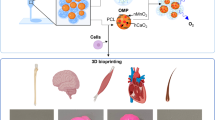
Abstract
Burns are a common medical problem globally, and wound infection is one of the major causes of inducing related complications. Although antibiotics effectively prevent wound infections, the misuse of antibiotics has created a new problem of superbugs. Herein, we propose a new strategy to obtain pH-responsive antimicrobial P-ZIF (ZIF: zeolitic imidazolate framework) by loading polyhexamethylenebiguanide (PHMB) into the framework of ZIF-8 nanoparticles. This will enable PHMB to be released in the weak acid environment of an infected wound. To address burn infections, P-ZIF nanoparticles were loaded into a hydrogel system made of sodium alginate (SA) and 3-aminophenylboronic acid modified human-like collagen (H-A) through borate ester bonds. The resulting H-A/SA/P-ZIF (HASPZ) hydrogel dressing not only possesses antibacterial and wound healing properties but also has dual pH responsiveness to prevent the overuse of medication while effectively treat deep second-degree burns. Therefore, P-ZIF nanoparticles and the corresponding HASPZ hydrogel dressing are considered of significant importance in antimicrobial, drug delivery, and wound repair.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jahromi, M. A. M.; Zangabad, P. S.; Basri, S. M. M.; Zangabad, K. S.; Ghamarypour, A.; Aref, A. R.; Karimi, M.; Hamblin, M. R. Nanomedicine and advanced technologies for burns: Preventing infection and facilitating wound healing. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2018, 123, 33–64.
Jeschke, M. G.; Van Baar, M. E.; Choudhry, M. A.; Chung, K. K.; Gibran, N. S.; Logsetty, S. Burn injury. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 11.
Church, D.; Elsayed, S.; Reid, O.; Winston, B.; Lindsay, R. Burn wound infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 403–434.
Huang, W. J.; Wang, Y. X.; Huang, Z. Q.; Wang, X. L.; Chen, L. Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L. N. On-demand dissolvable self-healing hydrogel based on carboxymethyl chitosan and cellulose nanocrystal for deep partial thickness burn wound healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 41076–41088.
Wang, Y. W.; Beekman, J.; Hew, J.; Jackson, S.; Issler-Fisher, A. C.; Parungao, R.; Lajevardi, S. S.; Li, Z.; Maitz, P. K. M. Burn injury: Challenges and advances in burn wound healing, infection, pain and scarring. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2018, 123, 3–17.
Jayakumar, A.; Jose, V. K.; Lee, J. M. Hydrogels for medical and environmental applications. Small Methods 2020, 4, 1900735.
Li, S. Q.; Dong, S. J.; Xu, W. G.; Tu, S. C.; Yan, L. S.; Zhao, C. W.; Ding, J. X.; Chen, X. S. Antibacterial hydrogels. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1700527.
Caló, E.; Khutoryanskiy, V. V. Biomedical applications of hydrogels: A review of patents and commercial products. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 65, 252–267.
Liang, Y. P.; He, J. H.; Guo, B. L. Functional hydrogels as wound dressing to enhance wound healing. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 12687–12722.
Huang, H. Y.; Dong, Z. C.; Ren, X. Y.; Jia, B.; Li, G. W.; Zhou, S. W.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W. Z. High-strength hydrogels: Fabrication, reinforcement mechanisms, and applications. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 3475–3515.
Maleki, A.; He, J. H.; Bochani, S.; Nosrati, V.; Shahbazi, M. A.; Guo, B. L. Multifunctional photoactive hydrogels for wound healing acceleration. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 18895–18930.
Huang, Y.; Mu, L.; Zhao, X.; Han, Y.; Guo, B. L. Bacterial growth-induced tobramycin smart release self-healing hydrogel for Pseudomonas aeruginosa-infected burn wound healing. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 13022–13036.
Xiong, Y. H.; Zhang, L. J.; Xiu, Z. P.; Yu, B. R.; Duan, S.; Xu, F. J. Derma-like antibacterial polysaccharide gel dressings for wound care. Acta Biomater. 2022, 148, 119–132.
