Abstract
Carbon dots derivatized from N-(β-aminoethyl)-γ-aminopropyl-methyldimethoxysilane (AEAPMS) were coated onto silica microparticles. These particles (Sil-CDs) are shown to be an excellent stationary phase for use in hydrophilic interaction chromatography. Analytes including sulfonamides, nucleosides and bases, flavones and amino acids can be well separated on this stationary phase. Compared to a silica stationary phase functionalized with AEAPMS only, the Sil-CDs show enhanced separation performance. The selectivity factors of three nucleosides and bases (1.02–1.09) and four sulfonamides (1.04–1.11) on AEAPMS functionalized silica stationary phase were improved to 1.10–1.20 and 1.13–1.15 respectively on Sil-CDs stationary phase. This is attributed to the higher number of surface functional groups due to the introduction of carbon dots. The successful application of the Sil-CDs stationary phase highlights the potential of carbon dots as a modified material in chromatography.

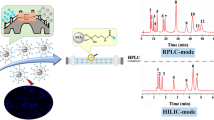
Schematic presentation of the preparation of silanized carbon dots coated onto silica microparticles. The material represents a new stationary phase for hydrophilic interaction chromatography. It shows improved separation performance compared to a silane-only functionalized silica stationary phase.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mallik AK, Qiu H, Kuwahara Y, Takafuji M, Ihara H (2015) A remarkable enhancement of selectivity towards versatile analytes by a strategically integrated H-bonding site containing phase. Chem Commun 51(75):14243–14246
Mallik AK, Qiu H, Oishi T, Kuwahara Y, Takafuji M, Ihara H (2015) Design of C18 organic phases with multiple embedded polar groups for Ultraversatile applications with ultrahigh selectivity. Anal Chem 87(13):6614–6621
Zhang M, Mai W, Zhao L, Guo Y, Qiu H (2015) A polar-embedded C30 stationary phase: preparation and evaluation. J Chromatogr A 1388:133–140
Qiao L, Shi X, Xu G (2016) Recent advances in development and characterization of stationary phases for hydrophilic interaction chromatography. Trends Anal Chem 81:23–33
Nguyen HP, Schug KA (2008) The advantages of ESI-MS detection in conjunction with HILIC mode separations: fundamentals and applications. J Sep Sci 31(9):1465–1480
Alpert AJ (1990) Hydrophilic-interaction chromatography for the separation of peptides, nucleic acids and other polar compounds. J Chromatogr 499(2):177–196
Guo Z, Lei A, Zhang Y, Xu Q, Xue X, Zhang F, Liang X (2007) "click saccharides": novel separation materials for hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography. Chem Commun 24:2491–2493
Liang T, Fu Q, Shen A, Wang H, Jin Y, Xin H, Ke Y, Guo Z, Liang X (2015) Preparation and chromatographic evaluation of a newly designed steviol glycoside modified-silica stationary phase in hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography and reversed phase liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1388:110–118
Shen A, Guo Z, Yu L, Cao L, Liang X (2011) A novel zwitterionic HILIC stationary phase based on "thiol-ene" click chemistry between cysteine and vinyl silica. Chem Commun 47(15):4550–4552
Jandera P (2011) Stationary and mobile phases in hydrophilic interaction chromatography: a review. Anal Chim Acta 692(1–2):1–25
Yu D, Shen A, Guo Z, Yan Y, Yan J, Jin G, Liang X (2015) A controlled thiol-initiated surface polymerization strategy for the preparation of hydrophilic polymer stationary phases. Chem Commun 51(79):14778–14780
Qiu H, Mallik AK, Takafuji M, Jiang S, Ihara H (2012) New poly(ionic liquid)-grafted silica multi-mode stationary phase for anion-exchange/reversed-phase/hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography. Analyst 137(11):2553–2555
Behbahani M, Najafi M, Amini MM, Sadeghi O, Bagheri A, Salarian M (2013) Dithizone-modified nanoporous fructose as a novel sorbent for solid-phase extraction of ultra-trace levels of heavy metals. Microchim Acta 180(9–10):911–920
Behbahani M, Bagheri A, Amini MM, Sadeghi O, Salarian M, Najafi F, Taghizadeh M (2013) Application of multiwalled carbon nanotubes modified by diphenylcarbazide for selective solid phase extraction of ultra traces cd(II) in water samples and food products. Food Chem 141(1):48–53
Tabani H, Fakhari AR, Shahsavani A, Behbahani M, Salarian M, Bagheri A, Nojavan S (2013) Combination of graphene oxide-based solid phase extraction and electro membrane extraction for the preconcentration of chlorophenoxy acid herbicides in environmental samples. J Chromatogr A 1300:227–235
Hosseini H, Behbahani M, Mahyari M, Kazerooni H, Bagheri A, Shaabani A (2014) Ordered carbohydrate-derived porous carbons immobilized gold nanoparticles as a new electrode material for electrocatalytical oxidation and determination of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. Biosens Bioelectron 59:412–417
Jiang B, Liang Y, Wu Q, Jiang H, Yang K, Zhang L, Liang Z, Peng X, Zhang Y (2014) New GO-PEI-au-L-Cys ZIC-HILIC composites: synthesis and selective enrichment of glycopeptides. Nano 6(11):5616–5619
