Abstract
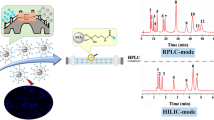
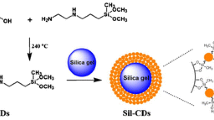
In this paper, silicon quantum dots (SiQDs) with green fluorescence are synthesized by solvothermal reaction of 3-(2,3-epoxypropoxy)propyltrimethoxysilane (GPTMS) and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), and then SiQDs are bonded to the surface of silica to obtain a new nano-on-micro stationary phase (SiO2-SiQDs) for reversed-phase chromatography. The successful preparation of SiO2-SiQDs stationary phase is demonstrated by a variety of characterizations, such as transmission electron microscopy, laser confocal microscopy, elemental analysis and Fourier infrared spectroscopy. In addition, the chromatographic performance of the prepared stationary phase is evaluated and it shows good separation performance for non-polar substances such as alkylbenzene, aniline and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in reversed-phase liquid chromatography. It is also verified that the stationary phase has good methyl selectivity and shape selectivity. More interestingly, the separation of prednisolone and hydrocortisone isomers can also be achieved at a low ratio of organic solvents, indicating that this new stationary phase has a good application prospect in isomer separation.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within this article and its supplementary materials.
References
Zhang L, Dai Q, Qiao X, Yu C, Qin X, Yan H. Mixed-mode chromatographic stationary phases: recent advancements and its applications for high-performance liquid chromatography. TrAC-Trends Anal Chem. 2016;82:143–63.
Dogra A, Sharma A, Kumar Mandal U, Kotwal P, Bhatt S, Nandi U. Liquid chromatography based methods for analysis of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) in biological matrices. Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2019;49(3):224–42.
Gülfen M, Canbaz Y, Özdemir A. Simultaneous determination of amoxicillin, lansoprazole, and levofloxacin in pharmaceuticals by HPLC with UV–vis detector. J Anal Test. 2020;4(1):45–53.
Hakami AAH, Wabaidur SM, Ali KM, Abdullah AZ, Rafatullah M, Siddiqui MR. Development of ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method for simultaneous determination of three cationic dyes in environmental samples. Molecules. 2020;25(19):4546.
Gao S, Wu G, Li X, Chen J, Wu Y, Wang J, Zhang Z. Determination of triazine herbicides in environmental water samples by acetonitrile inorganic salt aqueous two-phase microextraction system. J Anal Test. 2018;2(4):322–31.
Zhang X, Yang Y, Qin P, Han L, Zhu W, Duan S, Lu M, Cai Z. Facile preparation of nano-g-C3N4/UiO-66-NH2 composite as sorbent for high-efficient extraction and preconcentration of food colorants prior to HPLC analysis. Chin Chem Lett. 2022;33(2):903–6.
Yang J, Yim H, Lee J, Gu J, Lee B, Hwang YH, Ma Y. Simultaneous determination of nine bioactive compounds in Yijin-tang via high-performance liquid chromatography and liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. Integr Med Res. 2016;5(2):140–50.
Meng L, De L, Yang N, Yan L, Xiao Q. Exploiting styrene-maleic acid copolymer grafting chromatographic stationary phase materials for separation of membrane lipids. Chin Chem Lett. 2022;3:3123–6.
Bai YL, Hong ZD, Zhang TY, Cai BD, Zhang YZ, Feng YQ. A method for simultaneous determination of 14 carbonyl-steroid hormones in human serum by ultra high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Anal Test. 2020;4(1):1–12.
Chong HS, Sim S, Yamaguchi T, Park J, Lee C, Kim M, Lee G, Yun SS, Lim HS, Suh HJ. Simultaneous determination of sodium iron chlorophyllin and sodium copper chlorophyllin in food using high-performance liquid chromatography and ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2019;276:390–6.
Tijare LK, Nt R, Un M. A review on bioanalytical method development and validation. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. 2016;9(9):6–10.
Shen S, Chang C, Shen C, Xu H, Miao S, Wills S. Quantitative analysis of azodicarbonamide in insulation layers of extruded cables by HPLC–UV detection. J Anal Test. 2021;5:370–8.
