Abstract
Purpose
Due to growing concerns about the obesity pandemic as a worldwide phenomenon, a global effort has been made for managing it and associated disorders. Accordingly, metabolomics as a promising field of “OMICS” is presented for investigating different molecular pathways in obesity and related disorders through the evaluation of specific metabolites in both animal and human subjects. Herein, the aim of the present study as the first systematic review is to evaluate all available studies about different mechanisms and their biomarkers discovery using metabolomics approaches.
Method
The study was designed according to Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. Using a comprehensive search strategy we searched in databases including; Web of Science, PubMed, and Scopus using specific keywords. Based on predefined inclusion/exclusion criteria study selection has been conducted considering the type of studies, participant, and outcome measures. Quality assessment was done using CASP (Critical Appraisal Skills Programme) checklist followed by data extraction according to a predefined data extraction sheet.
Results
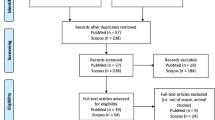
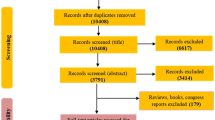
Among the articles that resulted from electronic search, a total of 74 articles met our inclusion criteria. The most prevalent studied metabolites were amino acids and lipid derivatives and both targeted and non-targeted approaches were applied for metabolomics studies.
Conclusion
This systematic review summarized a wide range of studies regardless of the age, history, language, and type of the study. Further studies are needed to compare the application of emerging methods in the treatment of obesity and related disorders.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AC-C0 :
-
Acylcarnitine-C0
- AC-C2:
-
Acylcarnitine-C2
- AC-C3:
-
Acylcarnitine-C3
- AC-C4:
-
Acylcarnitine-C4
- AC C4-OH:
-
Acylcarnitine C4-OH
- AC C5:
-
Acylcarnitine C5
- AC C8:
-
Acylcarnitine C8
- AC C8:1:
-
Acylcarnitine C8:1
- AC C10:
-
Acylcarnitine C10
- AC C10:1:
-
Acylcarnitine C10:1
- AC C10:2:
-
Acylcarnitine C10:2
- AC C10:3:
-
Acylcarnitine C10:3
- AC C12:1:
-
Acylcarnitine C12:1
- AC-C14:1:
-
Acylcarnitine-C14:1
- AC-C16:
-
Acylcarnitine-C16
- AC C16-OH/C14-DC:
-
Acylcarnitine C16-OH/C14-DC
- AC C16:1:
-
Acylcarnitine C16:1
- AC-C18:
-
Acylcarnitine-C18
- AC C18:1:
-
Acylcarnitine C18:1
- AC C18:1-OH/C16:1-DC:
-
Acylcarnitine C18:1-OH/C16:1-DC
- ADMA :
-
Asymmetric dimethylarginine
- AHB:
-
α-hydroxybutyrate
- AKB:
-
2-AMINO-3-KETOBUTYRIC ACID
- alpha-AAA:
-
alpha-amino adipic acid
- Arg:
-
Arginine
- Asn:
-
Asparagine
- BHBA:
-
Beta-Hydroxybutyric acid
- C0:
-
Carnitine (free)
- C3:
-
Propionylcarnitine
- C14:1 :
-
Tetradecadienoylcarnitine (C14:1)
- C14:1-OH:
-
3-Hydroxymyristoleylcarnitine
- C14:2 :
-
Tetradecadienoylcarnitine (C14:2)
- C16:0:
-
Hexadecanoic acid
- C16:1:
-
Palmitoleic acid
- C18:0 LPE:
-
C18:0 lysophosphatidyl-ethanolamine
- C18:1 :
-
Oleic acid
- C18:1 LPC:
-
C18:1 lysophosphatidylcholine
- C18:1 LPE:
-
C18:1 lysophosphatidyl-ethanolamine
- C18:2 LPC:
-
C18:2 lysophosphatidylcholine
- C20:3 CE:
-
C20:3 cholesterol ester
- C20:5 CE:
-
C20:5 cholesterol ester
- C22:1:
-
Erucic acid
- C22:2:
-
c -13,16-Docosadienoic acid
- C22:5n-6:
-
Dpan-6
- C22:6 CE:
-
C22:6 cholesterol esters
- C24:0:
-
Tetracosanoic acid
- C24:1:
-
Nervonic acid
- C30:0 DAG:
-
C30:0 diacylglycerol
- C32:0 DAG:
-
C32:0 diacylglycerol
- C32:1:
-
Dotriacontenylic acid
- C32:1 DAG:
-
C32:1 diacylglycerol
- C32:2 DAG:
-
C32:2 diacylglycerol
- C34:0 DAG:
-
C34:0 diacylglycerol
- C34:1:
-
Tetratriacontenylic acid
- C34:1 DAG:
-
C34:1 diacylglycerol
- C34:1 PC plasmalogen A:
-
C34:1 Phosphatidylcholine plasmalogen A
- C34:2:
-
Tetratriacontadienoic acid
- C34:2 DAG:
-
C34:2 diacylglycerol
- C34:3:
-
Acyl-akyl-phosphatidylcholine
- C34:3 DAG:
-
C34:3 diacylglycerol
- C34:4 PC:
-
C34:4 Phosphatidylcholine
- C36:0:
-
Hexatriacontanoic acid
- C36:0 DAG:
-
C36:0 diacylglycerol
- C36:1 DAG:
-
C36:1 diacylglycerol
- C36:1 PC plasmalogen:
-
C36:1 Phosphatidylcholine plasmalogen
- C36:2:
-
Hexatriacontadienoic acid
- C36:2 DAG:
-
C36:2 diacylglycerol
- C36:2 PC plasmalogen:
-
C36:2 Phosphatidylcholine plasmalogen
- C36:3 DAG:
-
C36:3 diacylglycerol
- C36:3 PC plasmalogen:
-
C36:3 Phosphatidylcholine plasmalogen
- C36:4 DAG:
-
C36:4 diacylglycerol
- C38:0:
-
Octatriactanoic acid
- C38:3 PC:
-
C38:3 Phosphatidylcholine
- C38:4 DAG:
-
C38:4 diacylglycerol
- C38:5 DAG:
-
C38:5 diacylglycerol
- C38:6 PC:
-
C38:6 Phosphatidylcholine
- C38:7 PE plasmalogen:
-
C38:7 Phosphatidylethanolamine plasmalogen
- C40:6 PE:
-
C40:6 Phosphatidylethanolamine
- C40:9 PC:
-
C40:9 Phosphatidylcholine
- C46:2 TAG:
-
C46:2 triacylglycerol
- C46:3 TAG:
-
C46:3 triacylglycerol
- C46:4 TAG:
-
C46:4 triacylglycerol
- C48:1 TAG:
-
C48:1 triacylglycerol
- C48:2 TAG:
-
C48:2 triacylglycerol
