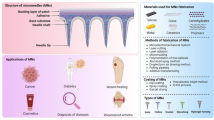
Abstract
In recent years, microneedle (MN) patches have emerged as an alternative technology for transdermal delivery of various drugs, therapeutics proteins, and vaccines. Therefore, there is an urgent need to understand the status of MN-based therapeutics. The article aims to illustrate the current status of microneedle array technology for therapeutic delivery through a comprehensive review. However, the PubMed search was performed to understand the MN's therapeutics delivery status. At the same time, the search shows the number no of publications on MN is increasing (63). The search was performed with the keywords “Coated microneedle,” “Hollow microneedle,” “Dissolvable microneedle,” and “Hydrogel microneedle,” which also shows increasing trend. Similarly, the article highlighted the application of different microneedle arrays for treating different diseases. The article also illustrated the current status of different phases of MN-based therapeutics clinical trials. It discusses the delivery of different therapeutic molecules, such as drug molecule delivery, using microneedle array technology. The approach mainly discusses the delivery of different therapeutic molecules. The leading pharmaceutical companies that produce the microneedle array for therapeutic purposes have also been discussed. Finally, we discussed the limitations and future prospects of this technology.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this article included within the article.
Abbreviations
- APCs:
-
Antigen presenting cells
- MN:
-
Microneedle
- TPMA:
-
Titanium porous microneedle array
- MEMS:
-
Microelectro-mechanical systems
- sCT:
-
Salmon calcitonin
- PLGA:
-
Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid)
- T2D:
-
Type 2 diabetes
- CGRP:
-
Calcitonin gene related peptide
- PGA:
-
Poly-glycolic acid
- FI-RSV:
-
Formalin-inactivated respiratory syncytial virus
- M2e VLP:
-
Matrix protein 2 virus-like particle
- ACE2:
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2
- MILD:
-
Mushroom-inspired imprintable and lightly detachable
- DMNA:
-
Dissolvable microneedle array
- AAV:
-
Adeno-associated virus
References
Prausnitz, M. R. (2004). Microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 56, 581–587.
Paudel, K. S., Milewski, M., Swadley, C. L., Brogden, N. K., Ghosh, P., & Stinchcomb, A. L. (2010). Challenges and opportunities in dermal/transdermal delivery. Therapeutic Delivery, 1, 109–131.
Suh, H., Shin, J., & Kim, Y. C. (2014). Microneedle patches for vaccine delivery. Clinical and Experimental Vaccine Research, 3, 42–49.
Al-Mayahy, M. H., Sabri, A. H., Rutland, C. S., Holmes, A., McKenna, J., Marlow, M., & Scurr, D. J. (2019). Insight into imiquimod skin permeation and increased delivery using microneedle pre-treatment. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 139, 33–43.
Alkilani, A. Z., McCrudden, M. T., & Donnelly, R. F. (2015). Transdermal drug delivery: Innovative pharmaceutical developments based on disruption of the barrier properties of the stratum corneum. Pharmaceutics, 7, 438–470.
Garland, M. J., Migalska, K., Mahmood, T. M., Singh, T. R., Woolfson, A. D., & Donnelly, R. F. (2011). Microneedle arrays as medical devices for enhanced transdermal drug delivery. Expert Review of Medical Devices, 8, 459–482.
Quan, F. S., Kim, Y. C., Compans, R. W., Prausnitz, M. R., & Kang, S. M. (2010). Dose sparing enabled by skin immunization with influenza virus-like particle vaccine using microneedles. Journal of Controlled Release, 147, 326–332.
Mistilis, M. J., Joyce, J. C., Esser, E. S., Skountzou, I., Compans, R. W., Bommarius, A. S., & Prausnitz, M. R. (2017). Long-term stability of influenza vaccine in a dissolving microneedle patch. Drug Delivery and Translational Research, 7, 195–205.
Wedlock, P. T., Mitgang, E. A., Elsheikh, F., Leonard, J., Bakal, J., Welling, J., Crawford, J., Assy, E., Magadzire, B. P., Bechtel, R., DePasse, J. V., Siegmund, Sheryl S., Brown, S. T., & Lee, B. Y. (2019). The potential effects of introducing microneedle patch vaccines into routine vaccine supply chains. Vaccine, 37, 645–651.
Iwata, H., Kakita, K., Imafuku, K., Takashima, S., Haga, N., Yamaguchi, Y., Taguchi, K., & Oyamada, T. (2022). Safety and dose-sparing effect of Japanese encephalitis vaccine administered by microneedle patch in uninfected, healthy adults (MNA-J): A randomised, partly blinded, active-controlled, phase 1 trial. The Lancet Microbe, 3, e96–e104.
Rouphael, N. G., Paine, M., Mosley, R., Henry, S., McAllister, D. V., Kalluri, H., Pewin, W., Frew, P. M., Yu, T., Thornburg, N. J., Kabbani, S., Lai, L., Vassilieva, E. V., Skountzou, I., Compans, R. W., Mulligan, M. J., Prausnitz, M. R., Beck, A., Edupuganti, Srilatha, & ⋯ Wendy Nesheim. (2017). The safety, immunogenicity, and acceptability of inactivated influenza vaccine delivered by microneedle patch (TIV-MNP 2015): a randomised, partly blinded, placebo-controlled, phase 1 trial. The Lancet, 390, 649–658.
Zheng, X., Zhu, J., Zheng, C., Tan, Z., Ji, Z., Tao, J., Zhao, Y., & Hu, Y. (2023). Dissolving microneedle arrays as a hepatitis B vaccine delivery system adjuvanted by APC-Targeted Poly (Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid) (PLGA) nanoparticles. An Official Journal of the American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists, 24, 42.
Fan, F., Zhang, X., Zhang, Z., Ding, Y., Wang, L., Xu, X., Pan, Y., Gong, F. Y., Jiang, L., Kang, L., Ha, Z., Lu, H., Hou, J., Kou, Z., Zhao, G., Wang, B., & Gao, X. M. (2023). Potent immunogenicity and broad-spectrum protection potential of microneedle array patch-based COVID-19 DNA vaccine candidates encoding dimeric RBD chimera of SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 variants. Emerging Microbes & Infections, 12, 2202269.
Feng, Y. X., Hu, H., Wong, Y. Y., Yao, X., & He, M. L. (2023). Microneedles: An emerging vaccine delivery tool and a prospective solution to the challenges of SARS-CoV-2 mass vaccination. Pharmaceutics, 15, 1349.
McNamee, M., Wong, S., Guy, O., & Sharma, S. (2023). Microneedle technology for potential SARS-CoV-2 vaccine delivery. Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery, 20, 799–814.
Nazary Abrbekoh, F., Salimi, L., Saghati, S., Amini, H., Fathi Karkan, S., Moharamzadeh, K., Sokullu, E., & Rahbarghazi, R. (2022). Application of microneedle patches for drug delivery; doorstep to novel therapies. Journal of Tissue Engineering, 13, 20417314221085390. https://doi.org/10.1177/20417314221085390
Menon, I., Bagwe, P., Gomes, K. B., Bajaj, L., Gala, R., Uddin, M. N., D’Souza, M. J., & Zughaier, S. M. (2021). Microneedles: A new generation vaccine delivery system. Micromachines (Basel), 12(4), 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12040435
Peyraud, N., Zehrung, D., Jarrahian, C., Frivold, C., Orubu, T., & Giersing, B. (2019). Potential use of microarray patches for vaccine delivery in low- and middle- income countries. Vaccine, 37(32), 4427–4434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.03.035
Priya, S., & Singhvi, G. (2022). Microneedles-based drug delivery strategies: A breakthrough approach for the management of pain. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 155, 113717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113717
Peng, T., Chen, Y., Hu, W., Huang, Y., Zhang, M., Lu, C., Pan, X., Wu, C. (2023). Microneedles for enhanced topical treatment of skin disorders: Applications, challenges, and prospects. Engineering (in press). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2023.05.009
Ma, S., Li, J., Pei, L., Feng, N., & Zhang, Y. (2023). Microneedle-based interstitial fluid extraction for drug analysis: Advances, challenges, and prospects. Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 13(2), 111–126.
