Abstract
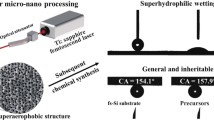
Superhydrophobic surfaces have attracted considerable interest due to their various functions and wide applications. Most of the existing methods for preparing superhydrophobic surfaces are only applicable to one or several specific substrate materials, which have the disadvantage of substrate-dependent. Here, an approach for the fabrication of substrate-independent superhydrophobic surfaces based on femtosecond laser-chemical hybrid processing is proposed. Micro/nanostructures are constructed on substrates via femtosecond laser direct writing technology, followed by modification with stearic acid. The laser-treated samples coated with stearic acid (LTx-SA, x presents different samples) surfaces have excellent superhydrophobic and self-cleaning properties. Moreover, it is worth noting that the LTx-SA surfaces remain stable superhydrophobicity after heating substrate from 20 °C to 100 °C, washing substrate 10 times, and exposing substrate to air for 60 days. This work provides an efficient and facile strategy for achieving substrate-independent superhydrophobic surfaces.
摘要
超疏水表面因具有多种功能和广泛的应用引起了人们极大的兴趣. 目前制备超疏水表面的方法大多只适用于一种或几种特定的基底材料, 具有依赖基底的缺点. 本文提出了一种基于飞秒激光-化学混合加工制备与基底无关的超疏水表面的方法. 通过飞秒激光直接写入技术在基底上构建出微/纳米结构, 然后用硬脂酸改性. 硬脂酸涂覆激光处理后的样品(LTx-SA, x表示不同的样品)表面具有优异的超疏水和自清洁性能. 此外, 值得注意的是, 将基底从20°C加热到100°C, 或清洗基板10次, 或将基板暴露在空气中60天后, LTx-SA 表面仍然保持稳定的超疏水特性. 这项工作为制备与基底无关的超疏水表面提供了一种有效而简单的策略.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
WANG De-hui, SUN Qiang-qiang, HOKKANEN M J, et al. Design of robust superhydrophobic surfaces [J]. Nature, 2020, 582: 55–59. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2331-8.
WU Zhi-peng, YIN Kai, WU Jun-rui, et al. Recent advances in femtosecond laser-structured Janus membranes with asymmetric surface wettability [J]. Nanoscale, 2021, 13(4): 2209–2226. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d0nr06639g.
HUHTAMÄKI T, TIAN Xue-lin, KORHONEN J T, et al. Surface-wetting characterization using contact-angle measurements [J]. Nature Protocols, 2018, 13: 1521–1538. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-018-0003-z.
CHEN Fa-ze, WANG Ya-quan, TIAN Yan-ling, et al. Robust and durable liquid-repellent surfaces [J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2022, 51(20): 8476–8583. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CS01033B.
ZHU Zhuo, WU Jun-rui, WU Zhi-peng, et al. Femtosecond laser micro/nano fabrication for bioinspired superhydrophobic or underwater superoleophobic surfaces [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2021, 28(12): 3882–3906. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4886-4.
DONG Jian-cheng, WANG Dan, PENG Yi-dong, et al. Ultrastretchable and superhydrophobic textile-based bioelectrodes for robust self-cleaning and personal health monitoring [J]. Nano Energy, 2022, 97: 107160. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2022.107160.
ZHOU Ze-hua, ZHU Qian-qian, LIU Yue, et al. Construction of self-assembly based tunable absorber: Lightweight, hydrophobic and self-cleaning properties [J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2023, 15(1): 137. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-023-01108-3.
DENG Qin-wen, YIN Kai, WANG Ling-xiao, et al. One droplet toward efficient alcohol detection using femtosecond laser textured micro/nanostructured surface with superwettability [J]. Small Methods, 2023, 7(9): e2300290. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/smtd.202300290.
SHI Zhen, ZENG Hang, YUAN Yu-sheng, et al. Constructing superhydrophobicity by self-assembly of SiO2@Polydopamine core-shell nanospheres with robust oil-water separation efficiency and anti-corrosion performance [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(16): 2213042. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202213042.
GUPTA R, VERMA R, KANGO S, et al. A critical review on recent progress, open challenges, and applications of corrosion-resistant superhydrophobic coating [J]. Materials Today Communications, 2023, 34: 105201. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.105201.
HAN Xin-ting, REN Lu-lu, MA Yan, et al. A mussel-inspired self-repairing superhydrophobic coating with good anticorrosion and photothermal properties [J]. Carbon, 2022, 197: 27–39. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2022.05.056.
NGUYEN N B, LY N H, TRAN H N, et al. Transparent oil-water separating spiky SiO2 nanoparticle supramolecular polymer superhydrophobic coatings [J]. Small Methods, 2023, 7(3): e2201257. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/smtd.202201257.