- C48:3 TAG:
-
C48:3 triacylglycerol
- C48:4 TAG:
-
C48:4 triacylglycerol
- C50:0 TAG:
-
C50:0 triacylglycerol
- C50:1 TAG:
-
C50:1 triacylglycerol
- C50:2 TAG:
-
C50:2 triacylglycerol
- C50:3 TAG:
-
C50:3 triacylglycerol
- C50:4 TAG:
-
C50:4 triacylglycerol
- C50:5 TAG:
-
C50:5 triacylglycerol
- C50:6 TAG:
-
C50:6 triacylglycerol
- C52:0 TAG:
-
C52:0 triacylglycerol
- C52:1 TAG:
-
C52:1 triacylglycerol
- C52:2 TAG:
-
C52:2 triacylglycerol
- C52:3 TAG:
-
C52:3 triacylglycerol
- C52:4 TAG:
-
C52:4 triacylglycerol
- C52:5 TAG:
-
C52:5 triacylglycerol
- C52:6 TAG:
-
C52:6 triacylglycerol
- C52:7 TAG:
-
C52:7 triacylglycerol
- C54:1 TAG:
-
C54:1 triacylglycerol
- C54:2 TAG:
-
C54:2 triacylglycerol
- C54:6 TAG:
-
C54:6 triacylglycerol
- C54:7 TAG:
-
C54:7 triacylglycerol
- C54:8 TAG:
-
C54:8 triacylglycerol
- C54:9 TAG:
-
C54:9 triacylglycerol
- C56:5 TAG:
-
C56:5 triacylglycerol
- C56:6 TAG:
-
C56:6 triacylglycerol
- C56:7 TAG:
-
C56:7 triacylglycerol
- C56:8 TAG:
-
C56:8 triacylglycerol
- C56:9 TAG:
-
C56:9 triacylglycerol
- C56:10 TAG:
-
C56:10 triacylglycerol
- C58:6 TAG:
-
C58:6 triacylglycerol
- C58:7 TAG:
-
C58:7 triacylglycerol
- C58:8 TAG:
-
C58:8 triacylglycerol
- C58:9 TAG:
-
C58:9 triacylglycerol
- C58:10 TAG:
-
C58:10 triacylglycerol
- C58:11 TAG:
-
C58:11 triacylglycerol
- CE:
-
Cholesterol ester
- CE(20:3):
-
cholesterol ester (20:3)
- CE(22:5):
-
cholesterol ester (22:5)
- CE(22:6):
-
cholesterol ester (22:6)
- Cer(d18:0/23:0):
-
ceramides(d18:0/23:0)
- Cer(d18:1/18:0):
-
ceramides(d18:1/18:0)
- DG(44:5):
-
Diacylglycerol (44:5)
- DHEA-S:
-
Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate
- Glu:
-
Glutamic acid
- Gly:
-
Glycine
- HDL:
-
High-density lipoprotein
- His:
-
Histidine
- Leu:
-
Leucine
- LPA 16:0:
-
[(2R)-2-(hexadecanoyloxy)-3-hydroxypropoxy]phosphonic acid
- LPC:
-
Lysophosphatidylcholines
- LPCa C14:0:
-
lysoPhosphatidylcholine a C14:0
- LPCa C16:0:
-
lysoPhosphatidylcholine a C16:0
- LPC a c16:0 / LPCa C20:3:
-
lysophophatidylcholine
- LPC a c16:0 / LPCa C20:4:
-
lysophophatidylcholine
- LPC a c16:0 / PC aa C32:0:
-
lysophophatidylcholine
- LPC a c16:0 / PC aa C36:2:
-
lysophophatidylcholine
- LPCa C16:1:
-
lysoPhosphatidylcholine a C16:1
- LPC a c18:0/ LPCa C20:3:
-
lysophophatidylcholine
- LPC a c18:0 / LPCa C20:4:
-
lysophophatidylcholine
- LPC a c18:0 / PC aa C36:2:
-
lysophophatidylcholine
- LPC a c18:0 / PC aa C36:1:
-
lysophophatidylcholine
- LPC Ac18:1:
-
lysophophatidylcholine
- LPC Ac18:2:
-
lysophophatidylcholine
- LPCa C18:3:
-
lysoPhosphatidylcholine a C18:3
- LPCa C20:3:
-
lysoPhosphatidylcholine a C20:3
- LPCa C20:4:
-
lysoPhosphatidylcholine a C20:4
- LPC Ac20:4:
-
lysophophatidylcholine
- LPE:
-
Lysophosphatidylethanolamines
- LysoPC(18:1):
-
lysoPhosphatidylcholine (18:1)
- LysoPC(18:2):
-
lysoPhosphatidylcholine (18:2)
- LysoPC(20:1):
-
lysoPhosphatidylcholine (20:1)
- lysoPC a C16:0:
-
lysoPhosphatidylcholine acyl C16:0
- LysoPC a C17:0:
-
Lysophosphatidylcholine a C17:0
- lysoPC a C17:0:
-
lysoPhosphatidylcholine acyl C17:0
- LysoPC a C18:0:
-
lysoPhosphatidylcholine a C18:0
- lysoPC a C18:0:
-
lysoPhosphatidylcholine acyl C18:0
- lyso.PC.a.C18.1:
-
lysoPhosphatidylcholine a C18:1
- lysoPC a C18:1:
-
lysoPhosphatidylcholine acyl C18:1
- LysoPC a C18:2:
-
lysoPhosphatidylcholine a C18:2
- lysoPC a C18:2:
-
lysoPhosphatidylcholine acyl C18:2
- lyso.PC.a.C18.3:
-
lysoPhosphatidylcholine a C18:3
- lysoPC a C20:4:
-
lysoPhosphatidylcholine a C20:4
- lysoPC a C26:0:
-
lysoPhosphatidylcholine acyl C26:0
- lyso.PC.e.C16.0:
-
lysoPhosphatidylcholine a C16.0
- lyso.PC.e.C18.0:
-
lysoPhosphatidylcholine a.C18.0
- LysoPE(22:4):
-
lysoPhosphatidylcholine (22:4)
- LysoPE a 18:0:
-
Lysophosphatidylethanolamine(0:0/18:0)
- LysoPE a 18:1:
-
Lysophosphatidylethanolamine(18:1/0:0)
- LysoPE a 18:2:
-
Lysophosphatidylethanolamine(18:2)
- N-C18-1-Cer:
-
N-(9Z-octadecenoyl)-ceramide; N-(oleoyl)-ceramide
- NEFA.12.1:
-
non-esterified fatty acids
- NEFA.14.0:
-
non-esterified fatty acids
- NEFA.14.1:
-
non-esterified fatty acids
- NEFA.14.2:
-
non-esterified fatty acids
- NEFA.14.4:
-
non-esterified fatty acids
- NEFA 15:0:
-
non-esterified fatty acids
- NEFA.16.0:
-
non-esterified fatty acids
- NEFA.16.1:
-
non-esterified fatty acids
- NEFA.16.2:
-
non-esterified fatty acids
- NEFA.17.0:
-
non-esterified fatty acids
- NEFA.17.1:
-
non-esterified fatty acids
- NEFA 18:1:
-
non-esterified fatty acids
- NEFA.18.2:
-
non-esterified fatty acids
- NEFA.18.3:
-
non-esterified fatty acids
- NEFA.18.4:
-
non-esterified fatty acids
- NEFA.19.1:
-
non-esterified fatty acids
- NEFA 20:1:
-
non-esterified fatty acids
- NEFA.20.2:
-
non-esterified fatty acids
- NEFA 20:3:
-
non-esterified fatty acids
- NEFA 20:4:
-
non-esterified fatty acids
- NEFA.20.5:
-
non-esterified fatty acids
- NEFA 22:4:
-
non-esterified fatty acids
- NEFA 22:5:
-
non-esterified fatty acids
- NEFA C20:5:
-
non-esterified fatty acids C20:5