Lee, M. S., Pan, C. X., & Nambudiri, V. E. (2021). Transdermal approaches to vaccinations in the COVID-19 pandemic era. Therapeutic Advances in Vaccines and Immunotherapy, 9, 25151355211039070.
Bilal, M., Mehmood, S., Raza, A., Hayat, U., Rasheed, T., & Iqbal, H. M. N. (2021). Microneedles in smart drug delivery. Advances in Wound Care (New Rochelle), 10(4), 204–219.
Mansoor, I., Eassa, H. A., Mohammed, K. H. A., Abd El-Fattah, M. A., Abdo, M. H., Rashad, E., Eassa, H. A., Saleh, A., Amin, O. M., Nounou, M. I., & Ghoneim, O. (2022). Microneedle-based vaccine delivery: Review of an emerging technology. An Official Journal of the American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists, 23(4), 103.
McAlister, E., Kearney, M. C., Martin, E. L., & Donnelly, R. F. (2021). From the laboratory to the end-user: A primary packaging study for microneedle patches containing amoxicillin sodium. Drug Delivery and Translational Research, 11(5), 2169–2185.
Donnelly, R. F., Raj Singh, T. R., & Woolfson, A. D. (2010). Microneedle-based drug delivery systems: Microfabrication, drug delivery, and safety. Drug Delivery, 17(4), 187–207.
Avcil, M., & Çelik, A. (2021). Microneedles in drug delivery: Progress and challenges. Micromachines (Basel), 12(11), 1321.
Jung, J. H., & Jin, S. G. (2021). Microneedle for transdermal drug delivery: Current trends and fabrication. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation, 51(5), 503–517.
Larrañeta, E., Lutton, R. E., Woolfson, A. D., & Donnelly, R. F. (2016). Microneedle arrays as transdermal and intradermal drug delivery systems: Materials science, manufacture and commercial development. Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports, 1(104), 1–32.
Migdadi, E. M., Courtenay, A. J., Tekko, I. A., McCrudden, M. T. C., Kearney, M. C., McAlister, E., McCarthy, H. O., & Donnelly, R. F. (2018). Hydrogel-forming microneedles enhance transdermal delivery of metformin hydrochloride. Journal of Controlled Release, 285, 142–151.
Niu, L., Chu, L. Y., Burton, S. A., Hansen, K. J., & Panyam, J. (2019). Intradermal delivery of vaccine nanoparticles using hollow microneedle array generates enhanced and balanced immune response. Journal of Controlled Release, 294, 268–278.
Leone, M., Monkare, J., Bouwstra, J. A., & Kersten, G. (2017). Dissolving microneedle patches for dermal vaccination. Pharmaceutical Research, 34, 2223–2240.
Davis, S. P., Martanto, W., Allen, M. G., & Prausnitz, M. R. (2005). Hollow metal microneedles for insulin delivery to diabetic rats. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 52, 909–915.
Gholami, S., Mohebi, M. M., Hajizadeh-Saffar, E., Ghanian, M. H., Zarkesh, I., & Baharvand, H. (2019). Fabrication of microporous inorganic microneedles by centrifugal casting method for transdermal extraction and delivery. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 558, 299–310.
Singh, P., Carrier, A., Chen, Y., Lin, S., Wang, J., Cui, S., & Zhang, X. (2019). Polymeric microneedles for controlled transdermal drug delivery. Journal of Controlled Release, 315, 97–113.
Li, J., Liu, B., Zhou, Y., Chen, Z., Jiang, L., Yuan, W., & Liang, L. (2017). Fabrication of a Ti porous microneedle array by metal injection molding for transdermal drug delivery. PLoS ONE, 12, e0172043.
Courtenay, A. J., McAlister, E., McCrudden, M. T. C., Vora, L., Steiner, L., Levin, G., Levy-Nissenbaum, E., Shterman, N., Kearney, M. C., McCarthy, H. O., & Donnelly, R. F. (2020). Hydrogel-forming microneedle arrays as a therapeutic option for transdermal esketamine delivery. Journal of Controlled Release, 322, 177–186.
Plamadeala, C., Gosain, S. R., Hischen, F., Buchroithner, B., Puthukodan, S., Jacak, J., Bocchino, A., Whelan, D., O’Mahony, C., Baumgartner, W., & Heitz, J. (2019). Bio-inspired microneedle design for efficient drug/vaccine coating. Biomedical Microdevices, 22, 8.
Wei-Ze, L., Mei-Rong, H., Jian-Ping, Z., Yong-Qiang, Z., Bao-Hua, H., Ting, L., & Yong, Z. (2010). Super-short solid silicon microneedles for transdermal drug delivery applications. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 389, 122–129.
Li, J., Zeng, M., Shan, H., & Tong, C. (2017). Microneedle patches as drug and vaccine delivery platform. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 24, 2413–2422.
Ita, K. (2015). Transdermal delivery of drugs with microneedles—potential and challenges. Pharmaceutics, 7, 90–105.
Prausnitz, M. R. (2017). Engineering microneedle patches for vaccination and drug delivery to skin. Annual Review of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, 8, 177–200.
Li, Q. Y., Zhang, J. N., Chen, B. Z., Wang, Q. L., & Guo, X. D. (2017). A solid polymer microneedle patch pretreatment enhances the permeation of drug molecules into the skin. RSC Advances, 7, 15408–15415.
van der Maaden, K., Sekerdag, E., Jiskoot, W., & Bouwstra, J. (2014). Impact-insertion applicator improves reliability of skin penetration by solid microneedle arrays. The AAPS Journal, 16, 681–684.
Zhang, Y., Brown, K., Siebenaler, K., Determan, A., Dohmeier, D., & Hansen, K. (2012). Development of lidocaine-coated microneedle product for rapid, safe, and prolonged local analgesic action. Pharmaceutical Research, 29, 170–177.
Tzafriri, A. R., Muraj, B., Garcia-Polite, F., Salazar-Martín, A. G., Markham, P., Zani, B., Spognardi, A., Albaghdadi, M., Alston, S., & Edelman, E. R. (2020). Balloon-based drug coating delivery to the artery wall is dictated by coating micro-morphology and angioplasty pressure gradients. Biomaterials, 260, 120337.
Jeong, H.-R., Jun, H., Cha, H.-R., Lee, J. M., & Park, J.-H. (2020). Safe coated microneedles with reduced puncture occurrence after administration. Micromachines, 11, 710.
Yang, J., Liu, X., Fu, Y., & Song, Y. (2019). Recent advances of microneedles for biomedical applications: Drug delivery and beyond. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 9, 469–483.
Yu, L., Tay, F., Guo, D., Xu, L., & Yap, K. (2009). A microfabricated electrode with hollow microneedles for ECG measurement. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 151, 17–22.
Donnelly, R. F., Majithiya, R., Singh, T. R. R., Morrow, D. I., Garland, M. J., Demir, Y. K., Migalska, K., Ryan, E., Gillen, D., & Scott, C. J. (2011). Design, optimization and characterisation of polymeric microneedle arrays prepared by a novel laser-based micromoulding technique. Pharmaceutical Research, 28, 41–57.
Cárcamo-Martínez, Á., Mallon, B., Anjani, Q. K., Domínguez-Robles, J., Utomo, E., Vora, L. K., Tekko, I., Larrañeta, E., & Donnelly, R. F. (2020). Enhancing intradermal delivery of tofacitinib citrate: Comparison between powder-loaded hollow microneedle arrays and dissolving microneedle arrays. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 593, 120152.
Zhang, L., Li, Y., Wei, F., Liu, H., Wang, Y., Zhao, W., Dong, Z., Ma, T., & Wang, Q. (2020). Transdermal delivery of salmon calcitonin using a dissolving microneedle array: Characterization, stability, and in vivo pharmacodynamics. An Official Journal of the American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists, 22, 1–9.
Kabir, S. F., Sikdar, P. P., Haque, B., Bhuiyan, M. R., Ali, A., & Islam, M. (2018). Cellulose-based hydrogel materials: Chemistry, properties and their prospective applications. Progress in Biomaterials, 7, 153–174.
