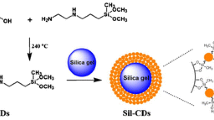
Abstract
In this work, phosphorus-doped carbon dots (P-DESCDs) were successfully prepared using choline chloride/lactic acid type deep eutectic solvent and phosphoric acid as ingredients, and (3-aminopropyl) trimethoxysilane was used as a bridge to graft P-DESCDs onto the silica surface to obtain a new mixed-mode stationary phase (Sil-P-DESCDs) for reversed-phase and hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography. The successful preparation of the stationary phase was confirmed by laser scanning confocal microscopy, elemental analysis, and Fourier transform infrared spectrometry. Interestingly, the doping of phosphorus greatly improved the separation performance and hydrophilicity of the Sil-P-DESCDs column. The Sil-P-DESCDs column was found to have certain hydrophobicity, hydrogen bonding ability and shape selectivity by Tanaka and Engelhardt standard test mixtures, and a series of hydrophilic and hydrophobic compounds such as alkylbenzenes, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, sulfonamides, aromatic amines, phenols, flavonoids, nucleoside bases, and alkaloids. In addition, the effects of mobile phase ratio, column temperature, flow rate, salt concentration, and pH on the retention of analytes on Sil-P-DESCDs columns were investigated. Finally, the Sil-P-DESCDs column was applied to the qualitative and quantitative analysis of calcein-7-glucoside in the real sample of medicinal Astragalus pellets, and it was found at a concentration of 0.02 mg/mL.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khoo HT, Leow CH. Advancements in the preparation and application of monolithic silica columns for efficient separation in liquid chromatography. Talanta. 2021;224:121777.
Fan F, Pan J, Li Y, Wang L, Wang S, Liang X, Guo Y. A novel double polymer modified hydrophobic/hydrophilic stationary phase for liquid chromatography. Chin Chem Lett. 2020;31:746–50.
Song L, Zhang H, Cai T, Chen J, Li Z, Guan M, Qiu H. Porous graphene decorated silica as a new stationary phase for separation of sulfanilamide compounds in hydrophilic interaction chromatography. Chin Chem Lett. 2019;30:863–6.
Liu Z, Quan K, Li H, Chen J, Guan M, Qiu H. Preparation of silica-based superficially porous silica and its application in enantiomer separations: a review. J Anal Test. 2021;5:242–57.
Fan C, Quan K, Chen J, Qiu H. Comparison of chromatographic performance of co-grafted silica using octadecene respectively with vinylpyrrolidone, vinylimidazole and vinylpyridine. J Chromatogr A. 2022;1661:462690.
Li X, Li B, Liu M, Zhou Y, Zhang L, Qiao X. Core-shell metal-organic frameworks as the mixed-mode stationary phase for hydrophilic interaction/reversed-phase chromatography. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11:10320–7.
Kioka K, Mizutani N, Hosono N, Uemura T. Mixed metal-organic framework stationary phases for liquid chromatography. ACS Nano. 2022;16:6771–80.
Wang L, Wei W, Xia Z, Jie X, Xia ZZ. Recent advances in materials for stationary phases of mixed-mode high-performance liquid chromatography. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 2016;80:495–506.
Luo Q, Zhong Z, Zheng Y, Gao D, Xia Z, Wang L. Preparation and evaluation of a poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) derived graphene quantum dots based hydrophilic interaction and reversed-phase mixed-mode stationary phase for complex sample analysis. Talanta. 2021;224:121869.
Fan F, Lu X, Wang L, Liang X, Guo Y. Hydrogel coating with temperature response retention behavior and its application in selective separation of liquid chromatography. Anal Chem. 2021;93:16017–24.
Chen J, Peng H, Zhang Z, Zhang Z, Ni R, Chen Y, Chen P, Peng J. Facile fabrication of silica@covalent organic polymers core-shell composites as the mixed-mode stationary phase for hydrophilic interaction/reversed-phase/ion-exchange chromatography. Talanta. 2021;233:122524.
Si T, Wang L, Zhang H, Lu X, Liang X, Wang S, Guo Y. Core-shell MOFs-based composites of defect-functionalized for mixed-mode chromatographic separation. J Chromatogr A. 2022;1671:463011.
