Abstract
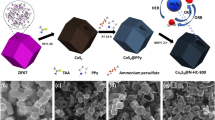
Encapsulating well-defined nanoparticles (NPs) into metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) to form core–shell structures not only combines their properties, but may also provide synergistic functionality. Much research attention has been focused on applying core–shell NP@MOF structures to gas storage and sensing, luminescence, lithium ion batteries, selective catalysis, and cascade reactions; however, their application as photocatalysts has been reported much more rarely. Herein, we report the design of a new core–shell structure composed of semiconductor CdS NPs as the core and ZIF-8 as the shell. Both single-core–shell and multiple-core–shell CdS@ZIF-8 were synthesized by varying the concentrations of the ZIF-8 precursor. Photocatalytic hydrogen generation from formic acid over CdS@ZIF-8 demonstrated that core–shell CdS@ZIF-8 structures exhibit increased photocatalytic selectivity for H2 generation from formic acid compared with pure CdS NPs. Furthermore, the concentration of CO in the products was significantly decreased, which benefits the application of CdS@ZIF-8 to proton-exchange membrane fuel cells. Our results provide guidance for the development of new photocatalysts based on NP@MOF core–shell materials.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cook, T. R.; Zheng, Y. R.; Stang, P. J. Metal–organic frameworks and self-assembled supramolecular coordination complexes: Comparing and contrasting the design, synthesis, and functionality of metal–organic materials. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 734–777.
Kitagawa, S.; Kitaura, R.; Noro, S. I. Functional porous coordination polymers. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 2334–2375.
Zhu, Q. L.; Xu, Q. Metal–organic framework composites. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5468–5512.
Liu, Y. L.; Tang, Z. Y. Multifunctional nanoparticle@MOF core–shell nanostructures. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5819–5825.
Chen, L. Y.; Peng, Y.; Wang, H.; Gu, Z. Z.; Duan, C. Y. Synthesis of Au@ZIF-8 single- or multi-core–shell structures for photocatalysis. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 8651–8654.
Hu, P.; Zhuang, J.; Chou, L. Y.; Lee, H. K.; Ling, X. Y.; Chuang, Y. C.; Tsung, C. K. Surfactant-directed atomic to mesoscale alignment: Metal nanocrystals encased individually in single-crystalline porous nanostructures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 10561–10564.
Dai, H. M.; Xia, B. Q.; Wen, L.; Du, C.; Su, J.; Luo, W.; Cheng, G. Z. Synergistic catalysis of AgPd@ZIF-8 on dehydrogenation of formic acid. Appl. Catal. B 2015, 165, 57–62.
Li, S. Z.; Huo, F. W. Hybrid crystals comprising metal–organic frameworks and functional particles: Synthesis and applications. Small 2014, 10, 4371–4378.
Chen, X. F.; Ding, N.; Zang, H.; Yeung, H.; Zhao, R. S.; Cheng, C. G.; Liu, J. H.; Chan, T. W. D. Fe3O4@MOF core–shell magnetic microspheres for magnetic solid-phase extraction of polychlorinated biphenyls from environmental water samples. J Chromatogr. A 2013, 1304, 241–245.
Ke, F.; Qiu, L. G.; Zhu, J. F. Fe3O4@MOF core–shell magnetic microspheres as excellent catalysts for the Claisen–Schmidt condensation reaction. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 1596–1601.
Ke, F.; Qiu, L. G.; Yuan, Y. P.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, J. F. Fe3O4@MOF core–shell magnetic microspheres with a designable metal–organic framework shell. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 9497–9500.
Lee, H. J.; Cho, W.; Oh, M. Advanced fabrication of metal–organic frameworks: Template-directed formation of polystyrene@ZIF-8 core–shell and hollow ZIF-8 microspheres. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 221–223.
Li, A. L.; Ke, F.; Qiu, L. G.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Y. M.; Tian, X. Y. Controllable synthesis of metal–organic framework hollow nanospheres by a versatile step-by-step assembly strategy. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 3554–3559.
Song, J.; Luo, Z.; Britt, D. K.; Furukawa, H.; Yaghi, O. M.; Hardcastle, K. I.; Hill, C. L. A multiunit catalyst with synergistic stability and reactivity: A polyoxometalate-metal organic framework for aerobic decontamination. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 16839–16846.
Sun, C. Y.; Liu, S. X.; Liang, D. D.; Shao, K. Z.; Ren, Y. H.; Su, Z. M. Highly stable crystalline catalysts based on a microporous metal–organic framework and polyoxometalates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1883–1888.
Koh, K.; Wong-Foy, A. G.; Matzger, A. J. MOF@MOF: Microporous core–shell architectures. Chem. Commun. 2009, 6162–6164.
