JJ, Chen HY (2018) A redox-activated theranostic nanoagent: toward multi-mode imaging guided chemo-photothermal therapy. Chem Sci 9:6749–6757
Bae Y, Fukushima S, Harada A, Kataoka K (2003) Design of environment-sensitive supramolecular assemblies for intracellular drug delivery: polymeric micelles that are responsive to intracellular pH change. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 42:4640–4643
Wang H, Di J, Sun YB, Fu JP, Wei ZY, Matsui H, Alonso AD, Zhou SQ (2015) Biocompatible PEG-Chitosan@Carbon dots hybrid nanogels for two-photon fluorescence imaging, near-infrared light/pH dual-responsive drug carrier, and synergistic therapy. Adv Func Mater 25:5537–5547
Xu X, Wu J, Liu Y, Yu M, Zhao L, Zhu X, Bhasin S, Li Q, Ha E, Shi J, Farokhzad OC (2016) Ultra-pH-responsive and tumor-penetrating nanoplatform for targeted siRNA delivery with robust anti-cancer efficacy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 55:7091–7094
Huang P, Gao Y, Lin J, Hu H, Liao H-S, Yan X, Tang Y, Jin A, Song J, Niu G, Zhang G, Horkay F, Chen X (2015) Tumor-specific formation of enzyme-instructed supramolecular self-assemblies as cancer theranostics. ACS Nano 9:9517–9527
Tanaka A, Fukuoka Y, Morimoto Y, Honjo T, Koda D, Goto M, Maruyama T (2015) Cancer cell death induced by the intracellular self-assembly of an enzyme-responsive supramolecular gelator. J Am Chem Soc 137:770–775
Zhang H, Fei J, Yan X, Wang A, Li J (2015) Enzyme-responsive release of doxorubicin from monodisperse dipeptide-based nanocarriers for highly efficient cancer treatment in vitro. Adv Func Mater 25:1193–1204
Yun CK, Hwang JW, Kwak TJ, Chang WJ, Ha S, Han K, Lee S, Choi YS (2019) Nanoinjection system for precise direct delivery of biomolecules into single cells. Lab Chip 19:580–588
Dong Y, Zhu X, Pan F, Deng B, Liu Z, Zhang X, Huang C, Xiang Z, Lu W (2021) Mace-like carbon fiber/ZnO nanorod composite derived from Typha orientalis for lightweight and high-efficient electromagnetic wave absorber. Adv Compos Hybrid Ma 4:1002–1014
Lee JH, Chen KJ, Noh SH, Garcia MA, Wang H, Lin WY, Jeong H, Kong BJ, Stout DB, Cheon J, Tseng HR (2013) On-demand drug release system for in vivo cancer treatment through self-assembled magnetic nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 52:4384–4388
Chen W, Cheng CA, Zink JI (2019) Spatial, temporal, and dose control of drug delivery using noninvasive magnetic stimulation. ACS Nano 13:1292–1308
Li M, Deng L, Li J, Yuan W, Gao X, Ni J, Jiang H, Zeng J, Ren J, Wang P (2018) Actively targeted magnetothermally responsive nanocarriers/doxorubicin for thermochemotherapy of hepatoma. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:41107–41117
Guo Y, Qiu H, Ruan K, Zhang Y, Gu J (2021) Hierarchically multifunctional polyimide composite films with strongly enhanced thermal conductivity. Nanomicro Lett 14:26
Gao Q, Pan Y, Zheng G, Liu C, Shen C, Liu X (2021) Flexible multilayered MXene/thermoplastic polyurethane films with excellent electromagnetic interference shielding, thermal conductivity, and management performances. Adv Compos Hybrid Ma 4:274–285
Chen L, Lan C, Xu B, Bi K (2021) Progress on material characterization methods under big data environment. Adv Compos Hybrid Ma 4:235–247
Moradi O, Madanpisheh MA, Moghaddas M (2021) Synthesis of GO/HEMA, GO/HEMA/TiO2, and GO/Fe3O4/HEMA as novel nanocomposites and their dye removal ability. Adv Compos Hybrid Ma 4:1185–1204
Fan HM, Yi JB, Yang Y, Kho KW, Tan HR, Shen ZX, Ding J, Sun XW, Olivo MC, Feng YPJAN (2009) Single-crystalline MFe(2)O(4) nanotubes/nanorings synthesized by thermal transformation process for biological applications. 3:2798–808
Liu XL, Yang Y, Ng CT, Zhao LY, Zhang Y, Bay BH, Fan HM, Ding J (2015) Magnetic vortex nanorings: a new class of hyperthermia agent for highly efficient in vivo regression of tumors. Adv Mater 27:1939–1944
Liu X, Zheng J, Sun W, Zhao X, Li Y, Gong N, Wang Y, Ma X, Zhang T, Zhao LY, Hou Y, Wu Z, Du Y, Fan H, Tian J, Liang XJ (2019) Ferrimagnetic vortex nanoring-mediated mild magnetic hyperthermia imparts potent immunological effect for treating cancer metastasis. ACS Nano 13:8811–8825
Wang X, Pan F, Xiang Z, Zeng Q, Pei K, Che R, Lu W (2020) Magnetic vortex core-shell Fe3O4@C nanorings with enhanced microwave absorption performance. Carbon 157:130–139
Yang Y, Liu X-L, Yi JB, Yang Y, Fan HM, Ding J (2012) Stable vortex magnetite nanorings colloid: Micromagnetic simulation and experimental demonstration. J Appl Phys 111:044303
Rothman J, Klaui M, Lopez-Diaz L, Vaz CA, Bleloch A, Bland JA, Cui Z, Speaks R (2001) Observation of a bi-domain state and nucleation free switching in mesoscopic ring magnets. Phys Rev Lett 86:1098–1101
