Abstract
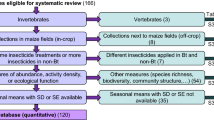
Maize with the insecticidal properties of the entomopathogenic bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner, known as Bt maize, has been sown in Europe since 1998. For several years, EU and Spanish regulations have required laboratory and field trials to assess risks of genetically modified crops for nontarget organisms prior to their authorization. Thirteen field trials were conducted in Spain to measure the effects of Bt maize on a broad range of arthropod taxa; no effects were found in accordance with most literature records. However, statistical analyses of single trials rarely have the statistical power to detect low effect sizes if they do not have a sufficient sample size. When sample size is low, meta-analysis may improve statistical power by combining several trials and assuming a common measure of effect size. Here we perform a meta-analysis of the results of 13 independent field trials conducted in Spain in which effects of single or stacked Bt traits on several arthropod taxa were measured with no significant results. Since the taxa included in each single trial were not the same for all trials, for the meta-analysis we selected only those taxa recorded in a minimum of six trials, resulting finally in 7, 7, and 12 taxa analyzed in visual counts, pitfall traps and yellow sticky traps, respectively. In comparison with single trial analysis, meta-analysis dramatically increased the detectability of treatment effects for most of the taxa regardless of the sampling technique; of the 26 taxa analyzed, only three showed poorer detectability in the meta-analysis than the best recorded in the 13 single trials. This finding reinforces the conclusion that Bt maize has no effect on the most common herbivore, predatory and parasitoid arthropods found in the maize ecosystems of southern Europe.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albajes R, Lumbierres B, Pons X (2009) Responsiveness of arthropod herbivores and their natural enemies to modified weed management in corn. Environ Entomol 38:944–954
Albajes R, Farinós GP, Pérez-Hedo M, de la Poza M, Lumbierres B, Ortego F, Pons X, Castañera P (2012) Post-market environmental monitoring of Bt maize in Spain: non-target effects of varieties derived from the event MON810 on predatory fauna. Spanish J Agric Res 10:977–985
Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JPT, Rothstein H (2009) Introduction to meta-analysis. Wiley, Chichester
Comas J, Lumbierres B, Pons X, Albajes R (2013) Ex ante determination of the capacity to detect treatment effects in field trials intended to assess risks of genetically modified maize on non-target arthropods. J Econ Entomol (in press)
Czarnak M, Rodríguez-Cerezo E (2010) Best practice documents for coexistence of genetically modified crops with conventional and organic farming 1. Maize crop production. EU Joint Research Centre—Institute for Prospective Technological Studies, Seville
de la Poza M, Pons X, Farinós GP, López C, Ortego F, Eizaguirre M, Castañera P, Albajes R (2005) Impact of farm-scale Bt maize on abundance of predatory arthropods in Spain. Crop Prot 24:677–684
EFSA Panel on Genetically Modified Organisms (2010) Guidance on the environmental risk assessment of genetically modified plants. EFSA J 8(11):1879
Gómez-Barbero M, Berbel J, Rodríguez-Cerezo E (2008) Bt corn in Spain—the performance of the EU’s first GM crop. Nat Biotech 26:384–386
Lumbierres B, Albajes R, Pons X (2004) Transgenic Bt maize and Rhopalosiphum padi (Hom., Aphididae) performance. Ecol Entomol 29:309–317
Lumbierres B, Stary P, Pons X (2011) Effect of Bt maize on the plant-aphid-parasitoid tritrophic relationships. Biocontrol 56:133–143
MAGRAMA (2012) Ministerio de Agricultura, Alimentación y Medio Ambiente. Estimación de la superficie total de variedades OMG cultivadas en España en. http://www.magrama.gob.es/es/calidad-y-evaluacion-ambiental/temas/biotecnologia/2012_tcm7-220599.pdf
Marvier M, McCreedy C, Regetz J, Kareiva P (2007) A meta-analysis of effects of Bt cotton and maize on nontarget invertebrates. Science 316:1475–1477
Meissle M, Mouron P, Musa T et al (2010) Pests, pesticide use and alternative options in European maize production: current status and future prospects. J Appl Entomol 134:357–375
Naranjo SE (2009) Impacts of Bt crops on non-target invertebrates and insecticide use patterns. CAB Rev: Perspect Agric Vet Sci Nutr Nat Resour 4:1–23 http://www.cababstractsplus.org/cabreviews
Perry JN, Rothery P, Clark SJ, Heard MS, Hawes C (2003) Design, analysis and statistical power of the farm-scale evaluations of genetically modified herbicide-tolerant crops. J Appl Ecol 40:17–31
Pons X, Lumbierres B, López C, Albajes R (2005) Abundance of non-target pests in transgenic Bt-maize: a farm scale study. Eur J Entomol 102:73–79
Romeis J, Meissle M, Bigler F (2006) Transgenic crops expressing Bacillus thuringiensis toxins and biological control. Nat Biotechnol 24:63–71
Romeis J, Bartch D, Bigler F et al (2008) Assessment of risk of insect-resistant transgenic crops to nontarget arthropods. Nat Biotechnol 26:203–208
R Development core team (2007) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. Available at: http://www.R-project.org
Viechtbauer W (2010) Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J Stat Softw 36:1–48
Whitehead A (2002) Meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials. Wiley, Chichester
Wolfenbarger LL, Naranjo SE, Lundgren JG, Bitzer RJ, Watrud LS (2008) Bt crops effects on functional guilds of non-target arthropods: a meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 3(5):e2118
Acknowledgments
The results analyzed herein were obtained in field trials that were funded by the following public agencies and private companies: the Ministerio de Ciencia y Tecnología (AGF99-0782, AGL2002-00204, AGL2005-06485, AGL2011-23996), INIA and the Ministerio de Medio Ambiente, Medio Rural y Marino, and the companies Pioneer Génétique, Monsanto Agricultura España S. L. and Syngenta Seeds companies. Moreover, the editor and referees are acknowledged with thanks. Their precise comments and suggestions have clearly improved an earlier version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Comas, C., Lumbierres, B., Pons, X. et al. No effects of Bacillus thuringiensis maize on nontarget organisms in the field in southern Europe: a meta-analysis of 26 arthropod taxa. Transgenic Res 23, 135–143 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-013-9737-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-013-9737-0