Abstract
Extreme ultra violet lithography (EUVL) is no longer a future technology but is going to be inserted into mass production of semiconductor devices of 7 nm technology node in 2018. EUVL is an extension of optical lithography using extremely short wavelength (13.5 nm). This short wavelength requires major modifications in the optical systems due to the very strong absorption of EUV light by materials. Refractive optics can no longer be used, and reflective optics is the only solution to transfer image from mask to wafer. This is why we need the multilayer (ML) mirror-based mask as well as an oblique incident angle of light. This paper discusses the principal theory on the EUV mask design and its component materials including ML reflector and EUV absorber. Mask shadowing effect (or mask 3D effect) is explained and its technical solutions like phase shift mask is reviewed. Even though not all the technical issues on EUV mask are handled in this review paper, you will be able to understand the principles determining the performance of EUV masks.



(Reprinted from Ref. 8)

(Reprinted from Ref. 11)

(Modified from Ref. 15)

(Reprinted from Ref. 22)

(Reprinted from Ref. 38)

(Reprinted from Ref. 45)

(Reprinted from Ref. 55)

(Reprinted from Ref. 54)

(Reproduced from Ref. 65, with the permission of the American Vacuum Society)

(Reprinted from Ref. 69)

(Reprinted from Ref. 78)

(Reprinted from Ref. 78)

(Reprinted from Ref. 90)

