Abstract
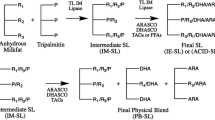
A structured lipid (SL) with a substantial amount of palmitic acid at the sn-2 position and enriched with capric acid (C), was produced in two enzymatic interesterification stages by using immobilized lipase, Lipozyme® TL IM (Novozymes North America Inc., Franklinton, NC, USA). The substrates for the reactions were high melting point palm stearin, high oleic sunflower oil and tricaprin. The SL was characterized for total and positional fatty acid profiles, triacylglycerol (TAG) molecular species, free fatty acid content, melting and crystallization profiles. The final SL contained 20.13 mol% of total palmitic acid, of which nearly 40 % was located at the sn-2 position. The total capric acid content was 21.22 mol%, mostly at the sn-1 and sn-3 positions. The predominant TAGs in the SL were oleic–palmitic–oleic, POP and CLC. The melting completion and crystallization onset temperatures of the SL were 27.7 and 6.1 °C, respectively. The yield for the overall reaction was 90 wt%. This SL might be totally or partially used in commercial fat blends for infant formula.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jensen RG (1989) The lipids of human milk. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Wells JCK (1996) Nutritional considerations in infant formula design. Semin Neonatal 1:19–26
Scott CE (2010) Structured lipid: a functional and fundamental ingredient to more closely matches infant formula to breast milk. Nutrafoods 9:7–13
Innis SM (1991) Essential fatty acids in growth and development. Prog Lipid Res 30:39–103
Bracco U (1994) Effect of triglyceride structure on fat absorption. Am J Clin Nutr 60:1002S–1009S
Lucas A, Quinlan P, Abrams S, Ryan S, Meah S, Lucas PJ (1997) Randomised controlled trial of a synthetic triglyceride milk formula for preterm infants. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal 77:F178–F184
Tomarelli RM, Meyer BJ, Weaber JR, Bernhart FW (1968) Effect of positional distribution on the absorption of the fatty acids of human milk and infant formulas. J Nutr 95:583–590
Høy CE, Xu X (2001) Structured triacylglycerols. In: Gunstone FD (ed) Structured and modified lipids. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 209–239
Akoh CC, Kim BH (2008) Structured Lipids. In: Akoh CC, Min DB (eds) Food lipids. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 841–872
Zock PL, Gerritsen J, Katan MB (1996) Partial conservation of the sn-2 position of dietary triglycerides in fasting plasma lipids in humans. Eur J Clin Investig 26:141–150
Zou X, Huang J, Jin Q, Guo Z, Liu Y, Cheong L, Xu X, Wang X (2013) Characterization and oxidative stability of human milk fat substitutes enzymatically produced from palm stearin. J Am Oil Chem Soc 91:481–495
Wang X, Huang J, Jin Q, Song Z, Liu Y, Zou X (2012) Lipase-catalyzed synthesis of human milk fat substitutes from palm stearin in a continuous packed bed reactor. J Am Oil Chem Soc 89:1463–1472
Teichert SA, Akoh CC (2011) Modifications of stearidonic acid soybean oil by enzymatic acidolysis for the production of human milk fat analogues. J Agric Food Chem 59:13300–13310
Turan D, Yeşilçubuk NS, Akoh CC (2012) Production of human milk fat analogue containing docosahexaenoic and arachidonic acids. J Agric Food Chem 60:4402–4407
Pande G, Sabir JSM, Baeshen NA, Akoh CC (2013) Enzymatic synthesis of extra virgin olive oil based infant formula fat analogues containing ARA and DHA: one-stage and two-stage syntheses. J Agric Food Chem 61:10590–10598
Pina-Rodriguez AM, Akoh CC (2009) Synthesis and characterization of a structured lipid from amaranth oil as a partial fat substitute in milk-based infant formula. J Agric Food Chem 57:6748–6756
Ifeduba EA, Akoh CC (2013) Chemoenzymatic method for producing stearidonic acid concentrates from stearidonic acid soybean oil. J Am Oil Chem Soc 90:1011–1022
Babayan VK (1988) Medium chain triglycerides. In: Babayan VK, Beare-Rogers J (eds) Dietary fat requirements in health and development. American Oil Chemists’ Society Press, Champaign, pp 73–86
Francois CA, Connor SL, Wander RS, Connor WE (1998) Acute effects of dietary fatty acids on the fatty acids of human milk. Am J Clin Nutr 67:301–308