- NEFA C22:6:
-
non-esterified fatty acids C22:6
- PA(28:0):
-
Phosphtatidic acid (28:0)
- PC:
-
Phosphatidylcholine
- PC(16:0/O-1:0):
-
Phosphatidylcholine(16:0/O-1:0)
- PC(16:0/O-16:0):
-
Phosphatidylcholine (16:0/O-16:0)
- PC(18:3/dm18:1):
-
Phosphatidylcholine(18:3/dm18:1)
- PC(19:3):
-
Phosphatidylcholine(19:3)
- PC(22:4/dm18:1):
-
Phosphatidylcholine(22:4/dm18:1)
- PC(35:2):
-
Phosphatidylcholine(35:2)
- PCA:
-
2-Pyrrolidone-5-carboxylic acid
- PC aa C28:1:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C28:1
- PC aa C30:2:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C 30:2
- PC aa C32:0:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C32:0
- PC aa C32:1:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C32:1
- PC.aa.C32.3:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C32.3
- PC aa C34:1:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C34:1
- PC aa C34:2:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C34:2
- PC aa C34:3:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C34:3
- PC aa C34:4:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C34:4
- PC.aa.C34.5:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C34.5
- PC aa C36:0:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C36:0
- PC aa C36:1:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C36:1
- PC aa C36:2:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C36:2
- PC aa C36:3:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C36:3
- PC aa C36:4:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C36:4
- PC aa C36:5:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C36:5
- PC aa C36:6:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C36:6
- PC aa C38:0:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C38:0
- PC aa C38:1:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C38:1
- PC.aa.C38.3:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C38:3
- PC.aa.C38.4:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C38:4
- PC aa C38:5:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C38:5
- PC aa C38:6:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C38:6
- PC aa C40:0:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C40:0
- PC aa C40:1:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C40:1
- PC aa C40:2:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C40:2
- PC aa C40:3:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C40:3
- PC.aa.C40.4:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C40.4
- PC.aa.C40.5:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C40:5
- PC aa C40:6:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C40:6
- PC aa C42:0:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C42:0
- PC aa C42:1:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C42:1
- PC.aa.C42.2:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C42.2
- PC aa C42:5:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C42:5
- PC aa C42:6:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C42:6
- PC.aa.C43.4:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C43:4
- PC.aa.C44.12:
-
Phosphatidylcholine diacyl C44.12
- PC ae C32:1 :
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C32:1
- PC ae C32:2 :
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C32:2
- PC ae C34:1:
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C34:1
- PC.ae.C34.2:
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C34.2
- PC ae C34:3:
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C34:3
- PC ae 36:0:
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl 36:0
- PC ae 36:1:
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl 36:1
- PC ae 36:2 :
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C 36:2
- PC ae 36:3 :
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C 36:3
- PC ae 36:4:
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl36:4
- PC.ae.C36.5:
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C36.5
- PC ae C38:0 :
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C38:0
- PC ae C38:1 :
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C38:1
- PC ae C38:2:
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C38:2
- PC.ae.C38.3:
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C38.3
- PC ae C38:4:
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C38:4
- PC ae C38:5:
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C38:5
- PC ae C38:6:
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C44:4
- PC ae C40:1 :
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C40:1
- PC ae C40:2 :
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C40:2
- PC ae C40:3 :
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C40:3
- PC ae C40:4 :
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C40:4
- PC ae C40:5 :
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C40:5
- PC ae C42:0 :
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C42:0