(Reprinted from Ref. 102, Copyright@ American Scientific Publishers)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, A., Miyazaki, J.: EUV lithography insertion for high volume manufacturing: status and outlook. In: Proceedings of IEEE Electron Devices Technology and Manufacturing Conference, p. 77. IEEE Electron Devices Society, Toyama, Japan (2017)
Buitrago, E., Meeuwissen, M., Yildrim, O., Custers, R., Hoefnagels, R., Rispens, G., Vockenhuber, M., Mochi, I., Fallica, R., Tasdemir, Z., Ekinci, Y.: State-of-the-art EUV materials and processes for the 7nm node and beyond. Proc. SPIE 10143, 101430T (2017)
Kim, S.-S., Chalykh, R., Kim, H., Lee, S., Park, C., Hwang, M., Park, J., Park, J., Kim, H., Jeon, J., Kim, I., Lee, D., Na, J., Kim, J., Lee, S., Kim, H., Nam, S.: Progress in EUV lithography toward manufacturing. Proc. SPIE 10143, 1014306 (2017)
van Es, R., van de Kerkhof, M., Jasper, H., Levasier, L., Peeters, R.: EUV lithography industrialization progress. Proc. SPIE 10450, 1045003 (2017)
Fomenkov, I., Brandt, D., Ershov, A., Schafgans, A., Tao, Y., Vaschenko, G., Rokitski, S., Kats, M., Vargas, M., Purvis, M., Rafac, R., La Fontaine, B., De Dea, S., LaForge, A., Stewart, J., Chang, S., Graham, M., Riggs, D., Taylor, T., Abraham, M., Brown, D.: Light sources for high-volume manufacturing EUV lithography: technology, performance, and power scaling. Adv. Opt. Technol. 6, 173 (2017)
Yabu, T., Kawasuji, Y., Hori, T., Okamoto, T., Tanaka, H., Miyao, K., Ishii, T., Watanabe, Y., Yanagida, T., Shiraishi, Y., Abe, T., Kodama, T., Nakarai, H., Yamazaki, T., Itou, N., Saito, T., Mizoguchi, H.: Key components development progress updates of the 250W high power LPP-EUV light source. Proc. SPIE 10450, 104501C (2017)
Yan, P.-Y.: Handbook of Photomask Manufacturing Technology, p. 234. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2005)
Hector, S.: Standards for EUV Masks. SEMI EUV Mask Standards Meeting. SEMATECH, San Francisco, California (2005)
Takeichi, Y., Nishiyama, I., Yamada, N.: High-precision (<1ppb/°C) optical heterodyne interferometric dilatometer for determining absolute CTE of EUVL materials. Proc. SPIE 6151, 61511Z (2006)
Schödel, R.: Ultra-high accuracy thermal expansion measurements with PTB’s precision interferometer. Meas. Sci. Technol. 19(8), 084003 (2008)
Hector, S.: Standards for EUV Masks. EUV Mask Workshop. SEMATECH, Miyazaki, Japan (2004)
Gullikson, E., Blaedel, K., Larson, C., Baker, S.L., Taylor, J.S.: EUV scattering from mask substrate roughness. 1st EUVL Symposium. SEMATECH, Dallas, Texas (2002)
Ballman, K., Lee, C., Dunn, T., Bean, A.: Error analysis of overlay compensation methodologies and proposed functional tolerances for EUV photomask flatness. Proc. SPIE 9984, 99840S (2016)
Turley, C., Rankin, J., Cehn, X., Ballman, K., Lee, C.A., Dunn, T.: EUV mask flatness compensation strategies and requirements for reticle flatness, scanner optimization and E-beam writer. Proc. SPIE 10450, 104500A (2017)
Blaedel, K.L., Taylor, J.S., Hector, S.D., Yan, P., Ramamoorthy, A., Brooker, P.D.: Vendor capability for low thermal expansion mask substrates for EUV lithography. Proc. SPIE 4688, 767 (2002)
Chen, X., Turley, C., Rankin, J., Brunner, T., Gabor, A.: Minimizing wafer overlay errors due to EUV mask non-flatness and thickness variations for N7 production. Proc. SPIE 10143, 101431F (2017)
Smith, B.W., Venkataraman, P., Kurinec, S.K., Mackay, R.S.: Materials for reflective multilayer coatings for EUV wavelengths. Proc. SPIE 3331, 544 (1998)