Mitura, S., Sionkowska, A., & Jaiswal, A. (2020). Biopolymers for hydrogels in cosmetics. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine, 31, 1–14.
Mantha, S., Pillai, S., Khayambashi, P., Upadhyay, A., Zhang, Y., Tao, O., Pham, H. M., & Tran, S. D. (2019). Smart hydrogels in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Materials, 12, 3323.
Turner, J. G., White, L. R., Estrela, P., & Leese, H. S. (2020). Hydrogel-forming microneedles: Current advancements and future trends. Macromolecular Bioscience, 21, 2000307.
Huber, L. A., Pereira, T. A., Ramos, D. N., Rezende, L. C., Emery, F. S., Sobral, L. M., Leopoldino, A. M., & Lopez, R. F. (2015). Topical skin cancer therapy using doxorubicin-loaded cationic lipid nanoparticles and lontophoresis. Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology, 11, 1975–1988.
Moreira, A. F., Rodrigues, C. F., Jacinto, T. A., Miguel, S. P., Costa, E. C., & Correia, I. J. (2019). Microneedle-based delivery devices for cancer therapy: A review. Pharmacological Research, 148, 104438.
Chen, G., Yu, J., & Gu, Z. (2019). Glucose-responsive microneedle patches for diabetes treatment. Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology, 13, 41–48.
Jana, B. A., & Wadhwani, A. D. (2019). Microneedle: Future prospect for efficient drug delivery in diabetes management. Indian Journal of Pharmacology, 51, 4–10.
Miller, P. R., Narayan, R. J., & Polsky, R. (2016). Microneedle-based sensors for medical diagnosis. Journal Material Chemistry B, 4, 1379–1383.
How, K. N., Yap, W. H., Lim, C. L. H., Goh, B. H., & Lai, Z. W. (2020). Hyaluronic acid-mediated drug delivery system targeting for inflammatory skin diseases: A mini review. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 11, 1105.
Xie, X., Pascual, C., Lieu, C., Oh, S., Wang, J., Zou, B., Xie, J., Li, Z., Xie, J., Yeomans, D. C., Wu, M. X., & Xie, X. S. (2017). Analgesic microneedle patch for neuropathic pain therapy. ACS Nano, 11, 395–406.
Ramoller, I. K., Tekko, I. A., McCarthy, H. O., & Donnelly, R. F. (2019). Rapidly dissolving bilayer microneedle arrays: A minimally invasive transdermal drug delivery system for vitamin B12. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 566, 299–306.
Lee, S. G., Jeong, J. H., Lee, K. M., Jeong, K. H., Yang, H., Kim, M., Jung, H., Lee, S., & Choi, Y. W. (2014). Nanostructured lipid carrier-loaded hyaluronic acid microneedles for controlled dermal delivery of a lipophilic molecule. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 9, 289–299.
Yang, J., Chen, Z., Ye, R., Li, J., Lin, Y., Gao, J., Ren, L., Liu, B., & Jiang, L. (2018). Touch-actuated microneedle array patch for closed-loop transdermal drug delivery. Drug Delivery, 25, 1728–1739.
Bhatnagar, S., Saju, A., Cheerla, K. D., Gade, S. K., Garg, P., & Venuganti, V. V. K. (2018). Corneal delivery of besifloxacin using rapidly dissolving polymeric microneedles. Drug Delivery and Translational Research, 8, 473–483.
González-Vázquez, P., Larrañeta, E., McCrudden, M. T., Jarrahian, C., Rein-Weston, A., Quintanar-Solares, M., Zehrung, D., McCarthy, H., Courtenay, A. J., & Donnelly, R. F. (2017). Transdermal delivery of gentamicin using dissolving microneedle arrays for potential treatment of neonatal sepsis. Journal of Controlled Release, 265, 30–40.
Lee, H. S., Ryu, H. R., Roh, J. Y., & Park, J.-H. (2017). Bleomycin-coated microneedles for treatment of warts. Pharmaceutical Research, 34, 101–112.
Anjani, Q. K., Permana, A. D., Cárcamo-Martínez, Á., Domínguez-Robles, J., Tekko, I. A., Larrañeta, E., Vora, L. K., Ramadon, D., & Donnelly, R. F. (2020). Versatility of hydrogel-forming microneedles in in vitro transdermal delivery of tuberculosis drugs. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 158, 294–312.
Nguyen, A. K., Yang, K.-H., Bryant, K., Li, J., Joice, A. C., Werbovetz, K. A., & Narayan, R. J. (2019). Microneedle-based delivery of amphotericin B for treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis. Biomedical Microdevices, 21, 8.
Kim, H.-G., Gater, D. L., & Kim, Y.-C. (2018). Development of transdermal vitamin D3 (VD3) delivery system using combinations of PLGA nanoparticles and microneedles. Drug Delivery and Translational Research, 8, 281–290.
Ramöller, I. K., Tekko, I. A., McCarthy, H. O., & Donnelly, R. F. (2019). Rapidly dissolving bilayer microneedle arrays–A minimally invasive transdermal drug delivery system for vitamin B12. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 566, 299–306.
Hutton, A. R., Quinn, H. L., McCague, P. J., Jarrahian, C., Rein-Weston, A., Coffey, P. S., Gerth-Guyette, E., Zehrung, D., Larrañeta, E., & Donnelly, R. F. (2018). Transdermal delivery of vitamin K using dissolving microneedles for the prevention of vitamin K deficiency bleeding. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 541, 56–63.
Menon, A., Eram, H., Kamath, P. R., Goel, S., & Babu, A. M. (2020). A split face comparative study of safety and efficacy of microneedling with tranexamic acid versus microneedling with Vitamin C in the treatment of melasma. Indian Dermatology Online Journal, 11, 41.
Lee, C.-A., Baek, J.-S., Kwag, D.-G., Lee, H.-J., Park, J., & Cho, C.-W. (2017). Enhancement of skin permeation of vitamin C using vibrating microneedles. Translational and Clinical Pharmacology, 25, 15–20.
Chaudhuri, B.P., Ceyssens, F., Celen, S., Bormans, G., Kraft, M., & Puers, R. (2019). In-vivo intradermal delivery of Co-57 labeled Vitamin B-12, and subsequent comparison with standard subcutaneous administration. In: 2019 41st Annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society (EMBC) (pp. 1670–1673). IEEE.
Courtenay, A. J., McCrudden, M. T. C., McAvoy, K. J., McCarthy, H. O., & Donnelly, R. F. (2018). Microneedle-mediated transdermal delivery of bevacizumab. Molecular Pharmaceutics, 15, 3545–3556.
Wang, C., Ye, Y., Hochu, G. M., Sadeghifar, H., & Gu, Z. (2016). Enhanced cancer immunotherapy by microneedle patch-assisted delivery of anti-PD1 antibody. Nano letters, 16, 2334–2340.
Korkmaz, E., Friedrich, E. E., Ramadan, M. H., Erdos, G., Mathers, A. R., Ozdoganlar, O. B., Washburn, N. R., & Falo, L. D., Jr. (2016). Tip-loaded dissolvable microneedle arrays effectively deliver polymer-conjugated antibody inhibitors of tumor-necrosis-factor-alpha into human skin. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 105, 3453–3457.
Mönkäre, J., Nejadnik, M. R., Baccouche, K., Romeijn, S., Jiskoot, W., & Bouwstra, J. A. (2015). IgG-loaded hyaluronan-based dissolving microneedles for intradermal protein delivery. Journal of Controlled Release, 218, 53–62.
Li, G., Badkar, A., Nema, S., Kolli, C. S., & Banga, A. K. (2009). In vitro transdermal delivery of therapeutic antibodies using maltose microneedles. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 368, 109–115.
Pettis, R. J., Ginsberg, B., Hirsch, L., Sutter, D., Keith, S., McVey, E., Harvey, N. G., Hompesch, M., Nosek, L., & Kapitza, C. (2011). Intradermal microneedle delivery of insulin lispro achieves faster insulin absorption and insulin action than subcutaneous injection. Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics, 13, 435–442.
