Abstract
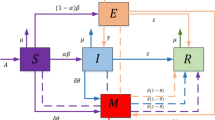
Media reports and refutation factors have an important impact on the spread of rumors. At present, most scholars have separately analyzed the effects of media reports and individual refutation on the spread of rumors. It is not common to comprehensively consider the two on the spread of rumors. This paper proposed a SIDRW (Susceptibility–Infection–Refutation–Recovery–Medium) model, which regarded media as a separate subcategory and comprehensively considered the influence of media reports and individual repudiation on rumor propagation. The existence and local asymptotic stability of the equilibrium point of the model are proved by calculation. The results of numerical simulation under the parameters given in this paper show that positive media publicity can reduce the spread of rumors, but cannot prevent the spread of rumors. In the process of spreading, with an increase in the initial value of rumormongers, the duration of rumor spreading decreases, and the time to reach the peak decreases. This is conducive to controlling the spread of rumors.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
This manuscript has no associated data.
References
Cohen, R., Havlin, S., Ben-Avraham, D.: Efficient immunization strategies for computer networks and populations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91(24), 247901 (2003)
Tian, R.Y., Zhang, X.F., Liu, Y.J.: SSIC model: a multi-layer model for intervention of online rumors spreading. Physica A 427, 181–191 (2015)
Liu, Q., Li, T., Sun, M.: The analysis of an SEIR rumor propagation model on heterogeneous network. Physica A 469, 372–380 (2017)
Hu, Y., Pan, Q., Hou, W., et al.: Rumor spreading model considering the proportion of wisemen in the crowd. Physica A 505, 1084–1094 (2018)
Ghosh, M., Das, S., Das, P.: Dynamics and control of delayed rumor propagation through social networks. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 68, 1–30 (2021)
Xu, Y., Sun, X., Hu, H.: Extinction and stationary distribution of a stochastic SIQR epidemic model with demographics and non-monotone incidence rate on scale-free networks. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 68, 1–29 (2021)
Wang, M., Hu, Y., Wu, L.: Dynamic analysis of a SIQR epidemic model considering the interaction of environmental differences. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 68, 1–17 (2021)
Hui, H., Zhou, C., Lÿ, X., et al.: Spread mechanism and control strategy of social network rumors under the influence of COVID-19. Nonlinear Dyn. 101(3), 1933–1949 (2020)
Yang, L., Wang, J., Gao, C., et al.: A crisis information propagation model based on a competitive relation. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 10(8), 2999–3009 (2019)
Daley, D.J., Kendall, D.G.: Stochastic rumors. IMA J. Appl. Math. 1(1), 42–55 (1965)
Daley, D.J., Kendall, D.G.: Epidemics and rumours. Nature 204(4963), 1118–1118 (1964)
Maki, D.P., Thompson, M.: Mathematical models and applications: with emphasis on the social, life, and management sciences. Prentice Hall 511(8), M3 (1973)
Moreno, Y., Nekovee, M., Pacheco, A.F.: Dynamics of rumor spreading in complex networks. Phys. Rev. E 69(6), 066130 (2004)
Yao, Y., Xiao, X., Zhang, C., et al.: Stability analysis of an SDILR model based on rumor recurrence on social media. Physica A 535, 122236 (2019)
Chen, J., Yang, L., Yang, X., et al.: Cost-effective anti-rumor message-pushing schemes. Physica A 540, 123085 (2020)
Chen, X., Wang, N.: Rumor spreading model considering rumor credibility, correlation and crowd classification based on personality. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 1–5 (2020)
Li, T., Liu, Y., Wu, X., et al.: Dynamic model of Malware propagation based on tripartite graph and spread influence. Nonlinear Dyn. 101(4), 2671–2686 (2020)
Al-Oraiqat, A.M., Ulichev, O.S., Meleshko, Y.V., et al.: Modeling strategies for information influence dissemination in social networks. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 13(5), 2463–2477 (2022)
Xd, A., Ylb, C., Chao, W.D., et al.: A double-identity rumor spreading model. Physica A 528, 121479 (2019)
Yu, S., Yu, Z., Jiang, H., et al.: The spread and control of rumors in a multilingual environment. Nonlinear Dyn. 100(3), 2933–2951 (2020)
