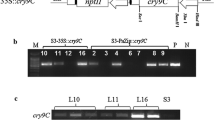
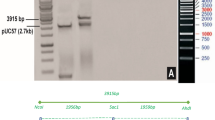
Abstract
Wide planting of transgenic Bt cotton in China since 1997 to control cotton bollworm (Helicoverpa armigera) has increased yields and decreased insecticide use, but the evolution of resistance to Bt cotton by H. armigera remains a challenge. Toward developing a new generation of insect-resistant transgenic crops, a chimeric protein of Vip3Aa1 and Vip3Ac1, named Vip3AcAa, having a broader insecticidal spectrum, was specifically created previously in our laboratory. In this study, we investigated cross resistance and interactions between Vip3AcAa and Cry1Ac with three H. armigera strains, one that is susceptible and two that are Cry1Ac-resistant, to determine if Vip3AcAa is a good candidate for development the pyramid cotton with Cry1Ac toxin. Our results showed that evolution of insect resistance to Cry1Ac toxin did not influence the sensitivity of Cry1Ac-resistant strains to Vip3AcAa. For the strains examined, observed mortality was equivalent to the expected mortality for all the combinations of Vip3AcAa and Cry1Ac tested, reflecting independent activity between these two toxins. When this chimeric vip3AcAa gene and the cry1Ac gene were introduced into cotton, mortality rates of Cry1Ac resistant H. armigera larvae strains that fed on this new cotton increased significantly compared with larvae fed on non-Bt cotton and cotton producing only Cry1Ac. These results suggest that the Vip3AcAa protein is an excellent option for a “pyramid” strategy for pest resistance management in China.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelkefi-Mesrati L, Boukedi H, Dammak-Karray M, Sellami-Boudawara T, Jaoua S, Tounsi S (2011) Study of the Bacillus thuringiensis Vip3Aa16 histopathological effects and determination of its putative binding proteins in the midgut of Spodoptera littoralis. J Invertebr Pathol 106:250–254
An JJ, Gao YL, Wu KM, Gould F, Gao JH, Shen ZC, Lei CL (2010) Vip3Aa tolerance response of Helicoverpa armigera populations from a Cry1Ac cotton planting region. J Econ Entomol 103:2169–2173
An J, Gao Y, Lei C, Gould F, Wu K (2014) Monitoring cotton bollworm resistance to Cry1Ac in two counties of northern China during 2009–2013. Pest Manag Sci 71:377–382
Barkhade UP, Thakare AS (2010) Protease mediated resistance mechanism to Cry1C and Vip3A in Spodoptera litura. Egypt Acad J Biol Sci 3:43–50
Baxter SW, Badenespérez FR, Morrison A, Vogel H, Crickmore N, Kain W, Wang P, Heckel DG, Jiggins CD (2011) Parallel evolution of Bacillus thuringiensis toxin resistance in lepidoptera. Genetics 189:675–679
Berg JVD, Hilbeck A, Bohn T (2013) Pest resistance to Cry1Ab Bt maize: field resistance, contributing factors and lessons from South Africa. Crop Prot 54:154–160
Bergamasco VB, Mendes DRP, Fernandes OA, Desidério JA, Lemos MVF (2013) Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ia10 and Vip3Aa protein interactions and their toxicity in Spodoptera spp. (Lepidoptera). J Invertebr Pathol 112:152–158
Bernardi O, Amado D, Sousa RS, Segatti F, Fatoretto J, Burd AD, Omoto C (2014) Baseline Susceptibility and Monitoring of Brazilian Populations of Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and Diatraea saccharalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) to Vip3Aa20 Insecticidal Protein. J Econ Entomol 107:781–790
Bird LJ, Akhurst RJ (2007) Effects of host plant species on fitness costs of Bt resistance in Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Biol Control 40:196–203
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brévault T, Heuberger S, Zhang M, Ellers-Kirk C, Ni X, Masson L, Li X, Tabashnik BE, Carrière Y (2013) Potential shortfall of pyramided transgenic cotton for insect resistance management. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:5806–5811
