Abstract
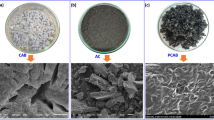
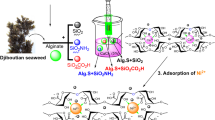
To resourcefully utilize algal biomass and effectively remove bisphenol A (BPA) from water, sodium alginate (SA) was prepared as the nitrogen-doped magnetic porous carbon material (SAC/N/Fe) with well-developed pore structure according to a one-step method using K2CO3, melamine, Fe(NO3)3·9H2O as the activator, nitrogen dopant, and magnetic precursor, respectively, in this study. The best product, SAC/N/Fe-0.2, was obtained by adjusting the mass ratio of raw materials, and its specific surface area and pore volume were 2240.65 m2 g−1 and 1.44 cm3 g−1, respectively, with a maximum adsorption capacity of 1248.23 mg g−1 for BPA at 308 K. SEM, XRD, XPS, VSM, and FT-IR characterization confirmed that the iron was successfully doped, giving the porous carbon a magnetic separation function. The adsorption process of BPA was more consistent with the Langmuir model and the proposed secondary kinetics, and the adsorption effect was stable and efficient in a wide pH range and under the interference of different metal ions. At the same time, the porous carbon was easy to separate and recover with good regeneration performance.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset used and/or analyzed during this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Chen A, Guan J, Wei X, Xie Y (2022) Efficient adsorption of BPA by alginate-based porous carbon with the preparation of synchronous activation and nitrogen doping. China Environ Sci 42(01):160–171. https://doi.org/10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.20210709.012. (in Chinese)
Chen A, Pang J, Wei X, Chen B, Xie Y (2021a) Fast one-step preparation of porous carbon with hierarchical oxygen-enriched structure from waste lignin for chloramphenicol removal. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28:27398–27410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12640-3
Chen A, Xie Y, Wei X, Chen B, Pang J (2021b) One-step preparation of sodium alginate-based porous carbon for the adsorption of Bisphenol A in water. J Chem Eng Data 66(2):1101–1109. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.0c00894
de Lima HHC, Llop MEG, Dos Santos Maniezzo R, Moisés MP, Janeiro V, Arroyo PA, Guilherme MR, Rinaldi AW (2021) Enhanced removal of bisphenol A using pine-fruit shell-derived hydrochars: adsorption mechanisms and reusability. J Hazard Mater 416:126167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126167
Do MH, Phan NH, Nguyen TD, Pham TTS, Vu TTT, Nguyen TKP (2011) Activated carbon/Fe3O4 nanoparticle composite: fabrication, methyl orange removal and regeneration by hydrogen peroxide. Chemosphere 85(8):1269–1276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.07.023
Godiya CB, Park BJ (2022) Removal of bisphenol A from wastewater by physical, chemical and biological remediation techniques. A review. Environ Chem Lett 1–37 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.04.004
Guo X, Huang Y, Yu W, Yu X, Han X, Zhai H (2020) Multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified with iron oxide and manganese dioxide (MWCNTs-Fe3O4− MnO2) as a novel adsorbent for the determination of BPA. Microchem J 157:104867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.104867
He S, Shi G, Xiao H, Sun G, Shi Y, Chen G, Dai H, Yuan B, Chen X, Yang X (2021) Self S-doping activated carbon derived from lignin-based pitch for removal of gaseous benzene. Chem Eng J 410:128286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.128286
Hernández-Abreu AB, Álvarez-Torrellas S, Águeda VI, Larriba M, Delgado JA, Calvo PA, García J (2020) Enhanced removal of the endocrine disruptor compound bisphenol A by adsorption onto green-carbon materials. Effect of real effluents on the adsorption process. J Environ Manag 266:110604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110604
Im J, Loffler FE (2016) Fate of bisphenol A in terrestrial and aquatic environments. Environ Sci Technol 50(16):8403–8416. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b00877
Inagaki M, Toyoda M, Soneda Y, Morishita T (2018) Nitrogen-doped carbon materials. Carbon N Y 132:104–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2018.02.024
Jeon IY, Noh HJ, Baek JB (2020) Nitrogen-doped carbon nanomaterials: synthesis, Characteristics and Applications. Chem-An Asian J 15(15):2282–2293. https://doi.org/10.1002/asia.201901318
Jin Y, Zhang B, Chen G, Chen H, Tang S (2022) Combining biological and chemical methods to disassemble of cellulose from corn straw for the preparation of porous carbons with enhanced adsorption performance. Int J Biol Macromol 209:315–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.04.033
