Abstract
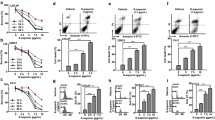
Evodiamine (EVO) is a bioactive alkaloid that exerts antitumor activity in various cancers, including prostate cancer (PCa). In this paper, we further investigated the molecular mechanisms underlying the anti-PCa effect of evodiamine. In the present study, cell proliferation, colony formation, migration, and invasion were assessed by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT), colony formation, and transwell assays, respectively. Animal studies were used to evaluate the effect of evodiamine on the tumorigenicity of LNCaP cells in vivo. The expression levels of steroid receptor coactivator (Src), androgene receptor (AR), and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) were detected by western blot, quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) or ELISA assay. Association between Src and AR was examined by Co-Immunoprecipitation (CoIP). The impact of evodiamine on AR-mediated transcriptional activity was confirmed by dual-luciferase reporter assay. The results showed that evodiamine reduced LNCaP and 22Rv1 cell proliferation, colony formation, migration, and invasion induced by dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in vitro, as well as diminished tumor growth in vivo. Mechanistically, evodiamine directly targeted Src and reduced DHT-induced Src activation. Moreover, the restoration of Src activation abolished evodiamine-mediated suppression of proliferation, migration, and invasion of DHT-treated LNCaP and 22Rv1 cells. Furthermore, evodiamine inhibited DHT-induced AR transcriptional activity through targeting Src. As a conclusion, our findings demonstrate the antitumor property of evodiamine in PCa by blocking AR transcriptional activity through targeting Src and provide a rationale for developing evodiamine as a promising antitumor agent against PCa.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Bray, J. Ferlay, I. Soerjomataram, R.L. Siegel, L.A. Torre, A. Jemal, Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 68, 394–424 (2018)
M.H. Tan, J. Li, H.E. Xu, K. Melcher, E.L. Yong, Androgen receptor: structure, role in prostate cancer and drug discovery. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 36, 3–23 (2015)
A.A. Shafi, A.E. Yen, N.L. Weigel, Androgen receptors in hormone-dependent and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 140, 223–238 (2013)
A.E. Gururaj, S.K. Rayala, R.K. Vadlamudi, R. Kumar, Novel mechanisms of resistance to endocrine therapy: genomic and nongenomic considerations. Clin. Cancer Res. 12, 1001s–1007s (2006)
C.S. Grasso, Y.M. Wu, D.R. Robinson, X. Cao, S.M. Dhanasekaran, A.P. Khan, M.J. Quist, X. Jing, R.J. Lonigro, J.C. Brenner, I.A. Asangani, B. Ateeq, S.Y. Chun, J. Siddiqui, L. Sam, M. Anstett, R. Mehra, J.R. Prensner, N. Palanisamy, G.A. Ryslik, F. Vandin, B.J. Raphael, L.P. Kunju, D.R. Rhodes, K.J. Pienta, A.M. Chinnaiyan, S.A. Tomlins, The mutational landscape of lethal castration-resistant prostate cancer. Nature 487, 239–243 (2012)
Z. Culig, F.R. Santer, Studies on steroid receptor coactivators in prostate cancer. Methods Mol. Biol. 1786, 259–262 (2018)
A. Migliaccio, G. Castoria, F. Auricchio, Analysis of androgen receptor rapid actions in cellular signaling pathways: receptor/Src association. Methods Mol. Biol. 776, 361–370 (2011)
M. Asim, I.A. Siddiqui, B.B. Hafeez, A. Baniahmad, H. Mukhtar, Src kinase potentiates androgen receptor transactivation function and invasion of androgen-independent prostate cancer C4-2 cells. Oncogene 27, 3596–3604 (2008)