Slaughter, J.M., Schulze, D.W., Hills, C.R., Mirone, A., Stalio, R., Watts, R.N., Tarrio, C., Lucatorto, T.B., Krumrey, M., Mueller, P., Falco, C.M.: Structure and performance of Si/Mo multilayer mirrors for the extreme ultraviolet. J. Appl. Phys. 76(4), 2144 (1994)
Yan, P.-Y.: Handbook of Photomask Manufacturing Technology, p. 238. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2005)
Melvin, L.S., Kandel, Y., Isoyan, A., Gao, W.: Individual multilayer reflectance and near field image formation in an EUV reticle. Proc. SPIE 10450, 104500F (2017)
Onoue, T., Shoki, T., Horikawa, J.: Progress of EUV blanks development. EUVL Symposium, S2.1. EIDEC, Hiroshima, Japan (2016)
Tomofuji, T., Kandaka, N., Komiya, T., Shiraishi, M., Murakami, K.: Mo/Si multilayer(ML) mirror depositied with ion beam sputtering using Kr gas. 3rd International EUVL Symposium, p. 937. SEMATECH, Miyazaki, Japan (2004)
Lee, S.Y., Hur, S.M., Kim, H.J., Yoon, C.S., Lee, Y.T., Kang, I.Y., Chung, Y.-C., Yi, M., Bok, C.K., Kim, O., Ahn, J.: Analysis of multilayer structure for reflection of extreme-ultraviolet wavelength. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 41, 4086 (2002)
Yulin, S., Benoit, N., Feigl, T., Kaiser, N.: Interface-engineered multilayer mirrors. Proc. SPIE 5963, 59630U (2005)
Chkhalo, N.I., Gusev, S.A., Nechay, A.N., Pariev, D.E., Polkovnikov, V.N., Salashchenko, N.N., Schafers, F., Sertsu, M.G., Sokolov, A., Svechnikov, M.V., Tatarsky, D.A.: High-reflection Mo/Be/Si multilayers for EUV lithography. Opt. Lett. 42, 5070 (2017)
Bajt, S., Alameda, J., Barbee, T., Clift, W.M., Folta, J.A., Kaufmann, B., Spiller, E.: Improved reflectance and stability of Mo/Si multilayers. Proc. SPIE 4506, 65 (2001)
Braun, S., Mai, H., Moss, M., Scholz, R., Leson, A.: Mo/Si multilayers with different barrier layers for applications as extreme ultraviolet mirrors. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 41, 4074 (2002)
Yan, P.Y., Zhang, G., Chegwidden, S., Spiller, E., Mirkarimi, P.: EUVL mask with Ru ML capping. Proc. SPIE 5256, 1281 (2003)
Nishiyama, I.: Model of Ru surface oxidation for the lifetime scaling of EUVL projection optics mirror. Proc. SPIE 6151, 61510G (2006)
Kim, T.G., Lee, S.Y., Kim, C.Y., Park, I.S., Kang, I.Y., Lee, N.E., Chung, Y.C., Ahn, J.: Characterization of Ru layer for capping/buffer application in EUVL mask. Microelectron. Eng. 83, 688 (2006)
Dattilo, D., Dietze, U., Hsu, J.-W.: Ruthenium capping layer preservation for 100X clean through pH driven effects. Proc. SPIE 9635, 96351B (2015)
Takase, H., Terashima, S., Gomei, Y., Tanabea, M., Watanabe, Y., Aoki, T., Murakami, K., Matsunari, S., Niibe, M., Kakutani, Y.: Study of ruthenium-capped multilayer mirror for EUV irradiation durability. Proc. SPIE 6151, 615135 (2006)
Lee, B.T., Hoshino, E., Takahashi, M., Yoneda, T., Yamanashi, H., Hoko, H., Chiba, A., Ito, M., Ogawa, T., Okazaki, S.: Characteristics of the Ru buffer layer for EUVL mask patterning. Proc. SPIE 4343, 746 (2001)
Kearney, P.A., Moore, C.E., Tan, S.I., Vernon, S.P., Levesque, R.A.: Mask blanks for extreme ultraviolet lithography: ion beam sputter deposition of low defect density Mo/Si multilayers. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 15(6), 2452 (1997)
Folta, J.A., Davidson, J.C., Larson, C.C., Walton, C.C., Kearney, P.A.: Advances in low-defect multilayers for EUVL mask blanks. Proc. SPIE 4688, 173 (2002)