Cai T, Zhang H, Li Z, Rahman AFMM, Qiu H (2016) A new nano-on-micro stationary phase based on nanodiamond bonded on silica for hydrophilic interaction chromatography. RSC Adv 6(39):32757–32760
Li Y, Xu L, Chen T, Liu X, Xu Z, Zhang H (2012) Carbon nanoparticles from corn stalk soot and its novel application as stationary phase of hydrophilic interaction chromatography and per aqueous liquid chromatography. Anal Chim Acta 726:102–108
Zhang M, Qiu H (2015) Progress in stationary phases modified with carbonaceous nanomaterials for high-performance liquid chromatography. Trends Anal Chem 65:107–121
Su Y, Zhang M, Zhou N, Shao M, Chi C, Yuan P, Zhao C (2016) Preparation of fluorescent N, P-doped carbon dots derived from adenosine 5′-monophosphate for use in multicolor bioimaging of adenocarcinomic human alveolar basal epithelial cells. Microchim Acta:1–8
Qu Q, Zhu A, Shao X, Shi G, Tian Y (2012) Development of a carbon quantum dots-based fluorescent Cu2+ probe suitable for living cell imaging. Chem Commun 48(44):5473–5475
Liu W, Li C, Ren Y, Sun X, Pan W, Li Y, Wang J, Wang W (2016) Carbon dots: surface engineering and applications. J Mater Chem B 4(35):5772–5788
Zhu S, Meng Q, Wang L, Zhang J, Song Y, Jin H, Zhang K, Sun H, Wang H, Yang B (2013) Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, sensors, and bioimaging. Angew Chem Int Ed 52(14):3953–3957
Zhou J, Zhou H, Tang J, Deng S, Yan F, Li W, Qu M (2016) Carbon dots doped with heteroatoms for fluorescent bioimaging: a review. Microchim Acta. doi:10.1007/s00604-016-2043-9
Guo Y, Yang L, Li W, Wang X, Shang Y, Li B (2016) Carbon dots doped with nitrogen and sulfur and loaded with copper (II) as a “turn-on” fluorescent probe for cystein, glutathione and homocysteine. Microchim Acta 183(4):1409–1416
Zhuang Z, Lin H, Zhang X, Qiu F, Yang H (2016) A glassy carbon electrode modified with carbon dots and gold nanoparticles for enhanced electrocatalytic oxidation and detection of nitrite. Microchim Acta 183(10):2807–2814
Fernando KA, Sahu S, Liu Y, Lewis WK, Guliants EA, Jafariyan A, Wang P, Bunker CE, Sun YP (2015) Carbon quantum dots and applications in photocatalytic energy conversion. ACS Appl Mater Inter 7(16):8363–8376
Wang Y, Hu A (2014) Carbon quantum dots: synthesis, properties and applications. J Mater Chem C 2(34):6921
Zuo P, Lu X, Sun Z, Guo Y, He H (2015) A review on syntheses, properties, characterization and bioanalytical applications of fluorescent carbon dots. Microchim Acta 183(2):519–542
Wang B, Song A, Feng L, Ruan H, Li H, Dong S, Hao J (2015) Tunable amphiphilicity and multifunctional applications of ionic-liquid-modified carbon quantum dots. ACS Appl Mater Inter 7(12):6919–6925
Gupta A, Chaudhary A, Mehta P, Dwivedi C, Khan S, Verma NC, Nandi CK (2015) Nitrogen-doped, thiol-functionalized carbon dots for ultrasensitive hg(II) detection. Chem Commun 51(53):10750–10753
Zhang H, Qiao X, Cai T, Chen J, Li Z, Qiu H (2017) Preparation and characterization of carbon dot-decorated silica stationary phase in deep eutectic solvents for hydrophilic interaction chromatography. Anal Bioanal Chem 409(9):2401–2410
Liu X, Zhang N, Bing T, Shangguan D (2014) Carbon dots based dual-emission silica nanoparticles as a ratiometric nanosensor for cu(2+). Anal Chem 86(5):2289–2296
Wang C, Xu Z, Lin H, Huang Y, Zhang C (2015) Large scale synthesis of Highly stable fluorescent carbon dots using silica spheres as carriers for targeted Bioimaging of cancer cells. Part Part Syst Charact 32(10):944–951
Xie Z, Wang F, Liu CY (2012) Organic-inorganic hybrid functional carbon dot gel glasses. Adv Mater 24(13):1716–1721
Wang F, Xie Z, Zhang H, C-y L, Zhang Y (2011) Highly luminescent Organosilane-functionalized carbon dots. Adv Funct Mater 21(6):1027–1031
Chirita RI, West C, Zubrzycki S, Finaru AL, Elfakir C (2011) Investigations on the chromatographic behaviour of zwitterionic stationary phases used in hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1218(35):5939–5963
Wang J, Guo Z, Shen A, Yu L, Xiao Y, Xue X, Zhang X, Liang X (2015) Hydrophilic-subtraction model for the characterization and comparison of hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography columns. J Chromatogr A 1398:29–46
Acknowledgements
Financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21475142, 21611140105), CAS President’s International Fellowship Initiative (SL: 191), the funds for Distinguished Young Scientists of Gansu (1506RJDA281) and the top priority program of “One-Three-Five” Strategic Planning of Chinese Academy of Sciences are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2075 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, T., Zhang, H., Rahman, A.F.M.M. et al. Silica grafted with silanized carbon dots as a nano-on-micro packing material with enhanced hydrophilic selectivity. Microchim Acta 184, 2629–2636 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2277-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2277-1