- PC ae C42:1 :
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C42:1
- PC ae C42:2 :
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C42:2
- PC ae C42:3 :
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C42:3
- PC ae C42:4 :
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C42:4
- PC ae C42:5 :
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C42:5
- PC ae C44:3:
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C44:3
- PC ae C44:4:
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C44:4
- PC ae C44:5:
-
Phosphatidylcholine acyl-alkyl C44:5
- PC(O-10:0/O-8:0):
-
Phosphatidylcholine(O-10:0/O-8:0)
- PC(O-10:0/O-10:0):
-
Phosphatidylcholine(O-10:0/O-10:0)
- PC (O-10:0/O-12:0):
-
Phosphatidylcholine (O-10:0/O-12:0)
- PE(22:1/dm18:1):
-
Phosphatidylethanolamine(22:1/dm18:1)
- PE(22:4/dm18:0):
-
Phosphatidylethanolamine(22:4/dm18:0)
- PG(38:3):
-
Prostaglandin(38:3)
- Phe:
-
Phenylalanine
- PS(24:0):
-
Phosphtatidylserines(24:0)
- SDMA:
-
Symmetric dimethylarginine
- SFA:
-
Saturated fatty acid
- SM:
-
Sphingomyelin
- SM C16:0 or SM (d18:1/16:0):
-
n-(hexadecanoyl)-sphing-4-enine-1-phosphocholine
- SM C24:1:
-
n-(hexadecanoyl)-sphing-4-enine-1-phosphocholine
- SM (d16:1/18:0):
-
N-(octadecanoyl)-hexadecasphing-4-enine-1-phosphocholine
- SM(d18:0/20:0):
-
Sphingomyelin(d18:0/20:0)
- SM(d18:1/16:0):
-
Sphingomyelin(d18:1/16:0)
- SM (d18:2/16:0):
-
N-(hexadecanoyl)-4E,14Z-sphingadienine-1-phosphocholine
- SM (d18:2/18:0):
-
N-(octadecanoyl)-4E,14Z-sphingadienine-1-phosphocholine
- SM (OH) C14:1:
-
Hydroxysphingomyeline C14:1
- SM (OH) C16:1 :
-
HydroxySphingomyelin C16:1
- SM (OH) C22:1 :
-
N-[(13Z)-3-Hydroxydocos-13-enoyl]sphing-4-enine-1-phosphocholine
- SM (OH) C22:2 :
-
HydroxySphingomyelin C22:2
- SM (OH) C24:1 :
-
HydroxySphingomyelin C24:1
- TAG:
-
Triacylglycerols
- TG(36:0):
-
Triglycerides(36:0)
- TG(56:11):
-
Triglycerides(56:11)
- Tyr:
-
Tyrosine
- Val:
-
Valine
References
Abarca-Gómez L, Abdeen ZA, Hamid ZA, Abu-Rmeileh NM, Acosta-Cazares B, Acuin C, Adams RJ, Aekplakorn W, Afsana K, Aguilar-Salinas CA. Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: a pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128· 9 million children, adolescents, and adults. The Lancet. 2017;390:2627–42.
Abu Bakar MH, Sarmidi MR, Cheng KK, Ali Khan A, Suan CL, Zaman Huri H, Yaakob H. Metabolomics - the complementary field in systems biology: a review on obesity and type 2 diabetes. Mol BioSyst. 2015;11:1742–74.
Ahmad MS, Alsaleh M, Kimhofer T, Ahmad S, Jamal W, Wali SO, Nicholson JK, Damanhouri ZA, Holmes E. Metabolic zzphenotype of obesity in a Saudi population. J Proteome Res. 2017;16:635–44.
Allam-Ndoul B, Guénard F, Garneau V, Cormier H, Barbier O, Pérusse L, Vohl M-C. Association between metabolite profiles, metabolic syndrome and obesity status. Nutrients. 2016;8:324.
Almanza-Aguilera E, Brunius C, Bernal-Lopez MR, Garcia-Aloy M, Madrid-Gambin F, Tinahones FJ, Gomez-Huelgas R, Landberg R, Andres-Lacueva C. Impact in plasma metabolome as effect of lifestyle intervention for weight-loss reveals metabolic benefits in metabolically healthy obese women. J Proteome Res. 2018;17:2600–10.
Andersen LW, Mackenhauer J, Roberts JC, Berg KM, Cocchi MN, Donnino MW. Etiology and therapeutic approach to elevated lactate levels. Mayo Clinic Proceedings: Elsevier; 2013. p. 1127–40.
Badoud F, Lam KP, Dibattista A, Perreault M, Zulyniak MA, Cattrysse B, Stephenson S, Britz-Mckibbin P, Mutch DM. Serum and adipose tissue amino acid homeostasis in the metabolically healthy obese. J Proteome Res. 2014;13:3455–66.
Badoud F, Perreault M, Zulyniak MA, Mutch DM. Molecular insights into the role of white adipose tissue in metabolically unhealthy normal weight and metabolically healthy obese individuals. FASEB J. 2015;29:748–58.
Baek SH, Kim M, Kim M, Kang M, Yoo HJ, Lee NH, Kim YH, Song M, Lee JH. Metabolites distinguishing visceral fat obesity and atherogenic traits in individuals with overweight. Obesity. 2017;25:323–31.
Bagheri M, Djazayery A, Qi L, Yekaninejad MS, Chamari M, Naderi M, Ebrahimi Z, Koletzko B, Uhl O, Farzadfar F. Effectiveness of vitamin D therapy in improving metabolomic biomarkers in obesity phenotypes: two randomized clinical trials. Int J Obes. 2018;42:1782–96.
Bagheri M, Djazayery A, Farzadfar F, Qi L, Yekaninejad MS, Aslibekyan S, Chamari M, Hassani H, Koletzko B, Uhl O. Plasma metabolomic profiling of amino acids and polar lipids in Iranian obese adults. Lipids Health Dis. 2019a;18:1–9.
Bagheri M, Djazayery A, Farzadfar F, Qi L, Yekaninejad MS, Aslibekyan S, Chamari M, Hassani H, Koletzko B, Uhl O. Plasma metabolomic profiling of amino acids and polar lipids in Iranian obese adults. Lipids Health Dis. 2019b;18:94.
Bakar MHA, Sarmidi MR, Cheng K-K, Khan AA, Suan CL, Huri HZ, Yaakob H. Metabolomics–the complementary field in systems biology: a review on obesity and type 2 diabetes. Mol BioSyst. 2015;11:1742–74.