A. Migliaccio, L. Varricchio, A. De Falco, G. Castoria, C. Arra, H. Yamaguchi, A. Ciociola, M. Lombardi, R. Di Stasio, A. Barbieri, A. Baldi, M.V. Barone, E. Appella, F. Auricchio, Inhibition of the SH3 domain-mediated binding of Src to the androgen receptor and its effect on tumor growth. Oncogene 26, 6619–6629 (2007)
J. Jiang, C. Hu, Evodiamine: a novel anti-cancer alkaloid from Evodia rutaecarpa. Molecules 14, 1852–1859 (2009)
X. Hu, D. Li, C. Chu, X. Li, X. Wang, Y. Jia, H. Hua, F. Xu, Antiproliferative effects of alkaloid evodiamine and its derivatives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 3403 (2018)
S. T. Hwang, J. Y. Um, A. Chinnathambi, S. A. Alharbi, A. S. Narula, O. A. Namjoshi, B. E. Blough, K. S. Ahn, Evodiamine mitigates cellular growth and promotes apoptosis by targeting the c-Met pathway in prostate cancer cells. Molecules 25, 1320 (2020)
S.F. Kan, W.J. Huang, L.C. Lin, P.S. Wang, Inhibitory effects of evodiamine on the growth of human prostate cancer cell line LNCaP. Int. J. Cancer 110, 641–651 (2004)
S.F. Kan, C.H. Yu, H.F. Pu, J.M. Hsu, M.J. Chen, P.S. Wang, Anti-proliferative effects of evodiamine on human prostate cancer cell lines DU145 and PC3. J. Cell. Biochem. 101, 44–56 (2007)
D.M. Huang, J.H. Guh, Y.T. Huang, S.C. Chueh, P.C. Chiang, C.M. Teng, Induction of mitotic arrest and apoptosis in human prostate cancer pc-3 cells by evodiamine. J. Urol. 173, 256–261 (2005)
Y.G. Jang, R.E. Go, K.A. Hwang, K.C. Choi, Resveratrol inhibits DHT-induced progression of prostate cancer cell line through interfering with the AR and CXCR4 pathway. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 192, 105406 (2019)
H.J. Kim, Y.I. Park, M.S. Dong, Effects of 2,4-D and DCP on the DHT-induced androgenic action in human prostate cancer cells. Toxicol. Sci. 88, 52–59 (2005)
A. D’Souza, C.M. Pearman, Y. Wang, S. Nakao, S. Logantha, C. Cox, H. Bennett, Y. Zhang, A.B. Johnsen, N. Linscheid, P.C. Poulsen, J. Elliott, J. Coulson, J. McPhee, A. Robertson, P.A. da Costa Martins, A. Kitmitto, U. Wisløff, E.J. Cartwright, O. Monfredi, A. Lundby, H. Dobrzynski, D. Oceandy, G.M. Morris, M.R. Boyett, Targeting miR-423-5p Reverses Exercise Training-Induced HCN4 Channel Remodeling and Sinus Bradycardia. Circ. Res. 121, 1058–1068 (2017)
E. Orangi, M. Motovali-Bashi, Evaluation of miRNA-9 and miRNA-34a as potential biomarkers for diagnosis of breast cancer in Iranian women. Gene 687, 272–279 (2019)
A. Migliaccio, G. Castoria, M. Di Domenico, A. de Falco, A. Bilancio, M. Lombardi, M.V. Barone, D. Ametrano, M.S. Zannini, C. Abbondanza, F. Auricchio, Steroid-induced androgen receptor-oestradiol receptor beta-Src complex triggers prostate cancer cell proliferation. EMBO J. 19, 5406–5417 (2000)
T. Shibahara, T. Onishi, O.E. Franco, K. Arima, K. Nishikawa, M. Yanagawa, T. Hioki, M. Watanabe, Y. Hirokawa, T. Shiraishi, Y. Sugimura, A G/A polymorphism in the androgen response element 1 of prostate-specific antigen gene correlates with the response to androgen deprivation therapy in Japanese population. Anticancer Res. 26, 3365–3371 (2006)
D. Wang, S. Ge, Z. Chen, Y. Song, Evodiamine exerts anticancer effects via induction of apoptosis and autophagy and suppresses the migration and invasion of human colon cancer cells. J. BUON 24, 1824–1829 (2019)