Luo Q, Ren X, Wei S, Zheng Y, Gao D, Fu Q, Xia Z, Wang L. Preparation and evaluation of a molybdenum disulfide quantum dots embedded C18 mixed-mode chromatographic stationary phase. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2020;412:1365–74.
He C, Xu P, Zhang X, Long W. The synthetic strategies, photoluminescence mechanisms and promising applications of carbon dots: Current state and future perspective. Carbon. 2022;186:91–127.
Fatahi Z, Esfandiari N, Ranjbar Z. A new anti-counterfeiting feature relying on invisible non-toxic fluorescent carbon dots. J Anal Test. 2020;4:307–15.
Liu C, Li H, Cheng R, Guo J, Li G-X, Li Q, Wang C-F, Yang X, Chen S. Facile synthesis, high fluorescence and flame retardancy of carbon dots. J Mater Sci Technol. 2022;104:163–71.
Shen C-L, Lou Q, Liu K-K, Dong L, Shan C-X. Chemiluminescent carbon dots: synthesis, properties, and applications. Nano Today. 2020;35:100954.
Yoo S, Song Y, Hahn S. Ultralong persistent luminescence from carbon dots. Light Sci Appl. 2022;11:132.
Zhao B, Ma H, Zheng M, Xu K, Zou C, Qu S, Tan Za. Narrow‐bandwidth emissive carbon dots: A rising star in the fluorescent material family. Carbon Energy. 2022;4:88–114.
Duan Q, Che M, Hu S, Zhao H, Li Y, Ma X, Zhang W, Zhang Y, Sang S. Rapid cancer diagnosis by highly fluorescent carbon nanodots-based imaging. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019;411:967–72.
Cheng R, Xiang Y, Guo R, Li L, Zou G, Fu C, Hou H, Ji X. Structure and interface modification of carbon dots for electrochemical energy application. Small. 2021;17:2102091.
Huang D, Chen Y, Cheng M, Lei L, Chen S, Wang W, Liu X. Carbon dots-decorated carbon-based metal-free catalysts for electrochemical energy storage. Small. 2021;17:2002998.
Zhou Y, ElMetwally AE, Chen J, Shi W, Cilingir EK, Walters B, Mintz KJ, Martin C, Ferreira B, Zhang W, Hettiarachchi SD, Serafim LF, Blackwelder PL, Wikramanayake AH, Peng Z, Leblanc RM. Gel-like carbon dots: a high-performance future photocatalyst. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2021;599:519–32.
Chen J, Gong Z, Tang W, Row KH, Qiu H. Carbon dots in sample preparation and chromatographic separation: recent advances and future prospects. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 2021;134:116135.
Yuan N, Chen J, Guan M, Zhao L, Qiu H. Application of carbon dots in sample pretreatment and chromatographic separation. Chin J Chromatogr. 2020;38:36–40.
Yuan N, Chen J, Cai T, Li Z, Guan M, Zhao L, Qiu H. Glucose-based carbon dots-modified silica stationary phase for hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 2020;1619:460930.
Cai T, Zhang H, Chen J, Li Z, Qiu H. Polyethyleneimine-functionalized carbon dots and their precursor co-immobilized on silica for hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 2019;1597:142–8.
Zhang H, Qiao X, Cai T, Chen J, Li Z, Qiu H. Preparation and characterization of carbon dot-decorated silica stationary phase in deep eutectic solvents for hydrophilic interaction chromatography. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2017;409:2401–10.
Song L, Zhang H, Chen J, Li Z, Guan M, Qiu H. Imidazolium ionic liquids-derived carbon dots-modified silica stationary phase for hydrophilic interaction chromatography. Talanta. 2020;209:120518.
Chen J, Yuan N, Jiang D, Lei Q, Liu B, Tang W, Row KH, Qiu H. Octadecylamine and glucose-coderived hydrophobic carbon dots-modified porous silica for chromatographic separation. Chin Chem Lett. 2021;32:3398–401.
Jiang D, Chen J, Guan M, Qiu H. Octadecylimidazolium ionic liquids-functionalized carbon dots and their precursor co-immobilized silica as hydrophobic chromatographic stationary phase with enhanced shape selectivity. Talanta. 2021;233:122513.
Wu Q, Hou X, Zhang X, Li H, Zhao L, Lv H. Amphipathic carbon quantum dots-functionalized silica stationary phase for reversed phase/hydrophilic interaction chromatography. Talanta. 2021;226:122148.