Brozinick J, Hawkins E, Bui HH, Kuo M, Tan B, Kievit P, Grove K. Plasma sphingolipids are biomarkers of metabolic syndrome in non-human primates maintained on a Western-style diet. Int J Obes. 2013;37:1064.
Butte NF, Liu Y, Zakeri IF, Mohney RP, Mehta N, Voruganti VS, Göring H, Cole SA, Comuzzie AG. Global metabolomic profiling targeting childhood obesity in the Hispanic population. Am J Clin Nutr. 2015;102:256–67.
Cetin I, Parisi F, Berti C, Mando C, Desoye G. Placental fatty acid transport in maternal obesity. J Dev Orig Health Dis. 2012;3:409–14.
Chashmniam S, Madani NH, Ghoochani BFNM, Safari-Alighiarloo N, Khamseh ME. The metabolome profiling of obese and non-obese individuals: metabolically healthy obese and unhealthy non-obese paradox. Iranian J Basic Med Sci. 2020;23:186.
Chen H-H, Tseng YJ, Wang S-Y, Tsai Y-S, Chang C-S, Kuo T-C, Yao W-J, Shieh C-C, Wu C-H, Kuo P-H. The metabolome profiling and pathway analysis in metabolic healthy and abnormal obesity. Int J Obes. 2015;39:1241.
Cho K, Moon J, Kang JH, Jang H, Lee HJ, Park S, Yu KS, Cho JY. Combined untargeted and targeted metabolomic profiling reveals urinary biomarkers for discriminating obese from normal-weight adolescents. Pediatric obesity. 2017;12:93–101.
Collaborators, G. O. Health effects of overweight and obesity in 195 countries over 25 years. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:13–27.
Crawford SO, Hoogeveen RC, Brancati FL, Astor BC, Ballantyne CM, Schmidt MI, Young JH. Association of blood lactate with type 2 diabetes: the atherosclerosis risk in communities carotid MRI study. Int J Epidemiol. 2010;39:1647–55.
Desert R, Canlet C, Costet N, Cordier S, Bonvallot N. Impact of maternal obesity on the metabolic profiles of pregnant women and their offspring at birth. Metabolomics. 2015;11:1896–907.
Dugas LR, Chorell E, Plange-Rhule J, Lambert EV, Cao G, Cooper RS, Layden BT, Scholten D, Olsson T, Luke A. Obesity-related metabolite profiles of black women spanning the epidemiologic transition. Metabolomics. 2016;12:45.
Dunn WB, Lin W, Broadhurst D, Begley P, Brown M, Zelena E, Vaughan AA, Halsall A, Harding N, Knowles JD. Molecular phenotyping of a UK population: defining the human serum metabolome. Metabolomics. 2015;11:9–26.
Elliott P, Posma JM, Chan Q, Garcia-Perez I, Wijeyesekera A, Bictash M, Ebbels TM, Ueshima H, Zhao L, van Horn L. Urinary metabolic signatures of human adiposity. Sci Transl Med. 2015;7:285ra62.
Fattuoni C, Mandò C, Palmas F, Anelli GM, Novielli C, Laudicina EP, Savasi VM, Barberini L, Dessì A, Pintus R. Preliminary metabolomics analysis of placenta in maternal obesity. Placenta. 2018;61:89–95.
Feng R, Sun G, Zhang Y, Sun Q, Ju L, Sun C, Wang C. Short-term high-fat diet exacerbates insulin resistance and glycolipid metabolism disorders in young obese men with hyperlipidemia, as determined by metabolomics analysis using ultra-HPLC-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J Diabetes. 2019;11:148–60.
Galili O, Versari D, Sattler KJ, Olson ML, Mannheim D, Mcconnell JP, Chade AR, Lerman LO, Lerman A. Early experimental obesity is associated with coronary endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress. Am J Phys Heart Circ Phys. 2007;292:H904–11.
Gault CR, Obeid LM, Hannun YA. An overview of sphingolipid metabolism: from synthesis to breakdown. Sphingolipids as Signaling and Regulatory Molecules: Springer; 2010.
Gawlik A, Shmoish M, Hartmann MF, Malecka-Tendera E, Wudy SA, Hochberg ZE. Steroid metabolomic disease signature of nonsyndromic childhood obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101:4329–37.
Gibney MJ, Walsh M, Brennan L, Roche HM, German B, van Ommen B. Metabolomics in human nutrition: opportunities and challenges. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005;82:497–503.
Hellmuth C, Demmelmair H, Schmitt I, Peissner W, Blüher M, Koletzko B. Association between plasma nonesterified fatty acids species and adipose tissue fatty acid composition. PLoS One. 2013;8:e74927.
Hellmuth C, Lindsay KL, Uhl O, Buss C, Wadhwa PD, Koletzko B, Entringer S. Association of maternal prepregnancy BMI with metabolomic profile across gestation. Int J Obes. 2017a;41:159.
Hellmuth C, Uhl O, Standl M, Demmelmair H, Heinrich J, Koletzko B, Thiering E. Cord blood metabolome is highly associated with birth weight, but less predictive for later weight development. Obesity Facts. 2017b;10:85–100.
Hellmuth C, Lindsay KL, Uhl O, Buss C, Wadhwa PD, Koletzko B, Entringer S. Maternal Metabolomic profile and fetal programming of offspring adiposity: identification of potentially protective lipid metabolites. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2019;63:e1700889.
Ho JE, Larson MG, Ghorbani A, Cheng S, Chen M-H, Keyes M, Rhee EP, Clish CB, Vasan RS, Gerszten RE. Metabolomic profiles of body mass index in the Framingham heart study reveal distinct cardiometabolic phenotypes. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0148361.
Houten SM, Wanders RJ. A general introduction to the biochemistry of mitochondrial fatty acid β-oxidation. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2010;33:469–77.
Hsu YH, Churchhouse C, Pers TH, Mercader JM, Metspalu A, Fischer K, Fortney K, Morgen EK, Gonzalez C, Gonzalez ME, Esko T, Hirschhorn JN. PAIRUP-MS: pathway analysis and imputation to relate unknowns in profiles from mass spectrometry-based metabolite data. PLoS Comput Biol. 2019;15:e1006734.