Jiang P, Lucy CA. Retentivity, selectivity and thermodynamic behavior of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on charge-transfer and hypercrosslinked stationary phases under conditions of normal phase high performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 2016;1437:176–82.
Guo D, Tang T, Huang S, Zhu Y. Methoxy terminated poly dimethylsiloxane bonded stationary phase for reversed-phase liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 2021;1652: 462348.
Liu X, Wang Y, Cong H, Shen Y, Yu B. A review of the design of packing materials for ion chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 2021;1653: 462313.
Francois I, Villiers A, Sandra P. Considerations on the possibilities and limitations of comprehensive normal phase-reversed phase liquid chromatography (NPLC × RPLC). J Sep Sci. 2006;29(4):492–8.
Mansfield ER, Mansfield DS, Patterson JE, Knotts TA. Effects of chain grafting positions and surface coverage on conformations of model reversed-phase liquid chromatography stationary phases. J Phys Chem C. 2012;116(15):8456–64.
Liu Z, Quan K, Li H, Chen J, Guan M, Qiu H. Preparation of silica-based superficially porous silica and its application in enantiomer separations: a review. J Anal Test. 2021;5(3):242–57.
Hong G, Diao S, Antaris AL, Dai H. Carbon nanomaterials for biological imaging and nanomedicinal therapy. Chem Rev. 2015;115(19):10816–906.
Speltini A, Merli D, Profumo A. Analytical application of carbon nanotubes, fullerenes and nanodiamonds in nanomaterials-based chromatographic stationary phases: a review. Anal Chim Acta. 2013;783:1–16.
Chen J, Gong Z, Tang W, Row KH, Qiu H. Carbon dots in sample preparation and chromatographic separation: recent advances and future prospects. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 2021;134: 116135.
Liu Q, Shi J, Sun J, Wang T, Zeng L, Jiang G. Graphene and graphene oxide sheets supported on silica as versatile and high-performance adsorbents for solid-phase extraction. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2011;50(26):5913–7.
Chen J, Yuan N, Jiang D, Lei Q, Liu B, Tang W, Row KH, Qiu H. Octadecylamine and glucose-coderived hydrophobic carbon dots-modified porous silica for chromatographic separation. Chin Chem Lett. 2021;32(11):3398–401.
Jiang D, Chen J, Guan M, Qiu H. Octadecylimidazolium ionic liquids-functionalized carbon dots and their precursor co-immobilized silica as hydrophobic chromatographic stationary phase with enhanced shape selectivity. Talanta. 2021;233: 122513.
Yuan N, Chen J, Cai T, Li Z, Guan M, Zhao L, Qiu H. Glucose-based carbon dots-modified silica stationary phase for hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 2020;1619: 460930.
Fu G, Chen J, Qiu H. Deep eutectic solvents-derivated carbon dots-decorated silica stationary phase with enhanced separation selectivity in reversed-phase liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 2022;1681: 463425.
Song L, Zhang H, Chen J, Li Z, Guan M, Qiu H. Imidazolium ionic liquids-derived carbon dots-modified silica stationary phase for hydrophilic interaction chromatography. Talanta. 2020;209: 120518.
Saraiva A, Lim WH, Yang CH, Escott CC, Laucht A, Dzurak AS. Materials for silicon quantum dots and their impact on electron spin qubits. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;32:2105488.
Yang J, Gao Y. A dipole-dipole interaction tuning the photoluminescence of silicon quantum dots in a water vapor environment. Nanoscale. 2019;11(4):1790–7.
Robidillo CJT, Veinot JGC. Functional bio-inorganic hybrids from silicon quantum dots and biological molecules. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(47):52251–70.
Han Y, Wang Y, Liu X, Chen J, Qiu H. Green- and red-emitting fluorescent silicon nanoparticles: synthesis, mechanism, and acid phosphatase sensing. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2022;5(1):295–304.
Chen Y, Sun L, Liao F, Dang Q, Shao M. Fluorescent-stable and water-soluble two-component-modified silicon quantum dots and their application for bioimaging. J Lumin. 2019;215: 116644.