Kong X, Wang C, Zheng H, Geng Z, Bao J, Zeng J (2021) Enhance the activity of multi-carbon products for Cu via P doping towards CO 2 reduction. Sci China Chem 64:1096–1102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-020-9934-0
Kwak D, Han S, Lee Y, Park H, Choi I, Ma K, Kim M, Kim S, Kim D, Sohn J (2017) Fe/N/S-doped mesoporous carbon nanostructures as electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction in acid medium. Appl Catal B 203:889–898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.10.084
Li Z, Li G, Jiang L, Li J, Sun G, Xia C, Li F (2015) Ionic liquids as precursors for efficient mesoporous iron-nitrogen-doped oxygen reduction electrocatalysts. Angew Chem Int Ed 54(5):1494–1498. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201409579
Liang L, Guan X, Shi Z, Li J, Wu Y, Tratnyek PG (2014) Coupled effects of aging and weak magnetic fields on sequestration of selenite by zero-valent iron. Environ Sci Technol 48(11):6326–6334. https://doi.org/10.1021/es500958b
Liu L, Lu Y, Qiu D, Wang D, Ding Y, Wang G, Liang Z, Shen Z, Li A, Chen X (2022) Sodium alginate-derived porous carbon: self-template carbonization mechanism and application in capacitive energy storage. J Colloid Interface Sci 620:284–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2022.04.022
Liu S, Zhao C, Wang Z, Ding H, Deng H, Yang G, Li J, Zheng H (2020) Urea-assisted one-step fabrication of a novel nitrogen-doped carbon fiber aerogel from cotton as metal-free catalyst in peroxymonosulfate activation for efficient degradation of carbamazepine. Chem Eng J 386:124015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124015
Lota G, Lota K, Frackowiak E (2007) Nanotubes based composites rich in nitrogen for supercapacitor application. Electrochem Commun 9(7):1828–1832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2007.04.015
Lou Z, Li R, Liu J, Wang Q, Zhang Y, Li Y (2021) Used dye adsorbent derived N-doped magnetic carbon foam with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance. J Alloys Compd 854:157286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.157286
Mpatani FM, Han R, Aryee AA, Kani AN, Li Z, Qu L (2021) Adsorption performance of modified agricultural waste materials for removal of emerging micro-contaminant bisphenol A: a comprehensive review. Sci Total Environ 780:146629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146629
Nafi’Shehab Z, Jamil NR, Aris AZ (2020) Modelling the fate and transport of colloidal particles in association with BPA in river water. J Environ Manag 274:111141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111141
Naveira C, Rodrigues N, Santos FS, Santos LN, Neves RA (2021) Acute toxicity of Bisphenol A (BPA) to tropical marine and estuarine species from different trophic groups. Environ Pollut 268:115911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115911
Park JM, Jhung SH (2021) Remarkable adsorbent for removal of bisphenol A and S from water: porous carbon derived from melamine/polyaniline. Chemosphere 268:129342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129342
Park JM, Woo HC, Jhung SH (2021) Effective CO2 adsorption at low pressure over nitrogen-enriched porous carbons, derived from melamine-loaded polyaniline. Chem Eng J 412:128641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.128641
Shao P, Pei J, Tang H, Yu S, Yang L, Shi H, Yu K, Zhang K, Luo X (2021) Defect-rich porous carbon with anti-interference capability for adsorption of bisphenol A via long-range hydrophobic interaction synergized with short-range dispersion force. J Hazard Mater 403:123705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123705
Shi W, Wang H, Yan J, Shan L, Quan G, Pan X, Cui L (2022) Wheat straw derived biochar with hierarchically porous structure for bisphenol A removal: preparation, characterization, and adsorption properties. Sep Purif Technol 289:120796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.120796
Su Y, Li S, Jiang G, Zheng Z, Wang C, Zhao S, Cui D, Liu Y, Zhang B, Zhang Z (2021) Synergic removal of tetracycline using hydrophilic three-dimensional nitrogen-doped porous carbon embedded with copper oxide nanoparticles by coupling adsorption and photocatalytic oxidation processes. J Colloid Interface Sci 581:350–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.07.071
Sueptitz R, Tschulik K, Uhlemann M, Schultz L, Gebert A (2011) Effect of high gradient magnetic fields on the anodic behaviour and localized corrosion of iron in sulphuric acid solutions. Corros Sci 53(10):3222–3230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2011.05.070
Sun J, Zhang J, Shang M, Zhang M, Zhao X, Liu S, Liu X, Liu S, Yi X (2023) N, O co-doped carbon aerogel derived from sodium alginate/melamine composite for all-solid-state supercapacitor. Appl Surf Sci 608:155109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.155109