Zhao, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y. N.; Song, X. Y.; Li, K. Y.; Yan, X. F.; Yu, L. M.; He, Z. Y. Nanomaterial-based strategies in antimicrobial applications: Progress and perspectives. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 4417–4441.
Maleki, A.; Shahbazi, M. A.; Alinezhad, V.; Santos, H. A. The progress and prospect of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks in cancer therapy, antibacterial activity, and biomineralization. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, 2000248.
Carraro, F.; Williams, J. D.; Linares-Moreau, M.; Parise, C.; Liang, W. B.; Amenitsch, H.; Doonan, C.; Kappe, C. O.; Falcaro, P. Continuous-flow synthesis of ZIF-8 biocomposites with tunable particle size. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 8123–8127.
Shi, L. X.; Wu, J.; Qiao, X. R.; Ha, Y.; Li, Y. P.; Peng, C.; Wu, R. B. In situ biomimetic mineralization on ZIF-8 for smart drug delivery. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 4595–4603.
Yang, N.; Venezuela, J.; Almathami, S.; Dargusch, M. Zinc-nutrient element based alloys for absorbable wound closure devices fabrication: Current status, challenges, and future prospects. Biomaterials 2022, 280, 121301.
Fu, J. T.; Zhou, Y. X.; Liu, T.; Wang, W. H.; Zhao, Y. T.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y. M.; Qin, W. X.; Chen, Z. W.; Lu, C. et al. A triple-enhanced chemodynamic approach based on glucose-powered hybrid nanoreactors for effective bacteria killing. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 2682–2694.
Taheri, M.; Ashok, D.; Sen, T.; Enge, T. G.; Verma, N. K.; Tricoli, A.; Lowe, A.; Nisbet, D. R.; Tsuzuki, T. Stability of ZIF-8 nanopowders in bacterial culture media and its implication for antibacterial properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 413, 127511.
Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Sun, M. L.; Cheng, Z. Q.; Jia, W. Y.; Jiao, K.; Wang, S. R.; Jiang, K. Z.; Yang, Y. H.; Dai, Z. H. et al. ZIF-8 modified multifunctional injectable photopolymerizable GelMA hydrogel for the treatment of periodontitis. Acta Biomater. 2022, 146, 37–48.
Su, L. Z.; Li, Y. F.; Liu, Y.; Ma, R. J.; Liu, Y.; Huang, F.; An, Y. L.; Ren, Y. J.; Van Der Mei, H. C.; Busscher, H. J. et al. Antifungal-inbuilt metal-organic-frameworks eradicate Candida albicans biofilms. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000537.
Peng, W.; Yin, H.; Liu, P. M.; Peng, J. M.; Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Gu, Y. H.; Dong, X. H.; Ma, Z. Z.; Shen, J. et al. Covalently construction of poly(hexamethylene biguanide) as high-efficiency antibacterial coating for silicone rubber. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 412, 128707.
Chindera, K.; Mahato, M.; Sharma, A. K.; Horsley, H.; Kloc-Muniak, K.; Kamaruzzaman, N. F.; Kumar, S.; McFarlane, A.; Stach, J.; Bentin, T. et al. The antimicrobial polymer PHMB enters cells and selectively condenses bacterial chromosomes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23121.
Zheng, M.; Liu, S.; Guan, X. G.; Xie, Z. G. One-step synthesis of nanoscale zeolitic imidazolate frameworks with high curcumin loading for treatment of cervical cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 22181–22187.
Wang, M. M.; Yao, J. X.; Shen, S. H.; Heng, C. N.; Zhang, Y. Y.; Yang, T.; Zheng, X. Y. A scaffold with zinc-whitlockite nanoparticles accelerates bone reconstruction by promoting bone differentiation and angiogenesis. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 757–770.
Shen, S. H.; Fan, D. D.; Yuan, Y.; Ma, X. X.; Zhao, J.; Yang, J. An ultrasmall infinite coordination polymer nanomedicine-composited biomimetic hydrogel for programmed dressing-chemo-low level laser combination therapy of burn wounds. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 130610.