Cao G, Zhang L, Liang G, Li X, Wu K (2013) Involvement of nonbinding site proteinases in the development of resistance of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) to Cry1Ac. J Econ Entomol 106:2514–2521
Carrière Y, Crickmore N, Tabashnik BE (2015) Optimizing pyramided transgenic Bt crops for sustainable pest management. Nature Biotechnol 33:161–168
Carrière Y, Fabrick JA, Tabashnik BE (2016) Can pyramids and seed mixtures delay resistance to Bt crops? Trends Biotechnol 34:291–302
Chakroun M, Banyuls N, Bel Y, Escriche B, Ferré J (2016a) Bacterial vegetative insecticidal proteins (Vip) from entomopathogenic bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol R 80:329–350
Chakroun M, Banyuls N, Walsh T, Downes S, James B, Ferré J (2016b) Characterization of the resistance to Vip3Aa in Helicoverpa armigera from Australia and the role of midgut processing and receptor binding. Sci Rep 6:24311. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep24311
Chang X, Liu GG, He KL, Shen ZC, Peng YF, Ye GY (2013) Efficacy evaluation of two transgenic maize events expressing fused proteins to Cry1Ab-susceptible and -resistant Ostrinia Fumacalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). J Econ Entomol 106:2548–2556
Chen W, Liu C, Xiao Y, Zhang D, Li X, Tabashnik BE, Wu K (2015) A toxin-binding alkaline phosphatase fragment synergizes Bt toxin Cry1Ac against susceptible and resistant Helicoverpa armigera. PLoS ONE 10:e0126288
Comas C, Lumbierres B, Pons X, Albajes R (2014) No effects of Bacillus thuringiensis maize on nontarget organisms in the field in southern Europe: a meta-analysis of 26 arthropod taxa. Transgenic Res 23:135–143
Dong F, Shi R, Zhang S, Zhan T, Wu G, Shen J, Liu Z (2012) Fusing the vegetative insecticidal protein Vip3Aa7 and the N terminus of Cry9Ca improves toxicity against Plutella xylostella larvae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96:921–929
Estruch JJ, Warren GW, Mullins MA, Nye GJ, Craig JA, Kozie MG, Koziel MG (1996) Vip3A, a novel Bacillus thuringiensis vegetative insecticidal protein with a wide spectrum of activities against lepidopteran insects. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:5389–5394
Fang J, Xu X, Wang P, Zhao JZ, Shelton AM, Cheng J, Feng MG, Shen Z (2007) Characterization of chimeric Bacillus thuringiensis Vip3 toxins. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:956–961
Gahan LJ, Pauchet Y, Vogel H, Heckel DG (2010) An ABC transporter mutation is correlated with Insect resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac toxin. PLoS Genet 6:e1001248. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1001248
Gao Y, Wu K, Gould F, Shen Z (2009) Cry2Ab tolerance response of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) populations from Cry1Ac cotton planting region. J Econ Entomol 102:1217–1223
Gassmann AJ, Petzold-Maxwell JL, Clifton EH, Dunbar MW, Hoffmann AM, Ingber DA, Keweshan RS (2014) Field-evolved resistance by western corn rootworm to multiple Bacillus thuringiensis toxins in transgenic maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:5141–5146
Gayen S, Hossain MA, Sen SK (2012) Identification of the bioactive core component of the insecticidal Vip3A toxin peptide of Bacillus thuringiensis. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 21:128–135
Hamadou-Charfi DB, Boukedi H, Abdelkefi-Mesrati L, Tounsi S, Jaoua S (2013) Agrotis segetum midgut putative receptor of Bacillus thuringiensis vegetative insecticidal protein Vip3Aa16 differs from that of Cry1Ac toxin. J Invertebr Pathol 114:139–143
James C (2015) Global status of commercialized biotech/GM Crops: 2015 ISAAA Briefs 51 Ithaca. International Service for the Acquisition of Agri-biotech Applications, NY