Mirkarimi, P.B., Spiller, E.A., Stearns, D.G., Sperry, V., Baker, S.L.: An ion-assisted Mo–Si deposition process for planarizing reticle substrates for extreme ultraviolet lithography. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 37(12), 1514 (2001)
Spiller, E.A., Baker, S.L., Mirkarimi, P.B., Sperry, V., Gullikson, E.M., Stearns, D.G.: High-performance Mo–Si multilayer coatings for extreme-ultraviolet lithography by ion-beam deposition. Appl. Opt. 42(12), 4049 (2003)
Mirkarimi, P.B., Spiller, E.A., Baker, S.L., Sperry, V.L., Stearns, D.G., Gullikson, E.M.: Developing a viable multilayer coating process for extreme ultraviolet lithography reticles. J. Microlithogr. Microfabr. Microsyst. 3(1), 139–145 (2004)
Randive, R., Ma, A., Reiss, I., Mirkarimi, P., Spiller, E., Beier, B., Uno, T., Kearney, P., Jeon, C.-U.: Defect mitigation and reduction in EUVL mask blanks. Proc. SPIE 6517, 651726 (2007)
Kearney, P., Ma, A., Jeon, C.U., Uno, T., Beier, B.: Defect mitigation and reduction in EUVL mask blanks. 5th EUVL Symposium, p. 734. SEMATECH, Barcelona, Spain (2006)
Rastegar, A., Eichenlaub, S., Kapila, V., Kadaksham, A.J., Marmillion, P.: New requirements for the cleaning of EUV mask blanks. Proc. SPIE 6517, 65171D (2007)
Rastegar, A., Eichenlaub, S., Popp, H., Goncher, K., Marmillion, P.: Removing sub-50nm particles during blank substrate cleaning. Solid State Technol. 49, 47 (2006)
Gullikson, E., Cerjan, C., Stearns, D., Mirkarimi, P., Sweeney, D.: Practical approach for modeling extreme ultraviolet lithography mask defects. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 20(1), 81 (2002)
Mirkarimi, P.B., Spiller, E., Baker, S.L., Stearns, D.G., Robinson, J.C., Olynick, D.L., Salmassi, F., Liddle, J.A., Liang, T., Stivers, A.R.: A silicon-based, sequential coat-and-etch process to fabricate nearly perfect substrate surfaces. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 6, 28 (2006)
Barty, A., Mirkarimi, P.B., Stearns, D.G., Sweeney, D.W., Chapman, H.N., Clift, W.M., Hector, S.D., Yi, M.: EUVL mask blank repair. Proc. SPIE 4688, 385 (2002)
Yan, P.-Y., Zhang, G., Kofron, P., Powers, J., Tran, M., Liang, T., Stivers, A., Lo, F.C.: EUV mask absorber characterization and selection. Proc. SPIE 4066, 116 (2000)
Niibe, M., Watanabe, T., Nii, H., Tanaka, T., Kinoshita, H.: Contrast measurement of reflection masks fabricated from Cr and Ta absorbers for extreme ultraviolet lithography. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 39, 6815 (2000)
Philipsen, V., Luong, K.V., Hendrickx, E., Erdmann, A., Xu, D., Evanschitzky, P., Kruijs, R.W., Edrisi, A., Scholze, F., Laubis, C., Irmscher, M., Naasz, S., Reuter, C.: Mitigating EUV mask 3D effects by alternative metal absorbers. EUVL Symposium, S4.2. EIDEC, Hiroshima, Japan (2016)
Philipsen, V., Luong, K.V., Souriau, L., Sanchez, E.A., Adelmann, C., Laubis, C., Scholtze, F., Kruemberg, J., Reuter, C., Hendrickx, E.: Single element and metal alloy novel EUV mask absorbers for improved imaging. Proc. SPIE 10450, 104500G (2017)
Mangat, P., Hector, S., Rose, S., Cardinale, G., Tejnil, E., Stivers, A.: EUV mask fabrication with Cr absorber. Proc. SPIE 3997, 76 (2000)
Hoshino, E., Ogawa, T., Hirano, N., Hoko, H., Takahashi, M., Yamanashi, H., Chiba, A., Ito, M., Okazaki, S.: Dry etching of Ta absorber for EUVL masks. Proc. SPIE 4186, 749 (2000)
Yan, P.-Y., Zhang, G., Ma, A., Liang, T.: TaN EUVL mask fabrication and characterization. Proc. SPIE 4343, 409 (2001)
Green, M., Choi, Y., Ham, Y., Kamberian, H., Progler, C., Tseng, S.-E., Chiou, T.-B., Miyazaki, J., Lammers, A., Chen, A.: EUV mask manufacturing readiness in the merchant mask industry. Proc. SPIE 10450, 1045005 (2017)