Zheng, G. C.; Chen, Z. W.; Sentosun, K.; Pérez-Juste, I.; Bals, S.; Liz-Marzán, L. M.; Pastoriza-Santos, I.; Pérez-Juste, J.; Hong, M. Shape control in ZIF-8 nanocrystals and metal nanoparticles@ZIF-8 heterostructures. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 16645–16651.
Zong, L.; Yang, Y. Q.; Yang, H.; Wu, X. C. Shapeable aerogels of metal-organic-frameworks supported by aramid nanofibrils for efficient adsorption and interception. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 7295–7301.
Souza, C.; Watanabe, E.; Borgheti-Cardoso, L. N.; De Abreu Fantini, M. C.; Lara, M. G. Mucoadhesive system formed by liquid crystals for buccal administration of poly(hexamethylene biguanide) hydrochloride. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 3914–3923.
Cruz, L.; Mateus, N.; De Freitas, V. pH-regulated interaction modes between cyanidin-3-glucoside and phenylboronic acid-modified alginate. Carbohyd. Polym. 2022, 280, 119029.
Shen, D.; Yu, H. J.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Feng, J. Y.; Li, C. J.; Xiong, W.; Zhang, Q. Glucose-responsive hydrogel-based microneedles containing phenylborate ester bonds and N-isopropylacrylamide moieties and their transdermal drug delivery properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 148, 110348.
Lei, H.; Fan, D. D. Conductive, adaptive, multifunctional hydrogel combined with electrical stimulation for deep wound repair. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 421, 129578.
Yuan, Y.; Shen, S. H.; Fan, D. D. A physicochemical double cross-linked multifunctional hydrogel for dynamic burn wound healing: Shape adaptability, injectable self-healing property and enhanced adhesion. Biomaterials 2021, 276, 120838.
Huang, Y.; Bai, L.; Yang, Y. T.; Yin, Z. H.; Guo, B. L. Biodegradable gelatin/silver nanoparticle composite cryogel with excellent antibacterial and antibiofilm activity and hemostasis for Pseudomonas aeruginosa-infected burn wound healing. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 608, 2278–2289.
Zhao, Y.; Yu, Y. P.; Gao, F.; Wang, Z. Y.; Chen, W. X.; Chen, C.; Yang, J.; Yao, Y. C.; Du, J. Y.; Zhao, C. et al. A highly accessible copper single-atom catalyst for wound antibacterial application. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 4808–4813.
Li, Y.; Fu, R. Z.; Duan, Z. G.; Zhu, C. H.; Fan, D. D. Construction of multifunctional hydrogel based on the tannic acid-metal coating decorated MoS2 dual nanozyme for bacteria-infected wound healing. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 9, 461–474.
Qu, J.; Zhao, X.; Liang, Y. P.; Xu, Y. M.; Ma, P. X.; Guo, B. L. Degradable conductive injectable hydrogels as novel antibacterial, anti-oxidant wound dressings for wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 548–560.
Gao, S.; Qu, L. L.; Zhu, C. H.; Ouyang, P. K.; Fan, D. D. A novel degradable injectable HLC-HPA hydrogel with anti-inflammatory activity for biomedical materials: Preparation, characterization, in vivo and in vitro evaluation. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2020, 63, 2449–2463.
Sun, G. M.; Zhang, X. J.; Shen, Y. I.; Sebastian, R.; Dickinson, L. E.; Fox-Talbot, K.; Reinblatt, M.; Steenbergen, C.; Harmon, J. W.; Gerecht, S. Dextran hydrogel scaffolds enhance angiogenic responses and promote complete skin regeneration during burn wound healing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20976–20981.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National key Research and Development Program of China (Nos. 2021YFC2101504, 2021YFC2103900, and 2019YFA0905200), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 22078265 and 21908179), and the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province, China (No. 218JQ2052).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, N., Liu, W., Zheng, X. et al. Antimicrobial hydrogel with multiple pH-responsiveness for infected burn wound healing. Nano Res. 16, 11139–11148 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5751-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5751-6