Janmaat AF, Myers JH (2005) The cost of resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis varies with the host plant of Trichoplusia ni. P Roy Soc B-Bio Sci 272:1031–1038
Jin L, Zhang H, Lu Y, Yang Y, Wu K, Tabashnik BE, Wu Y (2015) Large-scale test of the natural refuge strategy for delaying insect resistance to transgenic Bt crops. Nat Biotechnol 33:169–174
Lee MK, Walters FS, Hart H, Palekar N, Chen JS (2003) The mode of action of the Bacillus thuringiensis vegetative insecticidal protein Vip3A differs from that of Cry1Ab δ-endotoxin. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:4648–4657
Lee MK, Miles P, Chen JS (2006) Brush border membrane binding properties of Bacillus thuringiensis Vip3A toxin to Heliothis virescens and Helicoverpa zea midguts. Biochem Bioph Res Co 339:1043–1047
Lemes AR, Davolos CC, Legori PC, Fernandes OA, Ferré J, Lemos MV, Desiderio JA (2014) Synergism and Antagonism between Bacillus thuringiensis Vip3A and Cry1 Proteins in Heliothis virescens, Diatraea saccharalis and Spodoptera frugiperda. PLoS ONE 9:e107196
Liang G, Tan W, Guo Y (1999) An improvement in the technique of artificial rearing cotton bollworm. Plant Protect 25:15–17
Liu F, Xu Z, Chang J, Chen J, Meng F, Zhu YC, Shen J (2008) Resistance allele frequency to Bt cotton in field populations of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in China. J Econ Entomol 101:933–943
Liu JG, Yang AZ, Shen XH, Hua BG, Shi GL (2011) Specific binding of activated Vip3Aa10 to Helicoverpa armigera brush border membrane vesicles results in pore formation. J Invertebr Pathol 108:92–97
Liu C, Xiao Y, Li X, Oppert B, Tabashnik BE, Wu K (2014) Cis-mediated down-regulation of a trypsin gene associated with Bt resistance in cotton bollworm. Sci Rep 4:7219
Lu Y, Wu K, Jiang Y, Guo Y, Desneux N (2012) Widespread adoption of Bt cotton and insecticide decrease promotes biocontrol services. Nature 487:362–365
Mahon RJ, Downes SJ, James B (2012) Vip3A resistance alleles exist at high levels in Australian targets before release of cotton expressing this toxin. PLoS ONE 7:e39192
Mendelsohn M, Kough J, Vaituzis Z, Matthews K (2003) Are Bt crops safe? Nat Biotechnol 21:1003–1009
Mesrati LA, Tounsi S, Jaoua S (2005) Characterization of a novel Vip3-type gene from Bacillus thuringiensis and evidence of its presence on a large plasmid. FEMS MicrobiolLett 244:353–358
Nicolia A, Manzo A, Veronesi F, Rosellini D (2014) An overview of the last 10 years of genetically engineered crop safety research. Crit Rev Biotechnol 34:77–88
Palma L, Muñoz D, Berry C, Murillo J, Caballero P (2014) Bacillus thuringiensis toxins: an overview of their biocidal activity. Toxins 6:3296–3325
Pickett BR, Gulzar A, Ferré J, Wright DJ (2017) Laboratory selection and characterization of resistance to the Bacillus thuringiensis Vip3Aa toxin in Heliothis virescens (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Appl Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03506-16
Raymond B, Sayyed AH, Wright DJ (2007) Host plant and population determine the fitness costs of resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis. Biol Letters 3:82–85
Ruiz de Escudero I, Banyuls N, Bel Y, Maeztu M, Escriche B, Muñoz D, Caballero P, Ferré J (2014) A screening of five Bacillus thuringiensis Vip3A proteins for their activity against lepidopteran pests. J Invertebr Pathol 117:51–55
Russell RM, Robertson JL, Savin NE (1977) POLO: a new computer program for probit analysis. Bull Entomol Soc Am 23:209–213
Sanahuja G, Banakar R, Twyman RM, Capell T, Christou P (2011) Bacillus thuringiensis: a century of research, development and commercial applications. Plant Biotechnol J 9:283–300
Sena JA, Hernández-Rodríguez CS, Ferré J (2009) Interaction of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1 and Vip3A proteins with Spodoptera frugiperda midgut binding sites. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:2236–2237