Wu Q, Hou X, Lv H, Li H, Zhao L, Qiu H. Synthesis of octadecylamine-derived carbon dots and application in reversed phase/hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 2021;1656:462548.
Chen S, Chen C, Wang J, Luo F, Guo L, Qiu B, Lin Z. A bright nitrogen-doped-carbon-dots based fluorescent biosensor for selective detection of copper ions. J Anal Test. 2021;5:84–92.
Miao S, Liang K, Zhu J, Yang B, Zhao D, Kong B. Hetero-atom-doped carbon dots: doping strategies, properties and applications. Nano Today. 2020;33:100879.
Hu Y, Lin L, Li J, Ye J. P, N Codoped carbon dots as an efficient “off-on” fluorescent probe for lipoic acid detection and its cellular dual-color imaging. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019;411:3603–12.
Li M, Yu C, Hu C, Yang W, Zhao C, Wang S, Zhang M, Zhao J, Wang X, Qiu J. Solvothermal conversion of coal into nitrogen-doped carbon dots with singlet oxygen generation and high quantum yield. Chem Eng J. 2017;320:570–5.
Zhu Z, Li X, Luo M, Chen M, Chen W, Yang P, Zhou X. Synthesis of carbon dots with high photocatalytic reactivity by tailoring heteroatom doping. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022;605:330–41.
Park SK, Lee H, Choi MS, Suh DH, Nakhanivej P, Park HS. Straightforward and controllable synthesis of heteroatom-doped carbon dots and nanoporous carbons for surface-confined energy and chemical storage. Energy Storage Mater. 2018;12:331–40.
Das P, Ganguly S, Mondal S, Bose M, Das AK, Banerjee S, Das NC. Heteroatom doped photoluminescent carbon dots for sensitive detection of acetone in human fluids. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2018;266:583–93.
Jiang L, Ding H, Lu S, Geng T, Xiao G, Zou B, Bi H. Photoactivated fluorescence enhancement in F, N-doped carbon dots with piezochromic behavior. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2020;59:9986–91.
Garg P, Sangam S, Kochhar D, Pahari S, Kar C, Mukherjee M. Exploring the role of triazole functionalized heteroatom co-doped carbon quantum dots against human coronaviruses. Nano Today. 2020;35:101001.
Zhuo S, Fang J, Zhu C, Du J. Preparation of palladium/carbon dot composites as efficient peroxidase mimics for H2O2 and glucose assay. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2020;412:963–72.
Yuxin X, Laipeng S, Kang L, Haipeng S, Zonghua W, Wenjing W. Metal-doped carbon dots as peroxidase mimic for hydrogen peroxide and glucose detection. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2022;414:5857–67.
Yuan N, Chen J, Zhou H, Chand Ali M, Guan M, Qiu H. Nitrogen-doping to enhance the separation selectivity of glucose-based carbon dots-modified silica stationary phase for hydrophilic interaction chromatography. Talanta. 2020;218:121140.
Fu G, Chen J, Qiu H. Deep eutectic solvents-derivated carbon dots-decorated silica stationary phase with enhanced separation selectivity in reversed-phase liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 2022;1681:463425.
Mallik AK, Qiu H, Sawada T, Takafuji M, Ihara H. Molecular shape recognition through self-assembled molecular ordering: evaluation with determining architecture and dynamics. Anal Chem. 2012;84:6577–85.
Funding
This work was supported by Longyuan Youth Innovation and Entrepreneurship Talent (Team) Project (E20492SC), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22074154), Lanzhou talent innovation and Entrepreneurship Project (No. 2021-RC-35), Science and Technology Project of Science and Technology Bureau of Chengguan District in Lanzhou (No. 2020JSCX0033), and Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (No. 2021420).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Published in the topical collection Young Investigators in (Bio-)Analytical Chemistry 2023 with guest editors Zhi-Yuan Gu, Beatriz Jurado-Sánchez, Thomas H. Linz, Leandro Wang Hantao, Nongnoot Wongkaew, and Peng Wu.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, G., Gao, C., Quan, K. et al. Phosphorus-doped deep eutectic solvent-derived carbon dots-modified silica as a mixed-mode stationary phase for reversed-phase and hydrophilic interaction chromatography. Anal Bioanal Chem 415, 4255–4264 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-04405-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-04405-9