Gupta, J., Felner, E. I., & Prausnitz, M. R. (2011). Rapid pharmacokinetics of intradermal insulin administered using microneedles in type 1 diabetes subjects. Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics, 13, 451–456.
Yu, J., Zhang, Y., Ye, Y., DiSanto, R., Sun, W., Ranson, D., Ligler, F. S., Buse, J. B., & Gu, Z. (2015). Microneedle-array patches loaded with hypoxia-sensitive vesicles provide fast glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 112, 8260–8265.
Kim, S., Yang, H., Eum, J., Ma, Y., Fakhraei Lahiji, S., & Jung, H. (2020). Implantable powder-carrying microneedles for transdermal delivery of high-dose insulin with enhanced activity. Biomaterials, 232, 119733.
Tong, Z., Zhou, J., Zhong, J., Tang, Q., Lei, Z., Luo, H., Ma, P., & Liu, X. (2018). Glucose-and H2O2-responsive polymeric vesicles integrated with microneedle patches for glucose-sensitive transcutaneous delivery of insulin in diabetic rats. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 10, 20014–20024.
Wang, Z., Wang, J., Li, H., Yu, J., Chen, G., Kahkoska, A. R., Wu, V., Zeng, Y., Wen, D., & Miedema, J. R. (2020). Dual self-regulated delivery of insulin and glucagon by a hybrid patch. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 117, 29512–29517.
Chen, B. Z., Zhang, L. Q., Xia, Y. Y., Zhang, X. P., & Guo, X. D. (2020). A basal-bolus insulin regimen integrated microneedle patch for intraday postprandial glucose control. Science Advances, 6, eaba7260.
Lee, S., & Lee, D. Y. (2017). Glucagon-like peptide-1 and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism, 22, 15–26.
Liu, S., Wu, D., Quan, Y. S., Kamiyama, F., Kusamori, K., Katsumi, H., Sakane, T., & Yamamoto, A. (2016). Improvement of transdermal delivery of Exendin-4 using novel tip-loaded microneedle arrays fabricated from hyaluronic acid. Molecular Pharmaceutics, 13, 272–279.
Rong, L., & Perelson, A. S. (2010). Treatment of hepatitis C virus infection with interferon and small molecule direct antivirals: viral kinetics and modeling. Critical Reviews in Immunology, 30, 131–148.
Kusamori, K., Katsumi, H., Sakai, R., Hayashi, R., Hirai, Y., Tanaka, Y., Hitomi, K., Quan, Y.-s, Kamiyama, F., & Yamada, K. (2016). Development of a drug-coated microneedle array and its application for transdermal delivery of interferon alpha. Biofabrication, 8, 015006.
Chen, J., Qiu, Y., Zhang, S., & Gao, Y. (2016). Dissolving microneedle-based intradermal delivery of interferon-α-2b. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, 42, 890–896.
Tas, C., Mansoor, S., Kalluri, H., Zarnitsyn, V. G., Choi, S.-O., Banga, A. K., & Prausnitz, M. R. (2012). Delivery of salmon calcitonin using a microneedle patch. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 423, 257–263.
Donnelly, R. F., Garland, M. J., & Alkilani, A. Z. (2014). Microneedle-iontophoresis combinations for enhanced transdermal drug delivery. Drug delivery system (pp. 121–132). Springer.
Vemulapalli, V., Bai, Y., Kalluri, H., Herwadkar, A., Kim, H., Davis, S. P., Friden, P. M., & Banga, A. K. (2012). In vivo iontophoretic delivery of salmon calcitonin across microporated skin. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 101, 2861–2869.
Boopathy, A. V., Mandal, A., Kulp, D. W., Menis, S., Bennett, N. R., Watkins, H. C., Wang, W., Martin, J. T., Thai, N. T., He, Y., Schief, W. R., Hammond, P. T., & Irvin, D. J. (2019). Enhancing humoral immunity via sustained-release implantable microneedle patch vaccination. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 116, 16473–16478.
Raphael, A. P., Prow, T. W., Crichton, M. L., Chen, X., Fernando, G. J., & Kendall, M. A. (2010). Targeted, needle-free vaccinations in skin using multilayered, densely-packed dissolving microprojection arrays. Small (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany), 6, 1785–1793.
Fernando, G. J., Chen, X., Prow, T. W., Crichton, M. L., Fairmaid, E. J., Roberts, M. S., Frazer, I. H., Brown, L. E., & Kendall, M. A. (2010). Potent immunity to low doses of influenza vaccine by probabilistic guided micro-targeted skin delivery in a mouse model. PLoS ONE, 5, e10266.
Ono, A., Azukizawa, H., Ito, S., Nakamura, Y., Asada, H., Quan, Y. S., Kamiyama, F., Katayama, I., Hirobe, S., & Okada, N. (2017). Development of novel double-decker microneedle patches for transcutaneous vaccine delivery. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 532, 374–383.
Koutsonanos, D. G., Vassilieva, E. V., Stavropoulou, A., Zarnitsyn, V. G., Esser, E. S., Taherbhai, M. T., Prausnitz, M. R., Compans, R. W., & Skountzou, I. (2012). Delivery of subunit influenza vaccine to skin with microneedles improves immunogenicity and long-lived protection. Science and Reports, 2, 357.
Arnou, R., Icardi, G., De Decker, M., Ambrozaitis, A., Kazek, M. P., Weber, F., & Van Damme, P. (2009). Intradermal influenza vaccine for older adults: A randomized controlled multicenter phase III study. Vaccine, 27, 7304–7312.
Van Damme, P., Oosterhuis-Kafeja, F., Van der Wielen, M., Almagor, Y., Sharon, O., & Levin, Y. (2009). Safety and efficacy of a novel microneedle device for dose sparing intradermal influenza vaccination in healthy adults. Vaccine, 27, 454–459.
Weldon, W. C., Zarnitsyn, V. G., Esser, E. S., Taherbhai, M. T., Koutsonanos, D. G., Vassilieva, E. V., Skountzou, I., Prausnitz, M. R., & Compans, R. W. (2012). Effect of adjuvants on responses to skin immunization by microneedles coated with influenza subunit vaccine. PLoS ONE, 7, e41501.
Weldon, W. C., Martin, M. P., Zarnitsyn, V., Wang, B., Koutsonanos, D., Skountzou, I., Prausnitz, M. R., & Compans, R. W. (2011). Microneedle vaccination with stabilized recombinant influenza virus hemagglutinin induces improved protective immunity. Clinical and Vaccine Immunology, 18, 647–654.
Liu, Y., Ye, L., Lin, F., Gomaa, Y., Flyer, D., Carrion, R., Jr., Patterson, J. L., Prausnitz, M. R., Smith, G., Glenn, G., Wu, H., Compans, R. W., & Yang, C. (2018). Intradermal immunization by Ebola virus GP subunit vaccines using microneedle patches protects mice against lethal EBOV challenge. Scientific Reports, 8, 11193.
Duong, H. T. T., Kim, N. W., Thambi, T., Giang Phan, V. H., Lee, M. S., Yin, Y., Jeong, J. H., & Lee, D. S. (2018). Microneedle arrays coated with charge reversal pH-sensitive copolymers improve antigen presenting cells-homing DNA vaccine delivery and immune responses. Journal of Controlled Release, 269, 225–234.
Chen, F., Yan, Q., Yu, Y., & Wu, M. X. (2017). BCG vaccine powder-laden and dissolvable microneedle arrays for lesion-free vaccination. Journal of Controlled Release, 255, 36–44.
Kutzler, M. A., & Weiner, D. B. (2008). DNA vaccines: Ready for prime time? Nature Reviews Genetics, 9, 776–788.
Kim, Y. C., Song, J. M., Lipatov, A. S., Choi, S. O., Lee, J. W., Donis, R. O., Compans, R. W., Kang, S. M., & Prausnitz, M. R. (2012). Increased immunogenicity of avian influenza DNA vaccine delivered to the skin using a microneedle patch. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 81, 239–247.
