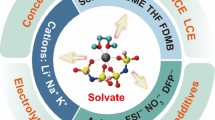
The large-scale application of lithium metal batteries remains a challenge due to the hydrolysis of LiPF6, which can induce capacity fade and series of safety issues. Prof. Ma and his co-workers have designed a hydrophobic Li+-solvated structure to obtain high performances lithium metal batteries. The specific functional groups of the additive, hexafluoroisopropyl acrylate, can promote the formation of a hydrophobic surface, which can protect the LiPF6 from trace H2O. The hexafluoroisopropyl acrylate can also promote the formation of a robust and stable solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) with rich polar C–F bonds, which can suppress the dendrite growth and improve battery performances by capturing lithium ions. This work reveals the mechanism that the introduction of hexafluoroisopropyl acrylate can improve lithium anode performances and further feature the innovative design of advanced materials for energy devices beyond lithium.
摘要
由于LiPF6的水解会诱发容量衰减和一系列的安全问题, 大规模应用对于锂金属电池仍然是一个挑战。马教授和他的同事们设计了一种疏水性的Li+溶剂化结构, 以获得高性能的锂金属电池。六氟异丙基丙烯酸酯的特定官能团可以促进疏水表面的形成, 从而保护LiPF6免受微量H2O的影响。丙烯酸六氟异丙酯还能促进形成具有丰富极性C‒F键的坚固稳定的固体电解质界面 (SEI), 从而抑制枝晶的生长, 并通过捕获锂离子提高电池性能。这项工作揭示了引入丙烯酸六氟异丙酯可以改善锂电负极性能的机制, 并进一步为锂电以外的能源设备设计先进材料提供思路。


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shi P, Zhang X, Shen X, Zhang R, Liu H, Zhang Q. Composite lithium anodes: a review of composite lithium metal anode for practical applications. Adv Mater Technol. 2020;5(1):2070002. https://doi.org/10.1002/admt.202070002.
Liu Y, Cui Y. Lithium metal anodes: a recipe for protection. Joule. 2017;1(4):649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2017.12.001.
Shen X, Zhang R, Shi P, Chen X, Zhang Q. How does external pressure shape Li dendrites in Li metal batteries? Adv Energy Mater. 2021;11(10):2003416. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.202003416.
Li X, Liu J, He J, Wang H, Qi S, Wu D, Huang JD, Li F, Hu W, Ma JM. Hexafluoroisopropyl trifluoromethanesulfonate-driven easily Li+ desolvated electrolyte to afford Li||NCM811 cells with efficient anode/cathode electrolyte interphases. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;31(37):21043. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202104395.
Wu DX, He J, Liu JD, Wu MG, Qi SA, Wang HP, Huang JD, Li F, Tang DL, Ma JM. Li2CO3/LiF-Rich heterostructured solid electrolyte interphase with superior lithiophilic and Li+-transferred characteristics via adjusting electrolyte additives. Adv Energy Mater. 2022;12(18):2200337. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.202200337.
Campion CL, Li W, Lucht BL. Thermal decomposition of LiPF6-based electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J Electrochem Soc. 2005;152(12):A2327. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2083267.
Jang EK, Ahn J, Yoon S, Cho KY. High dielectric, robust composite protective layer for dendrite-free and LiPF6 degradation-free lithium metal anode. Adv Funct Mater. 2019;29(48):1905078. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201905078.
Ye H, Zheng ZJ, Yao HR, Liu SC, Zuo TT, Wu XW, Yin YX, Li NW, Gu JJ, Cao FF. Guiding uniform Li plating/stripping through lithium-aluminum alloying medium for long-life li metal batteries. Angew Chem. 2019;58(4):1094. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201811955.
Liu L, Yin YX, Li JY, Wang SH, Guo YG, Wan LJ. Uniform lithium nucleation/growth induced by lightweight nitrogen-doped graphitic carbon foams for high-performance lithium metal anodes. Adv Mater. 2018;30(10):1706216. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201706216.
Tan SJ, Zeng XX, Ma Q, Wu XW, Guo YG. Recent advancements in polymer-based composite electrolytes for rechargeable lithium batteries. Electrochem Energy Rev. 2018;1(2):113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41918-018-0011-2.
Wei WQ, Liu BQ, Gan YQ, Ma HJ, Cui DW. Protecting lithium metal anode in all-solid-state batteries with a composite electrolyte. Rare Met. 2021;40(2):409. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01501-6.
Xu CX, Jiang JJ. Designing electrolytes for lithium metal batteries with rational interface stability. Rare Met. 2021;40(2):243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01629-5.
Yang F, Song X, Dong G, Tsui KL. A coulombic efficiency-based model for prognostics and health estimation of lithium-ion batteries. Energy. 2019;171:1173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.01.083.
Liu YC, Hong L, Jiang R, Wang YD, Patel SV, Feng XY, Xiang HF. Multifunctional electrolyte additive stabilizes electrode-electrolyte interface layers for high-voltage lithium metal batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(48):57430. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c18783.
Li F, Liu JD, He J, Hou YY, Wang HP, Wu DX, Huang JD, Ma JM. Additive-assisted hydrophobic Li+-solvated structure for stabilizing dual electrode electrolyte interphases through suppressing LiPF6 hydrolysis. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2022;61(27):e202205091. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202205091.
Yang S, He R, Zhang Z, Cao Y, Gao X, Liu X. CHAIN: cyber hierarchy and interactional network enabling digital solution for battery full-lifespan management. Matter. 2020;3(1):27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matt.2020.04.015.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52102470).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, B., Zhang, YL. & Liu, XH. Concept of hydrophobic Li+-solvated structure for high performances lithium metal batteries. Rare Met. 42, 1427–1430 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-022-02217-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-022-02217-5