López-López A, López-Sabater MC, Campoy-Folgoso C, Rivero-Urgell M, Castellote-Bargalló AI (2002) Fatty acid and sn-2 fatty acid composition in human milk from Granada (Spain) and in infant formulas. Eur J Clin Nutr 56:1242–1254
St-Onge MP, Mayrsohn B, O’Keeffe M, Kissileff HR, Choudhury AR, Laferrère B (2014) Impact of medium and long chain triglycerides consumption on appetite and food intake in overweight men. Eur J Clin Nutr 68:1134–1140
St-Onge MP, Ross R, Parsons WD, Jones PJ (2003) Medium-chain triglycerides increase energy expenditure and decrease adiposity in overweight men. Obes Res 11:395–402
Novozymes Biopharma DK A/S (2014) Enzymes for Biocatalysis: for smarter chemical synthesis. http://www.novozymes.com/en/solutions/biopharma/Brochures/Documents/2014-12576-01_Biocatalysis-Product-Sheet-Immobilised-Lipases-2.pdf. Accessed 20 Apr 2015
Pande G, Sabir JSM, Baeshen NA, Akoh CC (2013) Synthesis of infant formula fat analogs enriched with DHA from extra virgin olive oil and tripalmitin. J Am Oil Chem Soc 90:1311–1318
Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International (2012) Method 996.01. AOAC Int, Gaitherburg
Luddy FE, Bardford RA, Herb SF, Magidman P, Riemenschneider RW (1964) Pancreatic lipase hydrolysis of triacylglycerides as a semi-micro technique. J Am Oil Chem Soc 41:639–696
Official Methods and Recommended Practices of the American Oil Chemists’ Society (2011) Method Cj 1–94. AOCS, Champaign
Son JM, Lee KT, Akoh CC, Kim MR, Kim MJ, Lee JH (2010) Optimization of tripalmitin-rich fractionation from palm stearin by response surface methodology. J Sci Food Agric 90:1520–1526
Karupaiah T, Sundram K (2007) Effects of stereospecific positioning of fatty acids in triacylglycerol structures in native and randomized fats: a review of their nutritional implications. Nutr Metab 4:1–17
Kennedy K, Fewtrell MS, Morely R, Abbott R, Quinlan PT, Wells JC, Bindels JG, Lucas A (1999) Double-blind, randomized trial of a synthetic triacylglycerol in formula-fed term infants: effects on stool biochemistry, stool characteristics, and bone mineralization. Am J Clin Nutr 70:920–927
Yang T, Fruekilde MB, Xu X (2005) Suppression of acyl migration in enzymatic production of structured lipids through temperature programming. Food Chem 92:101–107
Xu X (2000) Production of specific-structured triacylglycerols by lipase-catalyzed reactions: a review. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 102:287–303
Xu X, Skands ARH, Høy CE, Mu H, Balchen S, Adler-Nissen J (1998) Production of specific-structured lipids by enzymatic interesterification: elucidation of acyl migration by response surface design. J Am Oil Chem Soc 75:1179–1186
Morera S, Castellote AI, Jauregui O, Casals I, López-Sabater MC (2003) Triacylglycerol markers of mature human milk. Eur J Clin Nutr 57:1621–1626
Mu H, Høy CE (2004) The digestion of dietary triacyglycerols: review. Prog Lipid Res 43:105–133
Sato K (2005) Polymorphism in fats and oils. In: Bailey’s industrial oil and fat products. Wiley, Hiroshima
Strayer D (2006) Food fats and oils. Institute of Shortening and Edible Oils, Washington DC
Bornaz S, Fanni J, Parmentier M (1994) Limit of the solid fat content modification of butter. J Am Oil Chem Soc 71:1373–1380
Malcata FX, Reyes HR, García HS, Hill CG Jr, Amundson CH (1992) Kinetics and mechanisms catalyzed by immobilized lipases. Enzyme Microb Technol 14:426–446
Briand D, Dubreucq E, Galzy P (1994) Enzymatic fatty esters synthesis in aqueous medium with lipase from Candida parapsilosis (Ashford) Langeron and Talice. Biotechnol Lett 16(813):818
Svesson I, Wehtje E, Adlercreutz P, Mattiasson B (1994) Effects of water activity on reaction rates and equilibrium positions in enzymatic esterifications. Biotechnol Bioeng 44:549–556
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Álvarez, C.A., Akoh, C.C. Enzymatic Synthesis of Infant Formula Fat Analog Enriched with Capric Acid. J Am Oil Chem Soc 92, 1003–1014 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-015-2662-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-015-2662-z