Song, J. M., Kim, Y. C., Barlow, P. G., Hossain, M. J., Park, K. M., Donis, R. O., Prausnitz, M. R., Compans, R. W., & Kang, S. M. (2010). Improved protection against avian influenza H5N1 virus by a single vaccination with virus-like particles in skin using microneedles. Antiviral Research, 88, 244–247.
Coulman, S. A., Barrow, D., Anstey, A., Gateley, C., Morrissey, A., Wilke, N., Allender, C., Brain, K., & Birchall, J. C. (2006). Minimally invasive cutaneous delivery of macromolecules and plasmid DNA via microneedles. Current Drug Delivery, 3, 65–75.
Fernando, G. J., Zhang, J., Ng, H. I., Haigh, O. L., Yukiko, S. R., & Kendall, M. A. (2016). Influenza nucleoprotein DNA vaccination by a skin targeted, dry coated, densely packed microprojection array (Nanopatch) induces potent antibody and CD8(+) T cell responses. Journal of Controlled Release, 237, 35–41.
Fernando, G. J., Chen, X., Primiero, C. A., Yukiko, S. R., Fairmaid, E. J., Corbett, H. J., Frazer, I. H., Brown, L. E., & Kendall, M. A. (2012). Nanopatch targeted delivery of both antigen and adjuvant to skin synergistically drives enhanced antibody responses. Journal of Controlled Release, 159, 215–221.
Kask, A. S., Chen, X., Marshak, J. O., Dong, L., Saracino, M., Chen, D., Jarrahian, C., Kendall, M. A., & Koelle, D. M. (2010). DNA vaccine delivery by densely-packed and short microprojection arrays to skin protects against vaginal HSV-2 challenge. Vaccine, 28, 7483–7491.
Gill, H. S., Soderholm, J., Prausnitz, M. R., & Sallberg, M. (2010). Cutaneous vaccination using microneedles coated with hepatitis C DNA vaccine. Gene Therapy, 17, 811–814.
Mikszta, J. A., Alarcon, J. B., Brittingham, J. M., Sutter, D. E., Pettis, R. J., & Harvey, N. G. (2002). Improved genetic immunization via micromechanical disruption of skin-barrier function and targeted epidermal delivery. Nature Medicine, 8, 415–419.
Arya, J. M., Dewitt, K., Scott-Garrard, M., Chiang, Y. W., & Prausnitz, M. R. (2016). Rabies vaccination in dogs using a dissolving microneedle patch. Journal of Controlled Release, 239, 19–26.
Moon, S., Wang, Y., Edens, C., Gentsch, J. R., Prausnitz, M. R., & Jiang, B. (2013). Dose sparing and enhanced immunogenicity of inactivated rotavirus vaccine administered by skin vaccination using a microneedle patch. Vaccine, 31, 3396–3402.
Kommareddy, S., Baudner, B. C., Oh, S., Kwon, S. Y., Singh, M., & O’Hagan, D. T. (2012). Dissolvable microneedle patches for the delivery of cell-culture-derived influenza vaccine antigens. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 101, 1021–1027.
Sullivan, S. P., Koutsonanos, D. G., Del Pilar, M. M., Lee, J. W., Zarnitsyn, V., Choi, S. O., Murthy, N., Compans, R. W., Skountzou, I., & Prausnitz, M. R. (2010). Dissolving polymer microneedle patches for influenza vaccination. Nature Medicine, 16, 915–920.
Kim, Y. C., Quan, F. S., Yoo, D. G., Compans, R. W., Kang, S. M., & Prausnitz, M. R. (2009). Improved influenza vaccination in the skin using vaccine coated microneedles. Vaccine, 27, 6932–6938.
Dean, C. H., Alarcon, J. B., Waterston, A. M., Draper, K., Early, R., Guirakhoo, F., Monath, T. P., & Mikszta, J. A. (2005). Cutaneous delivery of a live, attenuated chimeric flavivirus vaccine against Japanese encephalitis (ChimeriVax)-JE) in non-human primates. Human Vaccines, 1, 106–111.
Chu, L. Y., Ye, L., Dong, K., Compans, R. W., Yang, C., & Prausnitz, M. R. (2016). Enhanced stability of inactivated influenza vaccine encapsulated in dissolving microneedle patches. Pharmaceutical Research, 33, 868–878.
Choi, H. J., Bondy, B. J., Yoo, D. G., Compans, R. W., Kang, S. M., & Prausnitz, M. R. (2013). Stability of whole inactivated influenza virus vaccine during coating onto metal microneedles. Journal of Controlled Release, 166, 159–171.
Kim, Y. C., Quan, F. S., Compans, R. W., Kang, S. M., & Prausnitz, M. R. (2010). Formulation and coating of microneedles with inactivated influenza virus to improve vaccine stability and immunogenicity. Journal of Controlled Release, 142, 187–195.
Edens, C., Collins, M. L., Goodson, J. L., Rota, P. A., & Prausnitz, M. R. (2015). A microneedle patch containing measles vaccine is immunogenic in non-human primates. Vaccine, 33, 4712–4718.
Carey, J. B., Pearson, F. E., Vrdoljak, A., McGrath, M. G., Crean, A. M., Walsh, P. T., Doody, T., O’Mahony, C., Hill, A. V., & Moore, A. C. (2011). Microneedle array design determines the induction of protective memory CD8+ T cell responses induced by a recombinant live malaria vaccine in mice. PLoS ONE, 6, e22442.
Erdos, G., Balmert, S. C., Carey, C. D., Falo, G. D., Patel, N. A., Zhang, J., Gambotto, A., Korkmaz, E., & Falo, L. D., Jr. (2020). Improved cutaneous genetic immunization by microneedle array delivery of an adjuvanted adenovirus vaccine. The Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 140, 2528.
Turvey, M. E., Uppu, D., Mohamed Sharif, A. R., Bidet, K., Alonso, S., Ooi, E. E., & Hammond, P. T. (2019). Microneedle-based intradermal delivery of stabilized dengue virus. Bioengineering & Translational Medicine, 4, e10127.
Park, S., Lee, Y., Kwon, Y. M., Lee, Y. T., Kim, K. H., Ko, E. J., Jung, J. H., Song, M., Graham, B., Prausnitz, M. R., & Kang, S. M. (2018). Vaccination by microneedle patch with inactivated respiratory syncytial virus and monophosphoryl lipid A enhances the protective efficacy and diminishes inflammatory disease after challenge. PLoS ONE, 13, e0205071.
Braz Gomes, K., Vijayanand, S., Bagwe, P., Menon, I., Kale, A., Patil, S., Kang, S.-M., Uddin, M. N., & D’Souza, M. J. (2023). Vaccine-induced immunity elicited by microneedle delivery of influenza ectodomain matrix protein 2 virus-like particle (M2e VLP)-loaded PLGA nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24, 10612.
Kim, E., Erdos, G., Huang, S., Kenniston, T. W., Balmert, S. C., Carey, C. D., Raj, V. S., Epperly, M. W., Klimstra, W. B., Haagmans, B. L., & Korkmaz, E. (2020). Microneedle array delivered recombinant coronavirus vaccines: Immunogenicity and rapid translational development. EBioMedicine, 55, 102743.
Le Thanh, T., Andreadakis, Z., Kumar, A., Gomez Roman, R., Tollefsen, S., Saville, M., & Mayhew, S. (2020). The COVID-19 vaccine development landscape. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 19, 305–306.
Zhang, Y., Zheng, N., Hao, P., Cao, Y., & Zhong, Y. (2005). A molecular docking model of SARS-CoV S1 protein in complex with its receptor, human ACE2. Computational Biology and Chemistry, 29, 254–257.
Falo, L. D., Jr. (2020). Advances in skin science enable the development of a COVID-19 vaccine. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 83, 1226–1227.
Li, Q., Xu, R., Fan, H., Xu, J., Xu, Y., Cao, P., Zhang, Y., Liang, T., Chen, W., Wang, Z., & Chen, X. (2022). Smart mushroom-inspired imprintable and lightly detachable (MILD) microneedle patterns for effective COVID-19 vaccination and decentralized information storage. ACS Nano, 16, 7512–7524.