Huang C-F, Cheng M-L, Fan C-M, Hong C-Y, Shiao M-S. Nicotinuric acid: a potential marker of metabolic syndrome through a metabolomics-based approach. Diabetes Care. 2013;36:1729–31.
Hulver MW, Berggren JR, Carper MJ, Miyazaki M, Ntambi JM, Hoffman EP, Thyfault JP, Stevens R, Dohm GL, Houmard JA. Elevated stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 expression in skeletal muscle contributes to abnormal fatty acid partitioning in obese humans. Cell Metab. 2005;2:251–61.
Iida m, Harada s, Kurihara A, Fukai K, Kuwabara K, Sugiyama D, Takeuchi A, Okamura T, Akiyama M, Nishiwaki Y. Profiling of plasma metabolites in postmenopausal women with metabolic syndrome. Menopause (New York, NY). 2016;23:749.
Isherwood CM, van der veen DR, Johnston JD, Skene DJ. Twenty-four-hour rhythmicity of circulating metabolites: effect of body mass and type 2 diabetes. FASEB J. 2017;31:5557–67.
Jonas A. Lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids. 2000;1529:245–56.
Jourdan C, Petersen A-K, Gieger C, Döring A, Illig T, Wang-Sattler R, Meisinger C, Peters A, Adamski J, Prehn C. Body fat free mass is associated with the serum metabolite profile in a population-based study. PLoS One. 2012;7:e40009.
Kim JY, Park JY, Kim OY, Ham BM, Kim H-J, Kwon DY, Jang Y, Lee JH. Metabolic profiling of plasma in overweight/obese and lean men using ultra performance liquid chromatography and Q-TOF mass spectrometry (UPLC− Q-TOF MS). J Proteome Res. 2010;9:4368–75.
Kim Y-J, Lee H-S, Kim YK, Park S, Kim J-M, Yun JH, Yu H-Y, Kim B-J. Association of metabolites with obesity and type 2 diabetes based on FTO genotype. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0156612.
Kim MJ, Kim JH, Kim MS, Yang HJ, Lee M, Kwon DY. Metabolomics associated with genome-wide association study related to the basal metabolic rate in overweight/obese Korean women. J Med Food. 2019;22:499–507.
Klautzer L, Becker J, Mattke S. The curse of wealth–middle eastern countries need to address the rapidly rising burden of diabetes. Int J Health Policy Manag. 2014;2:109.
Klop B, Elte JWF, Cabezas MC. Dyslipidemia in obesity: mechanisms and potential targets. Nutrients. 2013;5:1218–40.
Kochhar S, Jacobs DM, Ramadan Z, Berruex F, Fuerholz A, Fay LB. Probing gender-specific metabolism differences in humans by nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabonomics. Anal Biochem. 2006;352:274–81.
Koletzko B, Beyer J, Brands B, Demmelmair H, Grote V, Haile G, Gruszfeld D, Rzehak P, Socha P, Weber M. Early influences of nutrition on postnatal growth. In: Recent advances in growth research: nutritional, molecular and endocrine perspectives: Karger Publishers; 2013.
Koves TR, Ussher JR, Noland RC, Slentz D, Mosedale M, Ilkayeva O, Bain J, Stevens R, Dyck JR, Newgard CB. Mitochondrial overload and incomplete fatty acid oxidation contribute to skeletal muscle insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2008;7:45–56.
Kupek E, Lobo AS, Leal DB, Bellisle F, de Assis MA. Dietary patterns associated with overweight and obesity among Brazilian schoolchildren: an approach based on the time-of-day of eating events. Br J Nutr. 2016;116:1954–65.
Leal-Witt MJ, Ramon-Krauel M, Samino S, Llobet M, Cuadras D, Jimenez-Chillaron JC, Yanes O, Lerin C. Untargeted metabolomics identifies a plasma sphingolipid-related signature associated with lifestyle intervention in prepubertal children with obesity. Int J Obes. 2018;42:72–8.
Lee SH, Kim SH, Lee W-Y, Chung BC, Park MJ, Choi MH. Metabolite profiling of sex developmental steroid conjugates reveals an association between decreased levels of steroid sulfates and adiposity in obese girls. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016;162:100–9.
Lei S, Huang F, Zhao A, Chen T, Chen W, Xie G, Zheng X, Zhang Y, Yu H, Zhang P. The ratio of dihomo-γ-linolenic acid to deoxycholic acid species is a potential biomarker for the metabolic abnormalities in obesity. FASEB J. 2017;31:3904–12.
Lin Z, Gonçalves CMV, Dai L, Lu H-M, Huang J-H, Ji H, Wang D-S, Yi L-Z, Liang Y-Z. Exploring metabolic syndrome serum profiling based on gas chromatography mass spectrometry and random forest models. Anal Chim Acta. 2014;827:22–7.
Lokhov PG, Balashova EE, Trifonova OP, Maslov DL, Ponomarenko EA, Archakov AI. Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics analysis of obese patients' blood plasma. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:568.
Mccormack SE, Shaham O, Mccarthy MA, Deik AA, Wang TJ, Gerszten RE, Clish CB, Mootha VK, Grinspoon SK, Fleischman A. Circulating branched-chain amino acid concentrations are associated with obesity and future insulin resistance in children and adolescents. Pediatric Obesity. 2013;8:52–61.
Menni C, Migaud M, Glastonbury CA, Beaumont M, Nikolaou A, Small KS, Brosnan MJ, Mohney RP, Spector TD, Valdes AM. Metabolomic profiling to dissect the role of visceral fat in cardiometabolic health. Obesity. 2016;24:1380–8.
Mihalik SJ, Goodpaster BH, Kelley DE, Chace DH, Vockley J, Toledo FG, Delany JP. Increased levels of plasma acylcarnitines in obesity and type 2 diabetes and identification of a marker of glucolipotoxicity. Obesity. 2010;18:1695–700.
Mihalik SJ, Michaliszyn SF, De Las Heras J, Bacha F, Lee S, Chace DH, Dejesus VR, Vockley J, Arslanian SA. Metabolomic profiling of fatty acid and amino acid metabolism in youth with obesity and type 2 diabetes: evidence for enhanced mitochondrial oxidation. Diabetes Care. 2012:DC_111577.