WU Jun-rui, YIN Kai, LI Ming, et al. Under-oil self-driven and directional transport of water on a femtosecond laser-processed superhydrophilic geometry-gradient structure [J]. Nanoscale, 2020, 12(6): 4077–4084. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NR09902F.
BAIG U, FAIZAN M, SAJID M. Multifunctional membranes with super-wetting characteristics for oil-water separation and removal of hazardous environmental pollutants from water: A review [J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2020, 285: 102276. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2020.102276.
YANG Shuai, YIN Kai, WU Jun-rui, et al. Ultrafast nanostructuring of superwetting Ti foam with robust antifouling and stability towards efficient oil-in-water emulsion separation [J]. Nanoscale, 2019, 11(38): 17607–17614. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c9nr04381k.
WANG Rui-jie, JIN Fan, LI Yu-fen, et al. Magnetic responsive on-site switching of the directional droplet self-transport in shape memory slippery tube [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(49): 2305766. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202305766.
LI Yu-fen, WANG Rui-jie, JIAO Shou-zheng, et al. Beetle-inspired oil-loaded shape memory micro-arrays with switchable adhesion to both solid and liquid [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 461: 141927. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.141927.
HAN Jian-hua, LIU En-hong, ZHOU Yu-qin, et al. Robust superhydrophobic film on aluminum alloy prepared with TiO2/SiO2-silane composite film for efficient self-cleaning, anti-corrosion and anti-icing [J]. Materials Today Communications, 2023, 34: 105085. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.105085.
ZHANG Yu-ting, LEI Ting-ping, LI Shuang-min, et al. Candle soot-based electrosprayed superhydrophobic coatings for self-cleaning, anti-corrosion and oil/water separation [J]. Materials, 2022, 15(15): 5300. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15155300.
WANG Zi-an, PENG Shu-qiang, WU Li-xin, et al. Construction of ultra-long service life self-cleaning slippery surface on superhydrophobicity functionalized by ATRP treatment [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 428: 130997. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130997.
ZHOU Lei, SU Cheng-zhuang, CHEN Bai-yi, et al. Durable ER@SiO2@PDMS superhydrophobic composite designed by double crosslinking strategy for efficient oil-water separation [J]. Polymer, 2022, 245: 124722. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2022.124722.
RUIDAS S, DAS A, KUMAR S, et al. Non-fluorinated and robust superhydrophobic modification on covalent organic framework for crude-oil-in-water emulsion separation [J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed in English), 2022, 61(41): e202210507. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202210507.
CHEN Chao-qi, LI Zhao-shuang, HU Yin-chun, et al. Rosin acid and SiO2 modified cotton fabric to prepare fluorine-free durable superhydrophobic coating for oil-water separation [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 440: 129797. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129797.
MAYOUSSI F, DOEVEN E H, KICK A, et al. Facile fabrication of micro-/ nanostructured, superhydrophobic membranes with adjustable porosity by 3D printing [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(37): 21379–21386. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ta03352b.
ZHANG Jian-wen, PEI Xin-yu, HUANG Jin-quan, et al. Construction of hierarchical micro/nanostructured ZnO/Cu-ZnMOFs@SA superhydrophobic composite coatings with excellent multifunctionality of anticorrosion, blood-repelling, and antimicrobial properties [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(1): 265–280. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c15102.
GHASEMLOU M, LE P H, DAVER F, et al. Robust and eco-friendly superhydrophobic starch nanohybrid materials with engineered lotus leaf mimetic multiscale hierarchical structures [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(30): 36558–36573. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c09959.
HE Yu-chun, WANG Ling-xiao, WU Ting-ni, et al. Facile fabrication of hierarchical textures for substrate-independent and durable superhydrophobic surfaces [J]. Nanoscale, 2022, 14(26): 9392–9400. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D2NR02157A.
HUANG Qiao-qiao, YIN Kai, WANG Ling-xiao, et al. Femtosecond laser-scribed superhydrophilic/superhydrophobic self-splitting patterns for one droplet multi-detection [J]. Nanoscale, 2023, 15(26): 11247–11254. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D3NR01395B.
YIN Kai, WU Zhi-peng, WU Jun-rui, et al. Solar-driven thermal-wind synergistic effect on laser-textured superhydrophilic copper foam architectures for ultrahigh efficient vapor generation [J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2021, 118(21): 211905. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0050623.
PEI Jia-qing, YIN Kai, WU Ting-ni, et al. Multifunctional polyimide-based femtosecond laser micro/nanostructured films with triple Janus properties [J]. Nanoscale, 2023, 15(38): 15708–15716. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D3NR03701K.
WU Ting-ni, WU Zhi-peng, HE Yu-chun, et al. Femtosecond laser textured porous nanowire structured glass for enhanced thermal imaging [J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2022, 20(3): 033801. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3788/col202220.033801.