Fu M, Fu R, Takada M, Sugimoto H. Silicon quantum dot supraparticles for fluorescence bioimaging. ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2020;3(6):6099–107.
Roy D, Mukhuty A, Fouzder C, Bar N, Chowdhury S, Kundu R, Chowdhury P. Multi-emissive biocompatible silicon quantum dots: synthesis, characterization, intracellular imaging and improvement of two-fold drug efficacy. Dyes Pigments. 2021;86: 109004.
Yi Z, Xiao S, Si W, Fei P, Feng B. Facile, large-quantity synthesis of stable, tunable-color silicon nanoparticles and their application for long-term cellular imaging. ACS Nano. 2015;9(6):5958–67.
Das A, Snee PT. Synthetic developments of nontoxic quantum dots. Chem Phys Chem. 2016;17(5):598–617.
Li X, He Y, Swihart MT. Surface functionalization of siliconnanoparticles roduced by laser-driven pyrolysis of silane followed by HF-HNO3 etching. Langmuir. 2004;20:4720–7.
Peng X, Long Q, Li H, Zhang Y, Yao S. “Turn on-off” fluorescent sensor for protamine and heparin based on label-free silicon quantum dots coupled with gold nanoparticles. Sens Actuat B Chem. 2015;213:131–8.
Tilley RD, Yamamoto K. The microemulsion synthesis of hydrophobic and hydrophilic silicon nanocrystals. Adv Mater. 2006;18(15):2053–6.
Atkins TM, Thibert A, Larsen DS, Dey S, Browning ND, Kauzlarich SM. Femtosecond ligand/core dynamics of microwave-assisted synthesized silicon quantum dots in aqueous solution. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133(51):20664–7.
Mei H, Wang R, Ren W, Zhang Y. The grafting reaction of epoxycyclohexyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes with carboxylic methoxypolyethylene glycols and the properties of composite solid polymer electrolytes with the graftomer. J Appl Polym Sci. 2017;134(7):44460.
Wei N, Wei X, Huang H, Guo F, Wang H. One-pot facile synthesis of green-emitting fluorescent silicon quantum dots for the highly selective and sensitive detection of nitrite in food samples. Dyes Pigments. 2021;184: 108848.
Borges EM, Euerby MR, Collins CH. Comparison of classical chromatographic tests with a chromatographic test applied to stationary phases prepared by thermal immobilization of poly(methyloctylsiloxane) onto silica. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012;404(10):2985–3002.
Castilho MB, Gama VS, Santos AL, Faria AM. Polar polymer-immobilized stationary phase for aqueous reversed-phase liquid chromatography. J Liq Chromatogr R T. 2020;44(1–2):25–32.
Finsgar M, Perva-Uzunalic A, Behr H, Ledinek N, Knez Z, Novak Z. An improved reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography method for the analysis of related substances of prednisolone in active ingredient. ACS Omega. 2020;5(14):7987–8000.
Wang Z, Chen J, Sun Q, Peijnenburg WJ. C60-DOM interactions and effects on C60 apparent solubility: a molecular mechanics and density functional theory study. Environ Int. 2011;37(6):1078–82.
Zhang Z, Xia M, Huang P, Di B, Su M. Preparation and evaluation of a bacitracin-bonded silica stationary phase for hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography. Micro Chem J. 2021;170: 106661.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (22074154), Longyuan Youth Innovation and Entrepreneurship Talent (Team) Project (E20492SC), Lanzhou talent innovation and Entrepreneurship Project (2021-RC-35), Science and Technology Project of Science and Technology Bureau of Chengguan District in Lanzhou City (2020JSCX0033), Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (2021420).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DW experiment, software, data curation, investigation, writing—original draft. HL software, discussion. HQ Writing—review & editing, discussion, supervision. JC conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing—review & editing, discussion, supervision. All authors agreed with the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Li, H., Qiu, H. et al. Preparation and Evaluation of Silicon Quantum Dots-Bonded Silica Stationary Phase for Reversed-Phase Chromatography. J. Anal. Test. 7, 8–15 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41664-022-00243-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41664-022-00243-x