Tian Y, Zhou H (2022) A novel nitrogen-doped porous carbon derived from black liquor for efficient removal of Cr (VI) and tetracycline: comparison with lignin porous carbon. J Clean Prod 333:130106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.130106
Wang H, Shan L, Lv Q, Cai S, Quan G, Yan J (2020) Production of hierarchically porous carbon from natural biomass waste for efficient organic contaminants adsorption. J Clean Prod 263:121352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121352
Wang X, Guan Y, Zhang R, Zhou P, Song Z, Wang M, Wang L, Zhang Q (2021) Facile synthesis of cobalt nanoparticles embedded in a rod-like porous carbon matrix with excellent electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Ceram Int 47(1):643–653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.08.172
Wei D, Li J, Chen Z, Liang L, Ma J, Wei M, Ai Y, Wang X (2020) Understanding bisphenol-A adsorption in magnetic modified covalent organic frameworks: experiments coupled with DFT calculations. J Mol Liq 301:112431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.112431
Wu P, Yu S, Feng M, Liu H, Liu S, Fu J (2021) Controllable synthesis of the polymorphic porous carbon with N-doping/Ni magnetic nanohybrids for high performance supercapacitor and environment applications. Appl Surf Sci 567:150875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.150875
Xiao W, Jiang X, Liu X, Zhou W, Garba ZN, Lawan I, Wang L, Yuan Z (2021) Adsorption of organic dyes from wastewater by metal-doped porous carbon materials. J Clean Prod 284:124773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124773
Yang S, Zhang X, Tang J, Zhang A (2022) Efficient degradation of bisphenol A by the UV-enhanced nano zero-valent iron-activated hydrogen peroxide advanced oxidation system. J Environ Chem Eng 10(6):108806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.108806
Yu F, Cao T, Ma H, Yang J, Jing L (2022) Enhancing the yield of H2O2 and bisphenol A degradation via a synergistic effect of photoelectric co-catalysis by using NPC/C3N4 electrode. Int J Hydrog Energy 47(38):16873–16886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.03.180
Zhang G, Bai Q, Wang X, Li C, Uyama H, Shen Y (2023) Preparation and mechanism research of walnut shell-based hierarchical porous carbon for supercapacitor. Bull Chem Soc Jpn. https://doi.org/10.1246/bcsj.20220314
Zhao J, Lai H, Lyu Z, Jiang Y, Xie K, Wang X, Wu Q, Yang L, Jin Z, Ma Y (2015) Hydrophilic hierarchical nitrogen-doped carbon nanocages for ultrahigh supercapacitive performance. Adv Mater 27(23):3541–3545. https://doi.org/10.1002/asia.201901318
Zhao Y, Wei M, Zhu Z, Zhang J, Xiao L, Hou L (2020) Facile preparation of NO codoped hierarchically porous carbon from alginate particles for high performance supercapacitor. J Colloid Interface Sci 563:414–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.12.027
Zhou B, Liu L, Cai P, Zeng G, Li X, Wen Z, Chen L (2017) Ferrocene-based porous organic polymer derived high-performance electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction. J Mater Chem a Mater 5(42):22163–22169. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TA06515A
Zhou T, Ma R, Zhang T, Li Z, Yang M, Liu Q, Zhu Y, Wang J (2019) Increased activity of nitrogen-doped graphene-like carbon sheets modified by iron doping for oxygen reduction. J Colloid Interface Sci 536:42–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.10.021
Zhu D, Shao J, Li Z, Yang H, Zhang S, Chen H (2021) Nano nickel embedded in N-doped CNTs-supported porous biochar for adsorption-reduction of hexavalent chromium. J Hazard Mater 416:125693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125693
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: Yaping Xie, Guoxing Du, and Linguo Lu. Acquisition of data: Yaping Xie, Guoxing Du, Jiaju Pang, and Linghan Kong. Analysis and interpretation of the data: Yaping Xie, Guoxing Du, and Jiaju Pang. Writing of the manuscript: Yaping Xie, Guoxing Du, and Linghan Kong. Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: Yaping Xie, Guoxing Du, and Linguo Lu.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• A one-step process can rapidly prepare magnetic N porous carbon.
• SAC/N/Fe-0.2 has a high specific surface area (2240.65 m2 g−1) and pore volume (1.44 cm3 g−1).
• SAC/N/Fe-0.2 had a super high adsorption capacity of 1248.23 mg g−1 for bisphenol A at 308 K.
• SAC/N/Fe-0.2 has great application potential due to its strong anti-interference ability and magnetic separation ability.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Y., Du, G., Pang, J. et al. One-step preparation of magnetic N-doped sodium alginate–based porous carbon and efficient adsorption of bisphenol A. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 99842–99854 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29346-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29346-3