Li, L., Zhao, Z., Yang, X., Su, Z., Li, W., Chen, S., Wang, L., Sun, T., Du, C., Li, Z., Wang, T., Wang, Y., Fan, Y., Wang, H., & Zhang, J. (2023). A newly identified spike protein targeted linear B-cell epitope based dissolvable microneedle array successfully eliciting neutralizing activities against SARS-CoV-2 wild-type strain in mice. Advanced Science (Weinh), 10, e2207474.
Tran, K. T. M., Gavitt, T. D., Le, T. T., Graichen, A., Lin, F., Liu, Y., Tulman, E. R., Szczepanek, S. M., & Nguyen, T. D. (2022). A single-administration microneedle skin patch for multi-burst release of vaccine against SARS-CoV-2. Advanced Materials Technologies, 8, 2200905.
Patil, S., Vijayanand, S., Joshi, D., Menon, I., Braz Gomes, K., Kale, A., Bagwe, P., Yacoub, S., Uddin, M. N., & D’Souza, M. J. (2023). Subunit microparticulate vaccine delivery using microneedles trigger significant SARS-spike-specific humoral and cellular responses in a preclinical murine model. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 632, 122583.
Kapnick, S. M. (2022). The nanoparticle-enabled success of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines and the promise of microneedle platforms for pandemic vaccine response. DNA and Cell Biology, 41, 25–29.
Guillot, A. J., Cordeiro, A. S., Donnelly, R. F., Montesinos, M. C., Garrigues, T. M., & Melero, A. (2020). Microneedle-based delivery: An overview of current applications and trends. Pharmaceutics, 12, 569.
Gualeni, B., Coulman, S., Shah, D., Eng, P., Ashraf, H., Vescovo, P., Blayney, G., Piveteau, L. D., Guy, O., & Birchall, J. (2018). Minimally invasive and targeted therapeutic cell delivery to the skin using microneedle devices. British Journal of Dermatology, 178, 731–739.
Chen, Y.-H., Lin, D.-C., Chern, E., & Huang, Y.-Y. (2020). The use of micro-needle arrays to deliver cells for cellular therapies. Biomedical Microdevices, 22, 1–8.
Farias, C., Lyman, R., Hemingway, C., Chau, H., Mahacek, A., Bouzos, E., & Mobed-Miremadi, M. (2018). Three-dimensional (3D) printed microneedles for microencapsulated cell extrusion. Bioengineering, 5, 59.
Tang, J., Wang, J., Huang, K., Ye, Y., Su, T., Qiao, L., Hensley, M. T., Caranasos, T. G., Zhang, J., & Gu, Z. (2018). Cardiac cell–integrated microneedle patch for treating myocardial infarction. Science Advances, 4, eaat9365.
Benson, P. J. (2018). A stem cell–integrated microneedle patch. American Association for the Advancement of Science, 362, 1014–1015.
Lee, K., Xue, Y., Lee, J., Kim, H. J., Liu, Y., Tebon, P., Sarikhani, E., Sun, W., Zhang, S., & Haghniaz, R. (2020). A patch of detachable hybrid microneedle depot for localized delivery of mesenchymal stem cells in regeneration therapy. Advanced Functional Materials, 30, 2000086.
Chen, W., Li, H., Shi, D., Liu, Z., & Yuan, W. (2016). Microneedles as a delivery system for gene therapy. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 7, 137.
Shi, H., Xue, T., Yang, Y., Jiang, C., Huang, S., Yang, Q., Lei, D., You, Z., Jin, T., & Wu, F. (2020). Microneedle-mediated gene delivery for the treatment of ischemic myocardial disease. Science Advances, 6, eaaz3621.
Ita, K. (2017). Dermal/transdermal delivery of small interfering RNA and antisense oligonucleotides-advances and hurdles. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 87, 311–320.
Pan, J., Ruan, W., Qin, M., Long, Y., Wan, T., Yu, K., Zhai, Y., Wu, C., & Xu, Y. (2018). Intradermal delivery of STAT3 siRNA to treat melanoma via dissolving microneedles. Scientific Reports, 8, 1–11.
Pires, L. R., Vinayakumar, K. B., Turos, M., Miguel, V., & Gaspar, J. (2019). A perspective on microneedle-based drug delivery and diagnostics in paediatrics. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 9(4), 49.
Zhang, W., Zhang, W., Li, C., Zhang, J., Qin, L., & Lai, Y. (2022). Recent advances of microneedles and their application in disease treatment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(5), 2401.
Kulkarni, D., Damiri, F., Rojekar, S., Zehravi, M., Ramproshad, S., Dhoke, D., Musale, S., Mulani, A. A., Modak, P., Paradhi, R., Vitore, J., Rahman, M. H., Berrada, M., Giram, P. S., & Cavalu, S. (2022). Recent advancements in microneedle technology for multifaceted biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics, 14(5), 1097. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14051097
Waghule, T., Singhvi, G., Dubey, S. K., Pandey, M. M., Gupta, G., Singh, M., & Dua, K. (2019). Microneedles: A smart approach and increasing potential for transdermal drug delivery system. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 109, 1249–1258.
Baker-Sediako, R. D., Richter, B., Blaicher, M., Thiel, M., & Hermatschweiler, M. (2023). Industrial perspectives for personalized microneedles. Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology, 14, 857–864.
Alimardani, V., Abolmaali, S. S., Yousefi, G., Rahiminezhad, Z., Abedi, M., Tamaddon, A., & Ahadian, S. (2021). Microneedle arrays combined with nanomedicine approaches for transdermal delivery of therapeutics. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(2), 181.
Wang, R., Jiang, G., Aharodnikau, U. E., Yunusov, K., Sun, Y., Liu, T., & Solomevich, S. O. (2022). Recent advances in polymer microneedles for drug transdermal delivery: Design strategies and applications. Macromolecular Rapid Communications, 43(8), e2200037.
Chen, Z., He, J., Qi, J., Zhu, Q., Wu, W., & Lu, Y. (2020). Long-acting microneedles: A progress report of the state-of-the-art techniques. Drug Discovery Today, 25(8), 1462–1468.
Xie, Z., Zhang, X., Chen, G., Che, J., & Zhang, D. (2022). Wearable microneedle-integrated sensors for household health monitoring. Engineered Regeneration, 3(4), 420–426.
Economidou, S. N., & Douroumis, D. (2021). 3D printing as a transformative tool for microneedle systems: Recent advances, manufacturing considerations and market potential. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 173, 60–69.
Dabholkar, N., Gorantla, S., Waghule, T., Rapalli, V. K., Kothuru, A., Goel, S., & Singhvi, G. (2021). Biodegradable microneedles fabricated with carbohydrates and proteins: Revolutionary approach for transdermal drug delivery. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 170, 602–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.177
Moffatt, K., Wang, Y., Raj Singh, T. R., & Donnelly, R. F. (2017). Microneedles for enhanced transdermal and intraocular drug delivery. Current Opinion in Pharmacology, 36, 14–21.
O’Shea, J., Prausnitz, M. R., & Rouphael, N. (2021). Dissolvable: Microneedle patches to enable increased access to vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 and future pandemic outbreaks. Vaccines (Basel), 9(4), 320.
Coppola, S., Vespini, V., D'Avino, G., Grilli, S., Maffettone, & P.L., Ferraro, P. (2021) Biocompatible micro-needles for smart therapy. In: 2021 IEEE 8th International workshop on metrology for AeroSpace (MetroAeroSpace) (pp. 459–463). IEEE.
Prausnitz, M. R., Goodson, J. L., Rota, P. A., & Orenstein, W. A. (2020). A microneedle patch for measles and rubella vaccination: A game changer for achieving elimination. Current Opinion in Virology, 41, 68–76.
O’Shea, J., Prausnitz, M. R., & Rouphael, N. (2021). Dissolvable microneedle patches to enable increased access to vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 and future pandemic outbreaks. Vaccines (Basel), 9(4), 320.