Zhu FQ, Chern GW, Tchernyshyov O, Zhu XC, Zhu JG, Chien CL (2006) Magnetic bistability and controllable reversal of asymmetric ferromagnetic nanorings. Phys Rev Lett 96:027205
Moroz P, Jones SK, Gray BN (2002) Magnetically mediated hyperthermia: current status and future directions. Int J Hyperth 18:267–284
Hergt R, Dutz S (2007) Magnetic particle hyperthermia-biophysical limitations of a visionary tumour therapy. J Magn Magn Mater 311:187–192
Das R, Alonso J, Nemati Porshokouh Z, Kalappattil V, Torres D, Phan M-H, Garaio E, García JÁ, Sanchez Llamazares JL, Srikanth H (2016) Tunable high aspect ratio iron oxide nanorods for enhanced hyperthermia. J Physical Chem C 120:10086–10093
Noh SH, Na W, Jang JT, Lee JH, Lee EJ, Moon SH, Lim Y, Shin JS, Cheon J (2012) Nanoscale magnetism control via surface and exchange anisotropy for optimized ferrimagnetic hysteresis. Nano Lett 12:3716–3721
Espinosa A, Di Corato R, Kolosnjaj-Tabi J, Flaud P, Pellegrino T, Wilhelm C (2016) Duality of iron oxide nanoparticles in cancer therapy: amplification of heating efficiency by magnetic hyperthermia and photothermal bimodal treatment. ACS Nano 10:2436–2446
He S, Zhang H, Liu Y, Sun F, Yu X, Li X, Zhang L, Wang L, Mao K, Wang G, Lin Y, Han Z, Sabirianov R, Zeng H (2018) Maximizing specific loss power for magnetic hyperthermia by hard-soft mixed ferrites. Small 14:1800135
Yang Y, Liu X, Lv Y, Herng TS, Xu X, Xia W, Zhang T, Fang J, Xiao W, Ding J (2015) Orientation mediated enhancement on magnetic hyperthermia of Fe3O4Nanodisc. Adv Func Mater 25:812–820
Fortin J-P, Wilhelm C, Servais J, Ménager C, Bacri J-C, Gazeau F (2007) Size-sorted anionic iron oxide nanomagnets as colloidal mediators for magnetic hyperthermia. J Am Chem Soc 129:2628–2635
Guardia P, Di Corato R, Lartigue L, Wilhelm C, Espinosa A, Garcia-Hernandez M, Gazeau F, Manna L, Pellegrino T (2012) Water-soluble iron oxide nanocubes with high values of specific absorption rate for cancer cell hyperthermia treatment. ACS Nano 6:3080–3091
Sathya A, Guardia P, Brescia R, Silyestri N, Pugliese G, Nitti S, Manna L, Pellegrino T (2016) CoxFe3-xO4 nanocubes for theranostic applications: effect of cobalt content and particle size. Chem Mater 28:1769–1780
Jung CW, Jacobs P (1995) Physical and chemical properties of superparamagnetic iron oxide MR contrast agents: ferumoxides, ferumoxtran, ferumoxsil. J Magnetic resonance imaging 13:661–674
Wang Y-XJ, Hussain SM, Krestin GP (2001) Superparamagnetic iron oxide contrast agents: physicochemical characteristics and applications in MR imaging. J European radiology 11:2319–2331
Wang Y-XJ (2011) Superparamagnetic iron oxide based MRI contrast agents: current status of clinical application. J Quantitative imaging in medicine surgery 1:35–40
Orza A, Wu H, Xu Y, Lu Q, Mao H (2017) One-step facile synthesis of highly magnetic and surface functionalized iron oxide nanorods for biomarker-targeted applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:20719–20727
Caetano BL, Guibert C, Fini R, Fresnais J, Pulcinelli SH, Ménager C, Santilli CV (2016) Magnetic hyperthermia-induced drug release from ureasil-PEO-γ-Fe2O3 nanocomposites. RSC Adv 6:63291–63295
Moroz P, Jones SK, Gray BN (2002) Magnetically mediated hyperthermia: current status and future directions. Int J Hyperthermia 18:267–284
Pankhurst QA, Connolly J, Jones SK, Dobson J (2003) Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J Phys D Appl Phys 36:167–181
Thirunavukkarasu GK, Cherukula K, Lee H, Jeong YY, Park I-K, Lee JY (2018) Magnetic field-inducible drug-eluting nanoparticles for image-guided thermo-chemotherapy. Biomaterials 180:240–252
May JP, Li SD (2013) Hyperthermia-induced drug targeting. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 10:511–527
Funding
This project has been assisted by the program of Shanghai Technology Research Leader (18XD1423800), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No 51671146, 51971162, U1933112), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, Shanghai Collaborative Innovation Program on Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research (2019CXJQ01), and the “Crossover” Research Fund of the Ninth People's Hospital of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (No. JYJC202102).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Qi, Y., Hu, Z. et al. Fe3O4@PVP@DOX magnetic vortex hybrid nanostructures with magnetic-responsive heating and controlled drug delivery functions for precise medicine of cancers. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5, 1786–1798 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00433-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00433-2