Swiatkiewicz S, Swiatkiewicz M, Arczewska-Wlosek A, Jozefiak D (2014) Genetically modified feeds and their effect on the metabolic parameters of food-producing animals: a review of recent studies. Anim Feed Sci Tech 198:1–19
Tabashnik BE, Brevault T, Carriere Y (2013a) Insect resistance to Bt crops: lessons from the first billion acres. Nat Biotechnol 31:510–521
Tabashnik BE, Fabrick JA, Unnithan GC, Yelich AJ, Masson L, Zhang J, Bravo A, Soberón M (2013b) Efficacy of genetically modified Bt toxins alone and in combinations against pink bollworm resistant to Cry1Ac and Cry2Ab. PLoS ONE 8:e80496
Wang R, Tetreau G, Wang P (2016) Effect of crop plants on fitness costs associated with resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxins Cry1Ac and Cry2Ab in cabbage loopers. Sci Rep 6:20959
Wei J, Guo Y, Liang G, Wu K, Zhang J, Tabashnik BE, Li X (2014) Cross-resistance and interactions between Bt toxins Cry1Ac and Cry2Ab against the cotton bollworm. Sci Rep 5:7714
Wei Y, Wu S, Yang Y, Wu Y (2017) Baseline susceptibility of field populations of Helicoverpa armigera to Bacillus thuringiensis Vip3Aa toxin and lack of cross-resistance between Vip3Aa and Cry toxins. Toxins 9:127
Welch KL, Unnithan GC, Degain BA, Wei J, Zhang J, Li X, Tabashnik BE, Carrière Y (2015) Cross-resistance to toxins used in pyramided Bt crops and resistance to Bt sprays in Helicoverpa zea. J Invertebr Pathol 132:149–156
Wolfersberger MG, Luethy P, Maurer A, Parenti P, Sacchi VF, Giordana B, Hanozet GM (1987) Preparation and partial characterization of amino acid transporting brush border membrane vesicles from the larval midgut of the cabbage butterfly (Pieris brassicae). Comp Biochem Physiol 86:301–308
Wu KM, Lu YH, Feng HQ, Jiang YY, Zhao JZ (2008) Suppression of cotton bollworm in multiple crops in China in areas with Bt toxin–containing cotton. Science 321:1676–1678
Xiao Y, Zhang T, Liu C, Heckel DG, Li X, Tabashnik BE, Wu K (2014) Mis-splicing of the ABCC2 gene linked with Bt toxin resistance in Helicoverpa armigera. Sci Rep 4:6184
Yu CG, Mullins MA, Warren GW, Koziel MG, Estruch JJ (1997) The Bacillus thuringiensis vegetative insecticidal protein Vip3A Lyses midgut epithelium cells of susceptible insects. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:532–536
Yu X, Liu T, Sun Z, Guan P, Zhu J, Wang S, Li S, Deng Q, Wang L, Zheng A, Li P (2012) Co-expression and synergism analysis of Vip3Aa29 and Cyt2Aa3 insecticidal proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis. Curr Microbiol 64:326–331
Zhang H, Tian W, Zhao J, Jin L, Yang Y, Wu S, Tabashnik BE, Wu Y (2011) Early warning of cotton bollworm resistance associated with intensive planting of Bt cotton in China. PLoS ONE 6:e22874
Zhang H, Tian W, Zhao J, Jin L, Yang J, Liu C, Yang Y, Wu S, Wu K, Cui J, Tabashnik BE, Wu Y (2012) Diverse genetic basis of field-evolved resistance to Bt cotton in cotton bollworm from China. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:10275–10280
Zhao Z, Li Y, Xiao Y, Ali A, Dhiloo KH, Chen W, Wu K (2016) Distribution and metabolism of Bt-Cry1Ac Toxin in tissues and organs of the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera. Toxins 8:212
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the supported by the National Natural Science Funds (Grant No. 31321004) and the Key Project for Breeding Genetic Modified Organisms (Grant Nos. 2014ZX0800912B and 2016ZX0812-004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Wb., Lu, Gq., Cheng, Hm. et al. Transgenic cotton co-expressing chimeric Vip3AcAa and Cry1Ac confers effective protection against Cry1Ac-resistant cotton bollworm. Transgenic Res 26, 763–774 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-017-0048-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-017-0048-8