Zhuang, J.; Chou, L. Y.; Sneed, B. T.; Cao, Y.; Hu, P.; Feng, L.; Tsung, C. K. Surfactant-mediated conformal overgrowth of core–shell metal–organic framework materials with mismatched topologies. Small 2015, 11, 5551–5555.
Li, T.; Sullivan, J. E.; Rosi, N. L. Design and preparation of a core–shell metal–organic framework for selective CO2 capture. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 9984–9987.
He, L. C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J. Z.; Xiong, Y. S.; Zheng, J. Z.; Liu, Y. L.; Tang, Z. Y. Core–shell noble-metal@metalorganic- framework nanoparticles with highly selective sensing property. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3741–3745.
Yang, D.; Yang, G. X.; Gai, S. L.; He, F.; An, G. H.; Dai, Y. L.; Lv, R. C.; Yang, P. P. Au25 cluster functionalized metal–organic nanostructures for magnetically targeted photodynamic/photothermal therapy triggered by single wavelength 808 nm near-infrared light. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 19568–19578.
Chen, R.; Zhang, J. F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X. F.; Zapien, J. A.; Lee, C. S. Graphitic carbon nitride nanosheet@metal–organic framework core–shell nanoparticles for photo-chemo combination therapy. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 17299–17305.
Yue, H. Y.; Shi, Z. P.; Wang, Q. X.; du, T.; Ding, Y. M.; Zhang, J.; Huo, N. N.; Yang, S. T. In situ preparation of cobalt doped ZnO@C/CNT composites by the pyrolysis of a cobalt doped MOF for high performance lithium ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 75653–75658.
Yang, J.; Zhang, F. J.; Lu, H. Y.; Hong, X.; Jiang, H. L.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. D. Hollow Zn/Co ZIF particles derived from core–shell ZIF-67@ZIF-8 as selective catalyst for the semihydrogenation of acetylene. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 10889–108893.
Yang, Y. F.; Wang, F. W.; Yang, Q. H.; Hu, Y. L.; Yan, H.; Chen, Y. Z.; Liu, H. R.; Zhang, G. Q.; Lu, J. L.; Jiang, H. L. et al. Hollow metal–organic framework nanospheres via emulsion-based interfacial synthesis and their application in size-selective catalysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 18163–18171.
Zhao, M. T.; Deng, K.; He, L. C.; Liu, Y.; Li, G. D.; Zhao, H. J.; Tang, Z. Y. Core–shell palladium nanoparticle@metal–organic frameworks as multifunctional catalysts for cascade reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 1738–1741.
Kubacka, A.; Fernández-García, M.; Colón, G. Advanced nanoarchitectures for solar photocatalytic applications. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1555–1614.
Zhao, K.; Zhao, S. L.; Qi, J.; Yin, H. J.; Gao, C.; Khattak, A. M.; Wu, Y. J.; Iqbal, A.; Wu, L.; Gao, Y. et al. Cu2O clusters grown on TiO2 nanoplates as efficient photocatalysts for hydrogen generation. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2016, 3, 488–493.
Zhao, K.; Qi, J.; Yin, H. J.; Wang, Z. M.; Zhao, S. L.; Ma, X.; Wan, J. W.; Chang, L.; Gao, Y.; Yu, R. B. et al. Efficient water oxidation under visible light by tuning surface defects on ceria nanorods. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 20465–20470.
Johnson, T. C.; Morris, D. J.; Wills, M. Hydrogen generation from formic acid and alcohols using homogeneous catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 81–88.
Zhu, Q. L.; Xu, Q. Liquid organic and inorganic chemical hydrides for high-capacity hydrogen storage. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 478–512.
Grasemann, M.; Laurenczy, G. Formic acid as a hydrogen source-recent developments and future trends. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 8171–8181.
Li, X. H.; Li, J. X.; Li, G. D.; Liu, D. P.; Chen, J. S. Controlled synthesis, growth mechanism, and properties of monodisperse CdS colloidal spheres. Chem.—Eur. J. 2007, 13, 8754–8761.
Cravillon, J.; Nayuk, R.; Springer, S.; Feldhoff, A.; Huber, K.; Wiebcke, M. Controlling zeolitic imidazolate framework nano- and microcrystal formation: Insight into crystal growth by time-resolved in situ static light scattering. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 2130–2141.
Guo, H. L.; Zhu, Y. Z.; Wang, S.; Su, S. Q.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, H. J. Combining coordination modulation with acid-base adjustment for the control over size of metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 444–450.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, M., Chai, Z., Deng, X. et al. Core–shell CdS@ZIF-8 structures for improved selectivity in photocatalytic H2 generation from formic acid. Nano Res. 9, 2729–2734 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1161-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1161-3