Yan, P.-Y.: The impact of EUVL mask buffer and absorber material properties on mask quality and performance. Proc. SPIE 4688, 150 (2002)
Wood, E.O., Raghunathan, S., Mangat, P., Philipsen, V., Luong, V., Kearney, P., Verduijn, E., Ku-mar, A., Patil, S., Laubis, C., Soltwisch, V., Scholze, F.: Alternative materials for high numerical aperture extreme ultraviolet lithography mask stacks. Proc. SPIE 9422, 94220I (2015)
Lee, J.U., Hong, S., Ahn, J.: Very thin extreme ultraviolet mask absorber material for extremely fine pitch patterning. Appl. Phys. Express 6, 076502 (2013)
Philipsen, V., Luong, K.V., Souriau, L., Hendrickx, E., Erdmann, A., Xu, D., Evanschitzky, P., van de Kruijs, R.W.E., Edrisi, A., Scholze, F., Laubis, C., Irmscher, M., Naasz, S., Reuter, C.: Reducing EUV mask 3D effects by alternative metal absorbers. Proc. SPIE 10143, 1014310 (2017)
Burkhardt, M.: Investigation of alternate mask absorbers in EUV lithography. Proc. SPIE 10143, 1014312 (2017)
Rastegar, A., House, M., Tian, R., Laursen, T., Antohe, A., Kearney, P.: Study of alternative capping and absorber layers for extreme ultraviolet (EUV) masks for sub-16 nm half-pitch nodes. Proc. SPIE 9048, 90480L (2014)
Civay, D., Hosler, E., Chauhan, V., Neogi, T.G., Smith, L., Pritchard, D.: EUV telecentricity and shadowing errors impact on process margins. Proc. SPIE 9422, 94220Z (2015)
Erdmann, A., Evanschitzky, P.: Imaging characteristics of binary and phase shift masks for EUV projection lithography. Proc. SPIE 8550, 85503K (2012)
Krautschik, C.G., Ito, M., Nishiyama, I., Otaki, K.: The impact of the EUV mask phase response on the asymmetry of Bossung curves as predicted by rigorous EUV mask simulations. Proc. SPIE 4343, 392 (2001)
Lam, M., Clifford, C., Raghunathan, A., Fenger, G., Adam, K.: Enabling full field physics based OPC via dynamic model generation. Proc. SPIE 10143, 1014316 (2017)
Mangat, P.J.S., Hector, S.D., Thompson, M.A., Dauksher, W.J., Cobb, J., Cummings, K.D., Mancini, D.P., Resnick, D.J., Cardinale, G., Henderson, C., Kearney, P., Wedowski, M.: Extreme ultraviolet lithography mask patterning and printability studies with a Ta-based absorber. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 17(6), 3029 (1999)
Wasson, J.R., Lu, B., Mangat, P.J.S., Nordquist, K., Resnick, D.J.: Writing, repairing, and inspecting of extreme ultraviolet lithography reticles considering the impact of the materials. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 19(6), 2635 (2001)
Park, W., Kwon, O., Lee, J., Whang, K.W.: Dry etching characteristics of TaN absorber for extreme ultraviolet mask with Ru buffer layer. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 30(4), 041301 (2012)
Liang, T., Stivers, A., Livengood, R., Yan, P.-Y., Zhang, G., Lo, F.-C.: Progress in extreme ultraviolet mask repair using a focused ion beam. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 18(6), 3216 (2000)
Jonckheere, R., Bret, T., Van den Heuvel, D., Magana, J., Gao, W., Waiblinger, M.: Repair of natural EUV reticle defects. Proc. SPIE 8166, 81661G (2011)
Waiblinger, M., Kornilov, K., Hofmann, T., Edinger, K.: E-beam induced EUV photomask repair – a perfect match. Proc. SPIE 7545, 75450P (2010)
Lee, S.-Y., Kim, G.-B., Sim, H.-S., Lee, S.-H., Kim, H.-S., Lee, J.-H., Seo, H.-S., Han, H.-S., Kim, S.-S., Moon, S.-Y., Woo, S.-G., Bozak, R., Dinsdale, A., Robinson, T., Lee, D., Cho, H.K.: Analysis of process margin in EUV mask repair with nano-machining. Proc. SPIE 7122, 71222I (2008)