Rozaini, M. N., Semail, N. F., Zango, Z. U., Lim, J. W., Yahaya, N., Setiabudi, H. D., Tong, W. Y., Shamsuddin, R., Chan, Y. J., Khoo, K. S., & Suliman, M. (2023). Advanced adsorptions of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from environmental waters in improving offline and online preconcentration techniques: An analytical review. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2023.105020
Chen, W., Cai, B., Geng, Z., Chen, F., Wang, Z., Wang, L., & Chen, X. (2020). Reducing false negatives in COVID-19 testing by using microneedle-based oropharyngeal swabs. Matter, 3, 1589–1600.
Hiraishi, Y., Nakagawa, T., Quan, Y.-S., Kamiyama, F., Hirobe, S., Okada, N., & Nakagawa, S. (2013). Performance and characteristics evaluation of a sodium hyaluronate-based microneedle patch for a transcutaneous drug delivery system. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 441, 570–579.
Kommareddy, S., Baudner, B. C., Oh, S., Kwon, S.-y, Singh, M., & O’hagan DT,. (2012). Dissolvable microneedle patches for the delivery of cell-culture-derived influenza vaccine antigens. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 101, 1021–1027.
Atmar, R. L., Patel, S. M., & Keitel, W. A. (2010). Intanza®: A new intradermal vaccine for seasonal influenza. Expert Review of Vaccines, 9, 1399–1409.
Hoon, S. H., Hee, J. W., Weber, F., Joo, K. W., Ran, P. K., Il Kim, S., Hwa, Y. C., & Myung, K. J. (2013). Immunogenicity and safety of Intanza®/IDflu® intradermal influenza vaccine in South Korean adults: A multicenter, randomized trial. Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics, 9, 1971–1977.
Matriano, J. A., Cormier, M., Johnson, J., Young, W. A., Buttery, M., Nyam, K., & Daddona, P. E. (2002). Macroflux® microprojection array patch technology: A new and efficient approach for intracutaneous immunization. Pharmaceutical Research, 19, 63–70.
Malik, D. K., Baboota, S., Ahuja, A., Hasan, S., & Ali. (2007). Recent advances in protein and peptide drug delivery systems. Current Drug Delivery, 4, 141–151.
Shi, X.-Y., & Tan, T.-W. (2002). Preparation of chitosan/ethylcellulose complex microcapsule and its application in controlled release of vitamin D2. Biomaterials, 23, 4469–4473.
Shi, X., & Tan, T. (2003). Preparation of complex chitosan microcapsule and its application in controlled release of vitamin D2. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 20, 26.
Hung, I. F., Levin, Y., To, K. K., Chan, K.-H., Zhang, A. J., Li, P., Li, C., Xu, T., Wong, T.-Y., & Yuen, K.-Y. (2012). Dose sparing intradermal trivalent influenza (2010/2011) vaccination overcomes reduced immunogenicity of the 2009 H1N1 strain. Vaccine, 30, 6427–6435.
Icardi, G., Orsi, A., Ceravolo, A., & Ansaldi, F. (2012). Current evidence on intradermal influenza vaccines administered by Soluvia™ licensed micro injection system. Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics, 8, 67–75.
Joshi, M., Pathak, S., Sharma, S., & Patravale, V. (2008). Design and in vivo pharmacodynamic evaluation of nanostructured lipid carriers for parenteral delivery of artemether: Nanoject. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 364, 119–126.
Özkur, E., Kıvanç Altunay, İ, & Aydın, Ç. (2020). Psychopathology among individuals seeking minimally invasive cosmetic procedures. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 19, 939–945.
Bandral, M. R., Padgavankar, P. H., Japatti, S. R., Gir, P. J., Siddegowda, C. Y., & Gir, R. J. (2019). Clinical evaluation of microneedling therapy in the management of facial scar: A prospective randomized study. Journal of Maxillofacial and Oral Surgery, 18, 572–578.
Kochba, E., Levin, Y., Raz, I., & Cahn, A. (2016). Improved insulin pharmacokinetics using a novel microneedle device for intradermal delivery in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics, 18, 525–531.
Dul, M., Stefanidou, M., Porta, P., Serve, J., O’Mahony, C., Malissen, B., Henri, S., Levin, Y., Kochba, E., & Wong, F. S. (2017). Hydrodynamic gene delivery in human skin using a hollow microneedle device. Journal of Controlled Release, 265, 120–131.
Peri, R., Aguilar, R. C., Tüffers, K., Erhardt, A., Link, A., Ehlermann, P., Angeli, W., Frank, T., Storr, M., & Glück, T. (2019). The impact of technical and clinical factors on fecal microbiota transfer outcomes for the treatment of recurrent Clostridioides difficile infections in Germany. United European Gastroenterology Journal, 7, 716–722.
Hagel, S., Stallmach, A., & Vehreschild, M. (2016). Fecal microbiota transplant in patients with recurrent clostridium difficile infection: A retrospective multicenter observational study from the MicroTrans registry. Deutsches Ärzteblatt International, 113, 583.
Dugam, S., Tade, R., Dhole, R., & Nangare, S. (2021). Emerging era of microneedle array for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications: Recent advances and toxicological perspectives. Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 7, 19.
Wilke, N., Hibert, C., O’Brien, J., & Morrissey, A. (2005). Silicon microneedle electrode array with temperature monitoring for electroporation. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 123, 319–325.
Narayanan, S. P., & Raghavan, S. (2017). Solid silicon microneedles for drug delivery applications. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 93, 407–422.
Das, A., Singha, C., & Bhattacharyya, A. (2019). Development of silicon microneedle arrays with spontaneously generated micro-cavity ring for transdermal drug delivery. Microelectronic Engineering, 210, 14–18.
Hopcroft, M. A., Nix, W. D., & Kenny, T. W. (2010). What is the Young’s modulus of silicon? Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems, 19, 229–238.
Verbaan, F., Bal, S., Van den Berg, D., Groenink, W., Verpoorten, H., Lüttge, R., & Bouwstra, J. (2007). Assembled microneedle arrays enhance the transport of compounds varying over a large range of molecular weight across human dermatomed skin. Journal of Controlled Release, 117, 238–245.
Niinomi, M., & Nakai, M. (2011). Titanium-based biomaterials for preventing stress shielding between implant devices and bone. International Journal of Biomaterials. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/836587
Ayittey, P. N., Walker, J. S., Rice, J. J., & De Tombe, P. P. (2009). Glass microneedles for force measurements: A finite-element analysis model. Pflügers Archiv-European Journal of Physiology, 457, 1415.
Martin, C., Allender, C. J., Brain, K. R., Morrissey, A., & Birchall, J. C. (2012). Low temperature fabrication of biodegradable sugar glass microneedles for transdermal drug delivery applications. Journal of Controlled Release, 158, 93–101.
Verhoeven, M., Bystrova, S., Winnubst, L., Qureshi, H., De Gruijl, T. D., Scheper, R. J., & Luttge, R. (2012). Applying ceramic nanoporous microneedle arrays as a transport interface in egg plants and an ex-vivo human skin model. Microelectronic Engineering, 98, 659–662.
Ita, K. (2018). Ceramic microneedles and hollow microneedles for transdermal drug delivery: Two decades of research. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 44, 314–322.
Larraneta, E., Lutton, R. E., Woolfson, A. D., & Donnelly, R. F. (2016). Microneedle arrays as transdermal and intradermal drug delivery systems: Materials science, manufacture and commercial development. Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports, 104, 1–32.
Lee, K., Lee, C. Y., & Jung, H. (2011). Dissolving microneedles for transdermal drug administration prepared by stepwise controlled drawing of maltose. Biomaterials, 32, 3134–3140.
GhavamiNejad, A., Li, J., Lu, B., Zhou, L., Lam, L., Giacca, A., & Wu, X. Y. (2019). Glucose-responsive composite microneedle patch for hypoglycemia-triggered delivery of native glucagon. Advanced Materials, 31, 1901051.
