Abstract
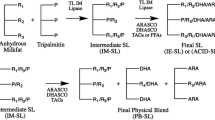
Structured lipids (SLs) containing palmitic, oleic, and docosahexaenoic acids for possible use in infant formulas were synthesized by enzymatic acidolysis reactions. The substrates used were tripalmitin, extra virgin olive oil free fatty acids (EVOOFFA), and docosahexaenoic acid single cell oil free fatty acids (DHASCOFFA) in 1:1:1, 1:2:1, 1:3:2, 1:4:2, and 1:5:1 molar ratios. Reactions were carried out at 65 °C for 24 h using Lipozyme® TL IM lipase. The products were analyzed for total and positional fatty acids by GC-FID, triacylglycerol (TAG) molecular species by HPLC-ELSD, and thermal behavior by DSC. The SLs, SL132, SL142, and SL151 had desirable fatty acid distribution for infant formula use with nearly 60 mol% palmitic acid at the sn-2 position and oleic acid predominantly at the sn-1,3 positions. The total DHA content of SL132, SL142, and SL151 were 7.54, 6.72, and 5.89 mol%, respectively. The major TAG molecular species in the SLs were PPP, OPO, and PPO. The melting completion temperature of SL132 was 37.1, 35.2 °C in SL142, and 32.9 °C in SL151. The SLs synthesized in this study have potential use in infant formulas.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jensen RG (1999) Lipids in human milk. Lipids 34:1243–1271
Hamosh M (1990) Lingual and gastric lipases. Nutr 6:421–428
Picciano MF (1998) Human milk: nutritional aspects of a dynamic food. Biol Neonates 74:84–93
Agostoni C (2008) Role of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in the first year of life. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 47:S41–S44
Zock PL, Gerritsen J, Katan MB (1996) Partial conservation of the sn-2 position of dietary triglycerides in fasting plasma lipids in humans. Eur J Clin Invest 26:141–150
Teichert SA, Akoh CC (2011) Modifications of stearidonic acid soybean oil by enzymatic acidolysis for the production of human milk fat analogues. J Agric Food Chem 59:13300–13310
Turan D, Yeşilçubuk NS, Akoh CC (2012) Production of human milk fat analogue containing docosahexaenoic and arachidonic acids. J Agric Food Chem 60:4402–4407
Nagachinta S, Akoh CC (2012) Enrichment of palm olein with long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids by enzymatic acidolysis. LWT-Food Sci Technol 46:29–35
Sørensen AM, Xu X, Zhang L, Kristensen JB, Jacobsen C (2010) Human milk fat substitute from butterfat: production by enzymatic interesterification and evaluation of oxidative stability. J Am Oil Chem Soc 87:185–194
Official Methods and Recommended Practices of the American Oil Chemists’ Society (2011) Cd 3a-94, 6th edn. 2nd printing AOCS, Champaign, IL
Wanasundara UN, Shahidi F (1999) Concentration of omega3-polyunsaturated fatty acids of seal blubber oil by urea complexation: optimization of reaction conditions. Food Chem 65:41–49
Lee KT, Akoh CC (1998) Characterization of enzymatically synthesized structured lipids containing eicosapentaenoic, docosahexaenoic, and caprylic acids. J Am Oil Chem Soc 75:495–499
Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International (2012) Method 996.01, 19th edn. AOAC Intl, Gaitherburg, MD
Official Methods and Recommended Practices of the American Oil Chemists’ Society (2011) Ch 3-91, 6th edn. 2nd printing AOCS, Champaign, IL
Official Methods and Recommended Practices of the American Oil Chemists’ Society (2011) Cj 1-94, 6th edn. 2nd printing AOCS, Champaign, IL
López-López A, López-Sabater MC, Campoy-Folgoso C, Rivero-Urgell M, Castellote-Bargalló AI (2002) Fatty acid and sn-2 fatty acid composition in human milk from Granada (Spain) and in infant formulas. Eur J Clin Nutr 56:1242–1254
Kennedy K, Fewtrell MS, Morely R, Abbott R, Quinlan PT, Wells JC, Bindels JG, Lucas A (1999) Double-blind, randomized trial of a synthetic triacylglycerol in formula-fed term infants: effects on stool biochemistry, stool characteristics, and bone mineralization. Am J Clin Nutr 70:920–927
Yang T, Fruekilde MB, Xu X (2005) Suppression of acyl migration in enzymatic production of structured lipids through temperature programming. Food Chem 92:101–107
Mu H, Kurvinen JP, Kallio H, Xu X, Høy CE (2001) Quantitation of acyl migration during lipase-catalyzed acidolysis and of the regioisomers of structured triacylglycerols formed. J Am Oil Chem Soc 78:959–964
Kim BH, Akoh CC (2005) Modeling of lipase-catalyzed acidolysis of sesame oil and caprylic acid by response surface methodology: optimization of reaction conditions by considering both acyl incorporation and migration. J Agric Food Chem 53:8033–8037
Xu X, Skands ARH, Høy CE, Mu H, Balchen S, Adler-Nissen J (1998) Production of specific-structured lipids by enzymatic interesterification: elucidation of acyl migration by response surface design. J Am Oil Chem Soc 75:1179–1186
Mu H, Høy CE (2004) The digestion of dietary triacyglycerols: review. Prog Lipid Res 43:105–133
Morera S, Castellote AI, Jauregui O, Casals I, López-Sabater MC (2003) Triacylglycerol markers of mature human milk. Eur J Clin Nutr 57:1621–1626
Acknowledgments
Research was supported by a grant from King Abdulaziz University (KAU) and KAU’s Vice President (Prof. Abdulrahaman O. Alyoubi).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
About this article
Cite this article
Pande, G., Sabir, J.S.M., Baeshen, N.A. et al. Synthesis of Infant Formula Fat Analogs Enriched with DHA from Extra Virgin Olive Oil and Tripalmitin. J Am Oil Chem Soc 90, 1311–1318 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-013-2281-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-013-2281-5