Waiblinger, M., Bret, T., Jonckheere, R., Van den Heuvel, D.: E-beam based mask repair as door opener for defect free EUV masks. Proc. SPIE 8522, 85221M (2012)
Liang, T., Stivers, A.: Damage-free mask repair using electron beam induced chemical reactions. Proc. SPIE 4688, 375 (2002)
Liang, T., Stivers, A.R., Penn, M., Bald, D., Sethi, C., Boegli, V., Budach, M., Edinger, K., Spies, P.: Demonstration of damage-free mask repair using electron beam-induced processes. Proc. SPIE 5466, 291 (2004)
Liang, T., Frendberg, E., Bald, D.J., Penn, M., Stivers, A.R.: E-Beam mask repair: fundamental capability and applications. Proc. SPIE 5567, 456 (2004)
Liang, T., Frendberg, E., Lieberman, B., Stivers, A.: Advanced photolithographic mask repair using electron beams. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 23(6), 3101 (2005)
Robinson, T., White, R., Bozak, R., Roessler, K., Arruza, B., Hogle, D., Archuletta, M., Lee, D.: New tools to enable photomask repair to the 32 nm node. Proc. SPIE 7488, 74880F (2009)
Bret, T., Jonckheere, R., Van den Heuvel, D., Baur, C., Waiblinger, M., Baralia, G.: Closing the gap for EUV mask repair. Proc. SPIE 8322, 83220C (2012)
Aramaki, F., Ogawa, T., Matsuda, O., Kozakai, T., Sugiyama, Y., Oba, H., Yasaka, A., Amano, T., Shigemura, H., Suga, O.: Development of new FIB technology for EUVL mask repair. Proc. SPIE 7969, 79691C (2011)
Yan, P.-Y.: EUVL alternating phase shift mask imaging evaluation. Proc. SPIE 4889, 1099 (2002)
Takai, K., Motokawa, T., Murano, K., Kamo, T., Hayashi, N.: Patterning of EUVL binary etched multilayer mask. Proc. SPIE 8880, 88802M (2013)
Kim, J.S., Hong, S., Lee, J.U., Lee, S.M., Ahn, J.: Attenuated phase-shift mask for mitigation of photon shot noise effect in contact hole pattern for extreme ultraviolet lithography. Appl. Phys. Express 7, 096502 (2014)
Erdmann, A., Xu, D., Evanschitzky, P., Luong, V., Philipsen, V., Hendrickx, E.: Characterization and mitigation of 3D mask effects in EUV lithography. EUVL Symposium, S2.1. EIDEC, Hiroshima, Japan (2016)
Sherwin, S., Pistor, T.V., Neureuther, A., Naulleau, P.: Rigorous 3D electromagnetic simulation of ultrahigh efficiency EUV contact-hole printing with chromeless phase shift mask. Proc. SPIE 10143, 1014317 (2017)
Deng, Y., Fontaine, B.L., Pawloski, A.R., Neureuther, A.R.: Simulation of fine structures and defects in EUV etched multilayer masks. Proc. SPIE 5374, 760 (2004)
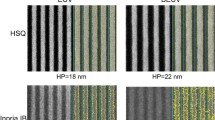
Takai, K., Murano, K., Kamo, T., Morikawa, Y., Hayashi, N.: Capability of etched multilayer EUV mask fabrication. Proc. SPIE 9235, 923515 (2014)
Deng, Y., Fontaine, B.L., Levinson, H.J., Neureuther, A.R.: Rigorous EM simulation of the influence of the structure of mask patterns on EUVL imaging. Proc. SPIE 5037, 302 (2003)
Kamo, T., Takai, K., Iida, N., Morikawa, Y., Hayashi, N., Watanabe, H.: Evaluation of etched multilayer mask for 0.33NA EUVL extension. EUVL Symposium, S4.4. EIDEC, Hiroshima, Japan (2016)
Yan, P.-Y.: Handbook of Photomask Manufacturing Technology, p. 265. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2005)
Lee, S., Lee, I., Doh, J., Lee, J., Hong, S., Ahn, J.: Improved imaging properties of thin attenuated phase shift masks for extreme ultraviolet lithography. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 31, 021606 (2013)