ZHANG Ya-chao, HU Yan-lei, XU Bing, et al. Robust underwater air layer retention and restoration on Salvinia-inspired self-grown heterogeneous architectures [J]. ACS Nano, 2022, 16(2): 2730–2740. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c09669.
MESHRAM T, YAN Ji-wang. Formation of laser-induced periodic surface structures on reaction-bonded silicon carbide by femtosecond pulsed laser irradiation [J]. Nanomanufacturing and Metrology, 2023, 6(1): 4. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41871-023-00184-8.
ZHANG Dong-shi, WU Liang-chun, UEKI M, et al. Femtosecond laser shockwave peening ablation in liquids for hierarchical micro/nanostructuring of brittle silicon and its biological application [J]. International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing, 2020, 2(4): 045001. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/2631-7990/abb5f3.
LUO Fang-fang, LIU Peng, QIU Tie-cheng, et al. Effects of femtosecond laser micropatterning on the surface properties and cellular response of biomedical tantalum-blended composites [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2022, 29(10): 3376–3384. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-022-5155-x.
CHAO Jia-qi, CHEN Fa-ze, XIA Lei, et al. Laser ablation and chemical oxidation synergistically induced micro/nano re-entrant structures for super-oleophobic surface with cassie state [J]. Nanomanufacturing and Metrology, 2023, 6(1): 18. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41871-023-00190-w.
SUN Ke, TAN De-zhi, FANG Xin-yuan, et al. Three-dimensional direct lithography of stable perovskite nanocrystals in glass [J]. Science, 2022, 375(6578): 307–310. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abj2691.
CHEN Jian-qiang, XIE Xiao-zhu, PENG Qing-fa, et al. Effect of surface roughness on femtosecond laser ablation of 4H-SiC substrates [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2022, 29(10): 3294–3303. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-022-5136-0.
GONG Lu, YANG Wen-shuai, SUN Yong-xiang, et al. Fabricating tunable superhydrophobic surfaces enabled by surface-initiated emulsion polymerization in water [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(18): 2214947. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202214947.
RANJAN D, ZOU An, MAROO S C. Durable and regenerative superhydrophobic surface using porous nanochannels [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 455: 140527. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.140527.
TIAN Wang, LI Chao, LIU Kong, et al. Fabrication of transferable and micro/nanostructured superhydrophobic surfaces using demolding and iCVD processes [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(1): 2368–2375. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c17613.
SONG Jun-yu, SHI Rui-xin, BAI Xiao-li, et al. An overview of surface with controllable wettability for microfluidic system, intelligent cleaning, water harvesting, and surface protection [J]. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials, 2022, 6(1): 22. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00603-2.
MA Chuan-long, NIKIFOROV A, HEGEMANN D, et al. Plasma-controlled surface wettability: Recent advances and future applications [J]. International Materials Reviews, 2023, 68(1): 82–119. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/09506608.2022.2047420.
CAI Bin, GUI Zhen-zhen, GUO Tao, et al. Fabrication of self-recovering superhydrophobic Cu-CNTs composite coatings via co-electrodeposition: Wettability transition is due to spontaneous adsorption of airborne hydrocarbons [J]. Colloid and Interface Science Communications, 2022, 46: 100524. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colcom.2021.100524.
ZHAO Wei-wei, JIANG Ye, YU Wen-jie, et al. Wettability controlled surface for energy conversion [J]. Small, 2022, 18(31): e2202906. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202202906.
TAN Yao, YANG Jin-long, LI Yong, et al. Liquid-pressure-guided superhydrophobic surfaces with adaptive adhesion and stability [J]. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(30): e2202167. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202202167.
CHEN Wei-yin, WANG W, LUONG D X, et al. Robust superhydrophobic surfaces via the sand-In method [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(30): 35053–35063. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c05076
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YIN Kai provided the concept and discussed the results. WENG Wei-xuan and DENG Qin-wen designed and conducted the experiment, edited the manuscript. YANG Peng-yu designed the experiment, discussed the results.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
WENG Wei-xuan, DENG Qin-wen, YANG Peng-yu, and YIN Kai declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(2023YFB4604200) supported by the National Key R&D Program of China; Projects(52222513, 52075557) supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2021JJ20067) supported by Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China; Project(2021RC3011) supported by Science and Technology Innovation Program of Hunan Province, China; Project(2023CXQD019) supported by Central South University Innovation-Driven Research Programme, China; Project(ZZYJKT2023-12) supported by State Key Laboratory of Precision Manufacturing for Extreme Service Performance, Central South University, China; Project(IMETKF2024018) supported by the State Key Laboratory of Intelligent Manufacturing Equipment and Technology, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weng, Wx., Deng, Qw., Yang, Py. et al. Femtosecond laser-chemical hybrid processing for achieving substrate-independent superhydrophobic surfaces. J. Cent. South Univ. 31, 1–10 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-023-5527-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-023-5527-x