Murphy RA, Moore SC, Playdon M, Meirelles O, Newman AB, Milijkovic I, Kritchevsky SB, Schwartz A, Goodpaster BH, Sampson J. Metabolites associated with lean mass and adiposity in older black men. Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biomedical Sciences and Medical Sciences. 2017;72:1352–9.
Newbern D, Balikcioglu PG, Balikcioglu M, Bain J, Muehlbauer M, Stevens R, Ilkayeva O, Dolinsky D, Armstrong S, Irizarry K. Sex differences in biomarkers associated with insulin resistance in obese adolescents: metabolomic profiling and principal components analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99:4730.
Okekunle AP, Li Y, Liu L, Du S, Wu X, Chen Y, Li Y, Qi J, Sun C, Feng R. Abnormal circulating amino acid profiles in multiple metabolic disorders. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017;132:45–58.
Organization, W. H. Global status report on noncommunicable diseases 2014: World Health Organization; 2014.
Palau-Rodriguez M, Tulipani S, Marco-Ramell A, Minarro A, Jauregui O, Gonzalez-Dominguez R, Sanchez-Pla A, Ramos-Molina B, Tinahones FJ, Andres-Lacueva C. Characterization of metabolomic profile associated with metabolic improvement after bariatric surgery in subjects with morbid obesity. J Proteome Res. 2018;17:2704–14.
Palmnas MSA, Kopciuk KA, Shaykhutdinov RA, Robson PJ, Mignault D, Rabasa-Lhoret R, Vogel HJ, Csizmadi I. Serum metabolomics of activity energy expenditure and its relation to metabolic syndrome and obesity. Sci Rep. 2018;8:3308.
Paris D, Maniscalco M, Melck D, D’Amato M, Sorrentino N, Zedda A, Sofia M, Motta A. Inflammatory metabolites in exhaled breath condensate characterize the obese respiratory phenotype. Metabolomics. 2015;11:1934–9.
Park S, Sadanala KC, KIM E-K. A metabolomic approach to understanding the metabolic link between obesity and diabetes. Mol Cells. 2015;38:587.
Payab M, Hasani-Ranjbar S, Larijani B. whether all obese subjects both in metabolic groups and non-metabolic groups should be treated or not: springer; 2014.
Payab M, Kelishadi R, Qorbani M, Motlagh ME, Ranjbar SH, Ardalan G, Zahedi H, Chinian M, Asayesh H, Larijani B. Association of junk food consumption with high blood pressure and obesity in Iranian children and adolescents: the Caspian-IV study. Jornal de Pediatria (Versão em Português). 2015a;91:196–205.
Payab M, Kelishadi R, Ranjbar SH, Motlagh ME, Ardalan G, Zahedi H, Sanaei M, Shafiee G, Asayesh H, Larijani B. Grains and potato consumption in association with anthropomet¬ ric measures and blood pressure in Iranian Chil¬ dren and adolescents: the CASPIAN-IV study. Iran J Public Health. 2015b;44:25–34.
Perng W, Gillman MW, Fleisch AF, Michalek RD, Watkins SM, Isganaitis E, Patti ME, Oken E. Metabolomic profiles and childhood obesity. Obesity. 2014;22:2570–8.
Phung DT, Wang Z, Rutherford S, Huang C, Chu C. Body mass index and risk of pneumonia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2013;14:839–57.
Pietiläinen KH, Sysi-Aho M, Rissanen A, Seppänen-Laakso T, Yki-Järvinen H, Kaprio J, Orešič M. Acquired obesity is associated with changes in the serum lipidomic profile independent of genetic effects–a monozygotic twin study. PLoS One. 2007;2:e218.
Putri SP, Yamamoto S, Tsugawa H, Fukusaki E. Current metabolomics: technological advances. J Biosci Bioeng. 2013;116:9–16.
Rangel-Huerta OD, Gil A. Nutrimetabolomics: an update on analytical approaches to investigate the role of plant-based foods and their bioactive compounds in non-communicable chronic diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17:2072.
Rauschert S, Uhl O, Koletzko B, Kirchberg F, Mori TA, Huang R-C, Beilin LJ, Hellmuth C, Oddy WH. Lipidomics reveals associations of phospholipids with obesity and insulin resistance in young adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101:871–9.
Rauschert S, Mori TA, Beilin LJ, Jacoby p, Uhl o, Koletzko B, Oddy WH, Hellmuth C. Early life factors, obesity risk, and the metabolome of young adults. Obesity. 2017;25:1549–55.
Romo-Hualde A, Huerta AE, Gonzalez-Navarro CJ, Ramos-Lopez O, Moreno-Aliaga MJ, Martinez JA. Untargeted metabolomic on urine samples after alpha-lipoic acid and/or eicosapentaenoic acid supplementation in healthy overweight/obese women. Lipids Health Dis. 2018;17:103.
Rousset X, Vaisman B, Amar M, Sethi AA, Remaley AT. Lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase: from biochemistry to role in cardiovascular disease. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2009;16:163.
Sallese A, Zhu J. Mass spectrometry based metabolomics: A novel analytical technique for detecting metabolic syndrome? Bioanalysis. 2017;9:1623–6.
Sandler V, Reisetter AC, Bain JR, Muehlbauer MJ, Nodzenski M, Stevens RD, Ilkayeva O, Lowe LP, Metzger BE, Newgard CB. Associations of maternal BMI and insulin resistance with the maternal metabolome and newborn outcomes. Diabetologia. 2017;60:518–30.
Schlecht I, Gronwald W, Behrens G, Baumeister SE, Hertel J, Hochrein J, Zacharias HU, Fischer B, Oefner PJ, Leitzmann MF. Visceral adipose tissue but not subcutaneous adipose tissue is associated with urine and serum metabolites. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0175133.
Schoeman JC, Hou J, Harms AC, Vreeken RJ, Berger R, Hankemeier T, Boonstra A. Metabolic characterization of the natural progression of chronic hepatitis B. Genome Med. 2016;8:64.
Seridi L, Leo GC, Dohm GL, Pories WJ, Lenhard J. Time course metabolome of roux-en-Y gastric bypass confirms correlation between leptin, body weight and the microbiome. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0198156.