Chu, L. Y., Choi, S.-O., & Prausnitz, M. R. (2010). Fabrication of dissolving polymer microneedles for controlled drug encapsulation and delivery: Bubble and pedestal microneedle designs. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 99, 4228–4238.
Han, M., Hyun, D.-H., Park, H.-H., Lee, S. S., Kim, C.-H., & Kim, C. (2007). A novel fabrication process for out-of-plane microneedle sheets of biocompatible polymer. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 17, 1184.
Aoyagi, S., Izumi, H., Isono, Y., Fukuda, M., & Ogawa, H. (2007). Laser fabrication of high aspect ratio thin holes on biodegradable polymer and its application to a microneedle. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 139, 293–302.
Meng, F., Hasan, A., Babadaei, M. M. N., Kani, P. H., Talaei, A. J., Sharifi, M., Cai, T., Falahati, M., & Cai, Y. (2020). Polymeric-based microneedle arrays as potential platforms in development of drugs delivery systems. Journal of Advanced Research, 26, 137–147.
Dong, L., Li, Y., Li, Z., Xu, N., Liu, P., Du, H., Zhang, Y., Huang, Y., Zhu, J., & Ren, G. (2018). Au nanocage-strengthened dissolving microneedles for chemo-photothermal combined therapy of superficial skin tumors. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 10, 9247–9256.
Uddin, M. J., Scoutaris, N., Economidou, S. N., Giraud, C., Chowdhry, B. Z., Donnelly, R. F., & Douroumis, D. (2020). 3D printed microneedles for anticancer therapy of skin tumours. Materials Science and Engineering C, 107, 110248.
Zhang, Y., Wu, M., Tan, D., Liu, Q., Xia, R., Chen, M., Liu, Y., Xue, L., & Lei, Y. (2020). A dissolving and glucose-responsive insulin releasing microneedle patch for type 1 diabetes therapy. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 9, 648–657.
Wu, M., Zhang, Y., Huang, H., Li, J., Liu, H., Guo, Z., Xue, L., Liu, S., & Lei, Y. (2020). Assisted 3D printing of microneedle patches for minimally invasive glucose control in diabetes. Materials Science and Engineering C, 117, 111299.
Arikat, F., Hanna, S. J., Singh, R. K., Vilela, L., Wong, F. S., Dayan, C. M., Coulman, S. A., & Birchall, J. C. (2020). Targeting proinsulin to local immune cells using an intradermal microneedle delivery system; a potential antigen-specific immunotherapy for type 1 diabetes. Journal of Controlled Release, 322, 593–601.
Dangol, M., Kim, S., Li, C. G., Lahiji, S. F., Jang, M., Ma, Y., Huh, I., & Jung, H. (2017). Anti-obesity effect of a novel caffeine-loaded dissolving microneedle patch in high-fat diet-induced obese C57BL/6J mice. Journal of Controlled Release, 265, 41–47.
Zhang, Y., Liu, Q., Yu, J., Yu, S., Wang, J., Qiang, L., & Gu, Z. (2017). Locally induced adipose tissue browning by microneedle patch for obesity treatment. ACS Nano, 11, 9223–9230.
Kearney, M.-C., Caffarel-Salvador, E., Fallows, S. J., McCarthy, H. O., & Donnelly, R. F. (2016). Microneedle-mediated delivery of donepezil: Potential for improved treatment options in Alzheimer’s disease. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 103, 43–50.
Matsuo, K., Okamoto, H., Kawai, Y., Quan, Y.-S., Kamiyama, F., Hirobe, S., Okada, N., & Nakagawa, S. (2014). Vaccine efficacy of transcutaneous immunization with amyloid β using a dissolving microneedle array in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Neuroimmunology, 266, 1–11.
Steeb, T., Niesert, A.-C., French, L. E., Berking, C., & Heppt, M. V. (2020). Microneedling-assisted photodynamic therapy for the treatment of actinic keratosis: Results from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 82, 515–519.
Redfearn, D. P., Trim, G. M., Skanes, A. C., Petrellis, B., Krahn, A. D., Yee, R., & Klein, G. J. (2005). Esophageal temperature monitoring during radiofrequency ablation of atrial fibrillation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 16, 589–593.
Kim, J. S., Choi, J.-a, Kim, J. C., Park, H., Yang, E., Park, J. S., Song, M., & Park, J.-H. (2020). Microneedles with dual release pattern for improved immunological efficacy of Hepatitis B vaccine. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 591, 119928.
Tas, C., Joyce, J. C., Nguyen, H. X., Eangoor, P., Knaack, J. S., Banga, A. K., & Prausnitz, M. R. (2017). Dihydroergotamine mesylate-loaded dissolving microneedle patch made of polyvinylpyrrolidone for management of acute migraine therapy. Journal of Controlled Release, 268, 159–165.
Al-Naggar, M. R., Al-Adl, A. S., Rabie, A. R., Abdelkhalk, M. R., & Elsaie, M. L. (2019). Intralesional bleomycin injection vs microneedling-assisted topical bleomycin spraying in treatment of plantar warts. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 18, 124–128.
Ryu, H. R., Jeong, H.-R., Seon-Woo, H.-S., Kim, J. S., Lee, S. K., Kim, H. J., Baek, J. O., Park, J.-H., & Roh, J. Y. (2018). Efficacy of a bleomycin microneedle patch for the treatment of warts. Drug Delivery and Translational Research, 8, 273–280.
Kaul, S., Kaur, I., Jakhar, D., Edigin, E., & Caldito, E. G. (2020). The diverse methods of bleomycin delivery in cutaneous warts: A literature review. Dermatologic Therapy, 34, e14401.
Frew, P. M., Paine, M. B., Rouphael, N., Schamel, J., Chung, Y., Mulligan, M. J., & Prausnitz, M. R. (2020). Acceptability of an inactivated influenza vaccine delivered by microneedle patch: Results from a phase I clinical trial of safety, reactogenicity, and immunogenicity. Vaccine, 38, 7175–7181.
Ellison, T. J., Talbott, G. C., & Henderson, D. R. (2020). VaxiPatch™, a novel vaccination system comprised of subunit antigens, adjuvants and microneedle skin delivery: An application to influenza B/Colorado/06/2017. Vaccine, 38, 6839–6848.
Jeong, H.-R., Bae, J.-Y., Park, J.-H., Baek, S.-K., Kim, G., Park, M.-S., & Park, J.-H. (2020). Preclinical study of influenza bivalent vaccine delivered with a two compartmental microneedle array. Journal of Controlled Release, 324, 280–288.
Kuwentrai, C., Yu, J., Rong, L., Zhang Bz, Hu., Yf, Gong Hr, Dou, Y., Deng, J., Huang, J. D., & Xu, C. (2020). Intradermal delivery of receptor-binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein with dissolvable microneedles to induce humoral and cellular responses in mice. Bioengineering & Translational Medicine, 6, e102022.
Soltani-Arabshahi, R., Wong, J. W., Duffy, K. L., & Powell, D. L. (2014). Facial allergic granulomatous reaction and systemic hypersensitivity associated with microneedle therapy for skin rejuvenation. JAMA DERMATOLOGY, 150, 68–72.
Donnelly, R. F., Singh, T. R. R., Tunney, M. M., Morrow, D. I., McCarron, P. A., O’Mahony, C., & Woolfson, A. D. (2009). Microneedle arrays allow lower microbial penetration than hypodermic needles in vitro. Pharmaceutical Research, 26, 2513–2522.
Gill, H. S., Denson, D. D., Burris, B. A., & Prausnitz, M. R. (2008). Effect of microneedle design on pain in human subjects. The Clinical Journal of Pain, 24, 585.
Gill, H. S., & Prausnitz, M. R. (2007). Does needle size matter? Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology, 1, 725–729.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, writing-original draft, review and editing, supervision: CC; figure and table preparation, validation: MB. Validation, formal analysis: SSL; All authors have read and approved the final version of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chakraborty, C., Bhattacharya, M. & Lee, SS. Current Status of Microneedle Array Technology for Therapeutic Delivery: From Bench to Clinic. Mol Biotechnol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-00961-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-00961-2