C. Y. Hu, H. T. Wu, Y. C. Su, C. H. Lin, C. J. Chang, C. L. Wu, Evodiamine exerts an anti-hepatocellular carcinoma activity through a WWOX-dependent pathway. Molecules 22, 1175 (2017)
Z.B. Jiang, J.M. Huang, Y.J. Xie, Y.Z. Zhang, C. Chang, H.L. Lai, W. Wang, X.J. Yao, X.X. Fan, Q.B. Wu, C. Xie, M.F. Wang, E.L. Leung, Evodiamine suppresses non-small cell lung cancer by elevating CD8(+) T cells and downregulating the MUC1-C/PD-L1 axis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 39, 249 (2020)
H.I. Yu, H.C. Chou, Y.C. Su, L.H. Lin, C.H. Lu, H.H. Chuang, Y.T. Tsai, E.C. Liao, Y.S. Wei, Y.T. Yang, Y.R. Lee, H.L. Chan, Proteomic analysis of evodiamine-induced cytotoxicity in thyroid cancer cells. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 160, 344–350 (2018)
F.S. Li, J. Huang, M.Z. Cui, J.R. Zeng, P.P. Li, L. Li, Y. Deng, Y. Hu, B.C. He, D.Z. Shu, BMP9 mediates the anticancer activity of evodiamine through HIF‑1α/p53 in human colon cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 43, 415–426 (2020)
R. Roskoski Jr, Src protein-tyrosine kinase structure and regulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 324, 1155–1164 (2004)
A. Aleshin, R.S. Finn, SRC: a century of science brought to the clinic. Neoplasia 12, 599–607 (2010)
A. Varkaris, A.D. Katsiampoura, J.C. Araujo, G.E. Gallick, P.G. Corn, Src signaling pathways in prostate cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 33, 595–606 (2014)
J. Yang, X. Cai, W. Lu, C. Hu, X. Xu, Q. Yu, P. Cao, Evodiamine inhibits STAT3 signaling by inducing phosphatase shatterproof 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 328, 243–251 (2013)
M. Nakka, I.U. Agoulnik, N.L. Weigel, Targeted disruption of the p160 coactivator interface of androgen receptor (AR) selectively inhibits AR activity in both androgen-dependent and castration-resistant AR-expressing prostate cancer cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 45, 763–772 (2013)
A.D. Lamb, C.E. Massie, D.E. Neal, The transcriptional programme of the androgen receptor (AR) in prostate cancer. BJU Int. 113, 358–366 (2014)
M. Thadani-Mulero, D.M. Nanus, P. Giannakakou, Androgen receptor on the move: boarding the microtubule expressway to the nucleus. Cancer Res. 72, 4611–4615 (2012)
L. Gan, S. Chen, Y. Wang, A. Watahiki, L. Bohrer, Z. Sun, Y.Z. Wang, H.J. Huang, Inhibition of the androgen receptor as a novel mechanism of taxol chemotherapy in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 69, 8386–8394 (2009)
M.L. Zhu, C.M. Horbinski, M. Garzotto, D.Z. Qian, T.M. Beer, N. Kyprianou, Tubulin-targeting chemotherapy impairs androgen receptor activity in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 70, 7992–8002 (2010)
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank Ms. P.C., X.Z., X.W., C.L, X.Z., J.F., who has helped me during the writing, design, and experiment performance of this thesis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P.C. designed and performed the experiments, wrote the manuscript. X.Z., X.W., C.L., X.Z., J.F. contributed to experimental work, data analysis and conducted the experiments. C.X. designed and revised the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, P., Zhang, X., Wang, X. et al. Identification of evodiamine as a suppressor of prostate cancer progression by reducing AR transcriptional activity via targeting Src. Endocrine 75, 635–645 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-021-02907-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-021-02907-7