Yan, P.-Y., Leeson, M., Lee, S., Zhang, G., Gullikson, E., Salmassi, F.: Extreme ultraviolet–embedded phase-shift mask. J. Micro/Nanolithogr. MEMS MOEMS 10, 033011 (2011)
Lee, J.U., Jeong, S.J., Hong, S., Lee, S.M., Ahn, J.: Imaging performance of attenuated phase-shift mask using coherent scattering microscope. Proc. SPIE 9048, 90481X (2014)
Woo, D.G., Lee, J.U., Hong, S., Kim, J.S., Ahn, J.: Coherent scattering microscopy as an effective inspection tool for analyzing performance of phase shift mask. Opt. Express 24, 12055 (2016)
van Ingen Schenau, K., Bottiglieri, G., van Schoot, J., Neumann, J.T., Roesch, M.: Imaging performance of the EUV high NA anamorphic system. Proc. SPIE 9661, 96610S (2015)
van Schoot, J., Troost, K., Bornebroek, F., van Ballegoij, R., Lok, S., Krabbendam, P., Stoeldraijer, J., Loopstra, E., Benschop, J., Finders, J., Meiling, H., van Setten, E., Kneer, B., Kuerz, P., Kaiser, W., Heil, T., Migura, S., Neumann, J.T.: High-NA EUV lithography enabling Moore’s law in the next decade. Proc. SPIE 10450, 104500U (2017)
Levinson, H.J., Mangat, P., Wallow, T., Sun, L., Ackmann, P., Meyers, S.: Considerations for high-numerical aperture EUV lithography. Proc. SPIE 8679, 867916 (2013)
Kneer, B., Migura, S., Kaiser, W., Neumann, J.T., van Schoot, J.: EUV lithography optics for sub 9 nm resolution. Proc. SPIE 9422, 94221G (2015)
Ruoff, J.: Impact of mask topography and multilayer stack on high NA imaging of EUV masks. Proc. SPIE 7823, 78231N (2010)
Pirati, A., van Schoot, J., Troost, K., van Ballegoij, R., Krabbendam, P., Stoeldraijer, J., Loopstra, E., Benschop, J., Finders, J., Meiling, H., van Setten, E., Mika, N., Driedonkx, J., Stamm, U.: The future of EUV lithography: enabling Moore’s law in the next decade. Proc. SPIE 10143, 101430G (2017)
Philipsen, V., Hendrickx, E., Verduijn, E., Raghunathan, S., Wood, O., Soltwisch, V., Scholze, F., Davydova, N., Mangat, P.: Imaging impact of multilayer tuning in EUV masks, experimental validation. Proc. SPIE 9235, 92350J (2014)
Hosler, E.R., Thiruvengadam, S., Cantone, J.R., Civay, D.E., Schroeder, U.P.: EUV and optical lithographic pattern shift at the 5nm node. Proc. SPIE 9776, 977616 (2015)
Wood, O., Wong, K., Parks, V., Kearney, P., Ilse, J.M., Luong, V., Philipsen, V., Faheem, M., Liang, Y., Kumar, A., Chen, E., Bennett, C., Fu, B., Gribelyuk, M., Zhao, W., Mangat, P., der Heide, P.V.: Improved Ru/Si multilayer reflective coatings for advanced extreme ultraviolet lithography photomasks. Proc. SPIE 9776, 977619 (2016)
Jang, Y.J., Kim, J.S., Hong, S., Ahn, J.: Phase shift mask to compensate for mask 3D effect in high-numerical-aperture extreme ultraviolet lithography. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 8, 729 (2016)
Liang, T., Magana, J., Chakravorty, K., Panning, E., Zhang, G.: EUV mask infrastructure readiness and gaps for TD and HVM. Proc. SPIE 9635, 963509 (2015)
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank all the authors of the technical papers referenced in this review paper. The author is indebted to all the students and colleagues for their dedicated assistance. This research was supported by the Commercialization Promotion Agency for R&D Outcomes (COMPA), funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) (Grant No. 2017K000389).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.S., Ahn, J. Mask Materials and Designs for Extreme Ultra Violet Lithography. Electron. Mater. Lett. 14, 533–547 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-018-0058-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-018-0058-6