Shokry E, Marchioro L, Uhl O, Bermudez MG, Garcia-Santos JA, Segura MT, Campoy C, Koletzko B. Impact of maternal BMI and gestational diabetes mellitus on maternal and cord blood metabolome: results from the PREOBE cohort study. Acta Diabetol. 2019a;56:421–30.
Subbaiah PV, Jiang X-C, Belikova NA, Aizezi B, Huang ZH, Reardon CA. Regulation of plasma cholesterol esterification by sphingomyelin: effect of physiological variations of plasma sphingomyelin on lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase activity. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids. 2012;1821:908–13.
Sun L, Hu C, Yang R, Lv Y, Yuan H, Liang Q, He B, Pang G, Jiang M, Dong J, Yang Z. Association of circulating branched-chain amino acids with cardiometabolic traits differs between adults and the oldest-old. Oncotarget. 2017;8:88882–93.
Troisi J, Belmonte F, Bisogno A, Pierri L, Colucci A, Scala G, Cavallo P, Mandato C, Di Nuzzi A, Di Michele L, Delli Bovi AP, Guercio Nuzio S, Vajro P. Metabolomic Salivary Signature of Pediatric Obesity Related Liver Disease and Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients. 2019:11.
Tulipani S, Palau-Rodriguez M, Alonso AM, Cardona F, Marco-Ramell A, Zonja B, De Alda ML, Muñoz-Garach A, Sanchez-Pla A, Tinahones FJ. Biomarkers of morbid obesity and prediabetes by metabolomic profiling of human discordant phenotypes. Clin Chim Acta. 2016;463:53–61.
Valcárcel B, Ebbels TM, Kangas AJ, Soininen P, Elliot P, Ala-Korpela M, Järvelin M-R, De Iorio M. Genome metabolome integrated network analysis to uncover connections between genetic variants and complex traits: an application to obesity. J R Soc Interface. 2014;11:20130908.
Vijay A, Valdes AM. The Metabolomic signatures of weight change. Metabolites. 2019;9:67.
Vitkin E, Ben-Dor A, Shmoish M, Hartmann MF, Yakhini Z, Wudy SA, Hochberg ZE. Peer group normalization and urine to blood context in steroid metabolomics: the case of CAH and obesity. Steroids. 2014;88:83–9.
Wahl S, Yu Z, Kleber M, Singmann P, Holzapfel C, He Y, Mittelstrass K, Polonikov A, Prehn C, Römisch-Margl W. Childhood obesity is associated with changes in the serum metabolite profile. Obesity Facts. 2012;5:660–70.
Wahl S, Drong A, Lehne B, Loh M, Scott WR, Kunze S, Tsai PC, Ried JS, Zhang W, Yang Y, Tan S, Fiorito G, Franke L, Guarrera S, Kasela S, Kriebel J, Richmond RC, Adamo M, Afzal U, et al. Epigenome-wide association study of body mass index, and the adverse outcomes of adiposity. Nature. 2017;541:81–6.
Wang C, Feng R, Sun D, Li Y, Bi X, Sun C. Metabolic profiling of urine in young obese men using ultra performance liquid chromatography and Q-TOF mass spectrometry (UPLC/Q-TOF MS). J Chromatogr B. 2011;879:2871–6.
Wang Y, Liu D, Li Y, Guo L, Cui Y, Zhang X, Li E. Metabolomic analysis of serum from obese adults with hyperlipemia by UHPLC-Q-TOF MS/MS. Biomed Chromatogr. 2016;30:48–54.
Wang SM, Yang RY, Wang M, Ji FS, Li HX, Tang YM, Chen WX, Dong J. Identification of serum metabolites associated with obesity and traditional risk factors for metabolic disease in Chinese adults. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2018;28:112–8.
Wijayatunga NN, Sams VG, Dawson JA, Mancini ML, Mancini GJ, Moustaid-Moussa N. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery alters serum metabolites and fatty acids in patients with morbid obesity. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2018;34:e3045.
Würtz P, Wang Q, Kangas AJ, Richmond RC, Skarp J, Tiainen M, Tynkkynen T, soininen P, Havulinna AS, Kaakinen M. Metabolic signatures of adiposity in young adults: Mendelian randomization analysis and effects of weight change. PLoS Med. 2014;11:e1001765.
Xia B, Zhu Q, Zhao Y, Ge W, Zhao Y, Song Q, Zhou Y, Shi H, Zhang Y. Phthalate exposure and childhood overweight and obesity: urinary metabolomic evidence. Environ Int. 2018;121:159–68.
Xie G, Ma X, Zhao A, Wang C, Zhang Y, Nieman D, Nicholson JK, Jia W, Bao Y, Jia W. The metabolite profiles of the obese population are gender-dependent. J Proteome Res. 2014;13:4062–73.
Yin X, Subramanian S, Willinger CM, Chen G, Juhasz P, Courchesne P, Chen BH, Li X, Hwang S-J, Fox CS. Metabolite signatures of metabolic risk factors and their longitudinal changes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101:1779–89.
Yu HT, Fu XY, Xu B, Zuo LL, Ma HB, Wang SR. Untargeted metabolomics approach (UPLC-Q-TOF-MS) explores the biomarkers of serum and urine in overweight/obese young men. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2018;27:1067–76.
Zhang A, Sun H, Wang X. Emerging role and recent applications of metabolomics biomarkers in obesity disease research. RSC Adv. 2017;7:14966–73.
Zhao Q, Zhu Y, Best LG, Umans JG, Uppal K, Tran VT, Jones DP, Lee ET, Howard BV, Zhao J. Metabolic profiles of obesity in American Indians: the strong heart family study. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0159548.
Zhong F, Xu M, Bruno RS, Ballard KD, Zhu J. Targeted high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry-based metabolomics differentiates metabolic syndrome from obesity. Exp Biol Med. 2017;242:773–80.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(RAR 529 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Payab, M., Tayanloo-Beik, A., Falahzadeh, K. et al. Metabolomics prospect of obesity and metabolic syndrome; a systematic review. J Diabetes Metab Disord 21, 889–917 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-021-00917-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-021-00917-w