Rani, P., Jain, V., Shokeen, J., et al.: Blockchain-based rumor detection approach for COVID-19. J. Ambient Intell. Human. Comput. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-022-03900-2
Jl, A., Hj, A., Xm, A., et al.: Dynamical analysis of rumor spreading model in multi-lingual environment and heterogeneous complex networks. Inf. Sci. 536, 391–408 (2020)
Afassinou, K.: Analysis of the impact of education rate on the rumor spreading mechanism. Physica A 414, 43–52 (2014)
Chen, J., Yang, L., Yang, X., et al.: Cost-effective anti-rumor message-pushing schemes. Physica A 540, 123085 (2020)
Wang, J., Jiang, H., Ma, T., et al.: Global dynamics of the multi-lingual SIR rumor spreading model with cross-transmitted mechanism. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 126, 148–157 (2019)
Zhu, L., Wang, X., Zhang, Z., et al.: Global stability and bifurcation analysis of a rumor propagation model with two discrete delays in social networks. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 30(12), 2050175 (2020)
Cheng, Y., Huo, L., Zhao, L.: Dynamical behaviors and control measures of rumor-spreading model in consideration of the infected media and time delay. Inf. Sci. 564(3), 237–253 (2020)
Zhu, L., He, L.: Pattern formation in a reaction-diffusion rumor propagation system with Allee effect and time delay. Nonlinear Dyn. 107(3), 3041–3063 (2022)
Guan, G., Guo, Z.: Stability behavior of a two-susceptibility SHIR epidemic model with time delay in complex networks. Nonlinear Dyn. 106(1), 1083–1110 (2021)
Zhu, L., He, L.: Pattern formation in a reaction-diffusion rumor propagation system with Allee effect and time delay. Nonlinear Dyn. 107(3), 3041–3063 (2022)
Zhu, L., Liu, W., Zhang, Z.: Delay differential equations modeling of rumor propagation in both homogeneous and heterogeneous networks with a forced silence function. Appl. Math. Comput. 370, 124925 (2020)
Zhu, L., Wang, B.: Stability analysis of a SAIR rumor spreading model with control strategies in online social networks. Inf. Sci. 526, 1–19 (2020)
Xu, J., Tang, W., Zhang, Y., et al.: A dynamic dissemination model for recurring online public opinion. Nonlinear Dyn. 99(5947), 1269 (2020)
Abta, A., Laarabi, H., Rachik, M., et al.: Optimal control of a delayed rumor propagation model with saturated control functions and \(L^1\)-type objectives. Soc. Netw. Anal. Mining 10(1), 1–5 (2020)
Zhu, L., Yang, F., Guan, G., et al.: Modeling the dynamics of rumor diffusion over complex networks. Inf. Sci. 562(1), 240–58 (2021)
Jahanbakhsh-Nagadeh, Z., Feizi-Derakhshi, M. R., Ramezani, M., et al: A Model to Measure the Spread Power of Rumors. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.07563, 1-31 (2020)
Yin, F., Zhu, X., Shao, X., et al.: Modeling and quantifying the influence of opinion involving opinion leaders on delayed information propagation dynamics. Appl. Math. Lett. 121(4), 107356 (2021)
Asghar, M.Z., Habib, A., Habib, A., et al.: Exploring deep neural networks for rumor detection. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 12(4), 4315–4333 (2021)
Zhang, Y., Xu, J., Wu, Y.: A rumor control competition model considering intervention of the official rumor-refuting information. Int. J. Modern Phys. C 31(3), 2050123 (2020)
Ding, X., Zhang, X., Fan, R., et al.: Rumor recognition behavior of social media users in emergencies. J. Manag. Sci. Eng. 7(1), 36–47 (2021)
Van den Driessche, P., Watmough, J.: Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission. Math. Biosci. 180(1–2), 29–48 (2002)
Acknowledgements
We thank the anonymous Editors and Reviewers warm work earnestly. This work was supported by the Humanities and Social Sciences Research Projects of Education Department of Liaoning Province China(No. 2020LNJC11) and the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Science and Technology Agency of China (No. 2022-MS-356).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
The authors state that this article complies with ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, W., Yan, W., Hu, Y. et al. Dynamic analysis of a SIDRW rumor propagation model considering the effect of media reports and rumor refuters. Nonlinear Dyn 111, 3925–3936 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07947-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07947-w